Which Statement Is True Of Mitochondria Inside The Human Body
Mitochondria, often hailed as the powerhouses of the cell, play a critical role in human health. But amidst the scientific jargon and complex cellular processes, a simple question often arises: Which statement accurately describes these vital organelles inside the human body?
Understanding the true nature and function of mitochondria is paramount, not only for biology students and researchers but also for anyone seeking to comprehend the fundamental processes that keep us alive. This article delves into the key aspects of mitochondrial function, dispelling common misconceptions and clarifying their multifaceted role within our cells.
Mitochondria: More Than Just Powerhouses
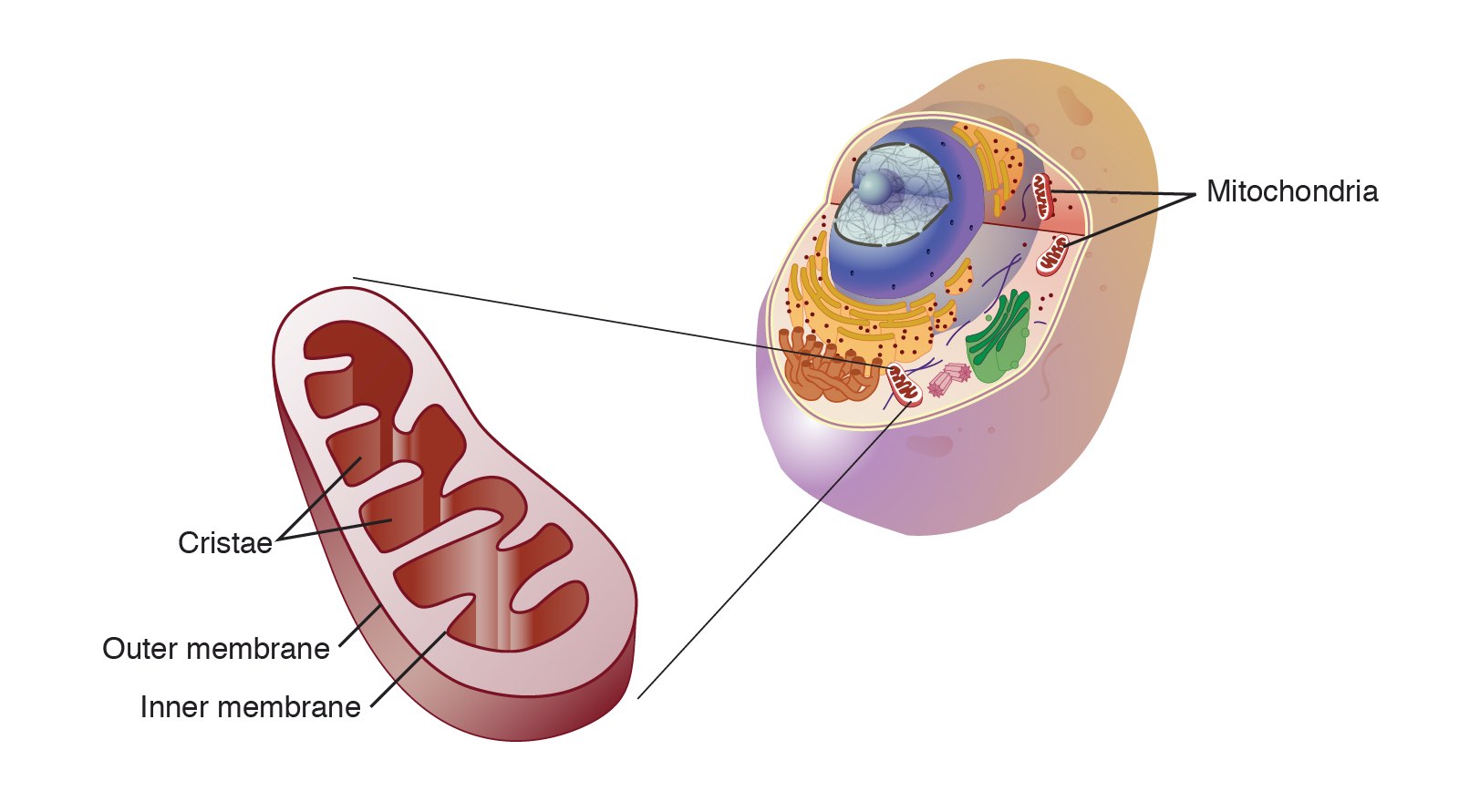
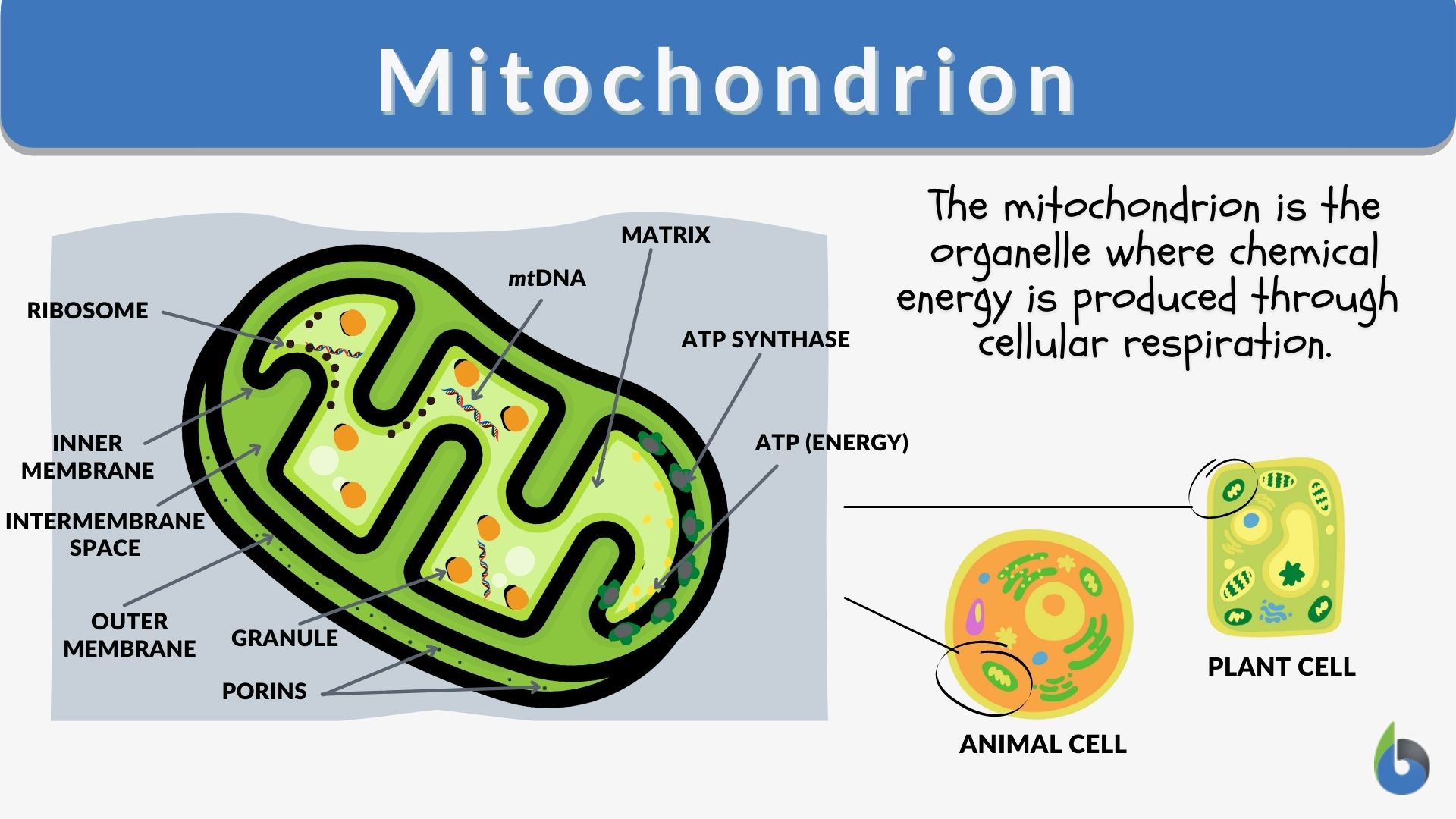
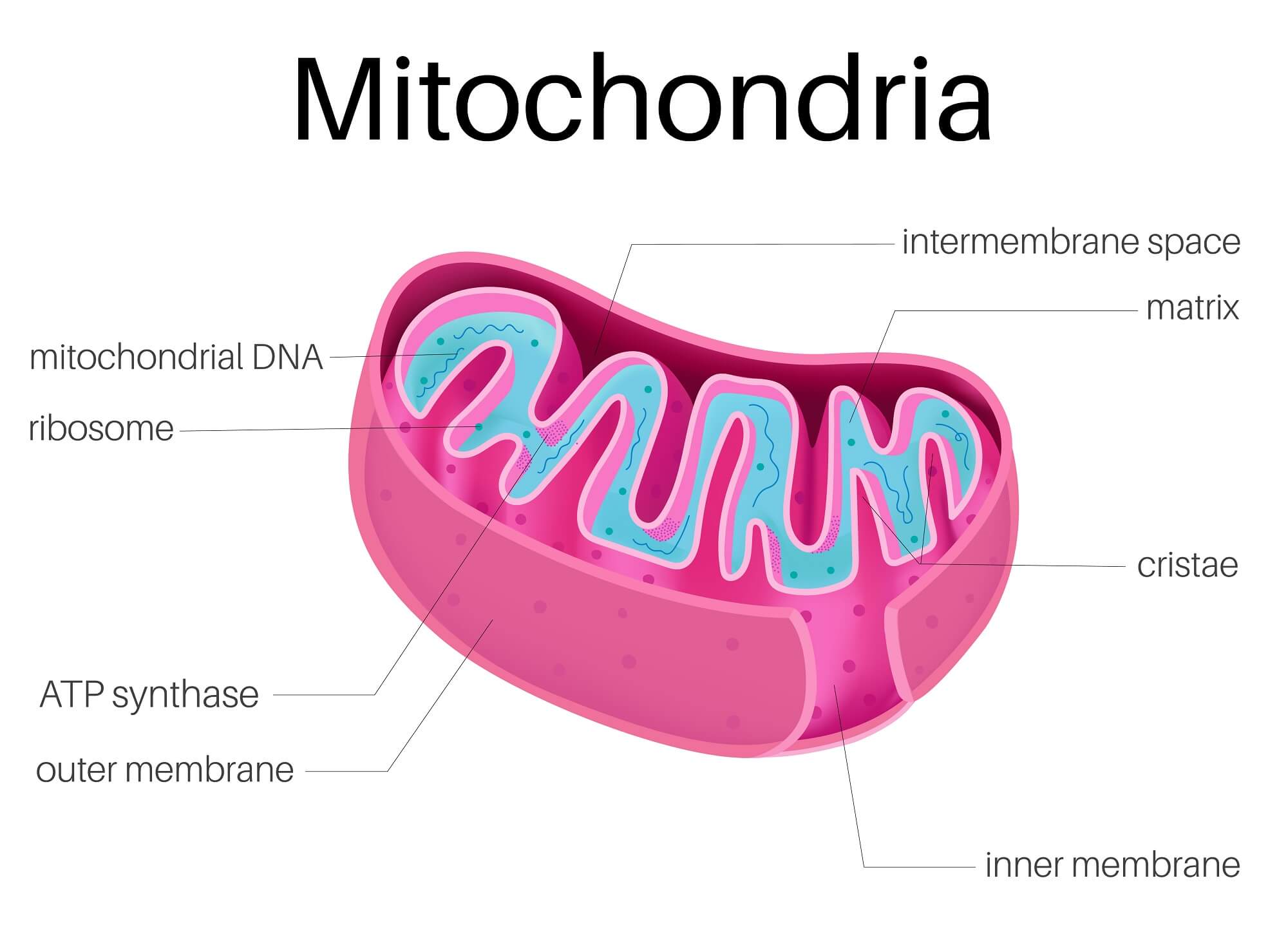
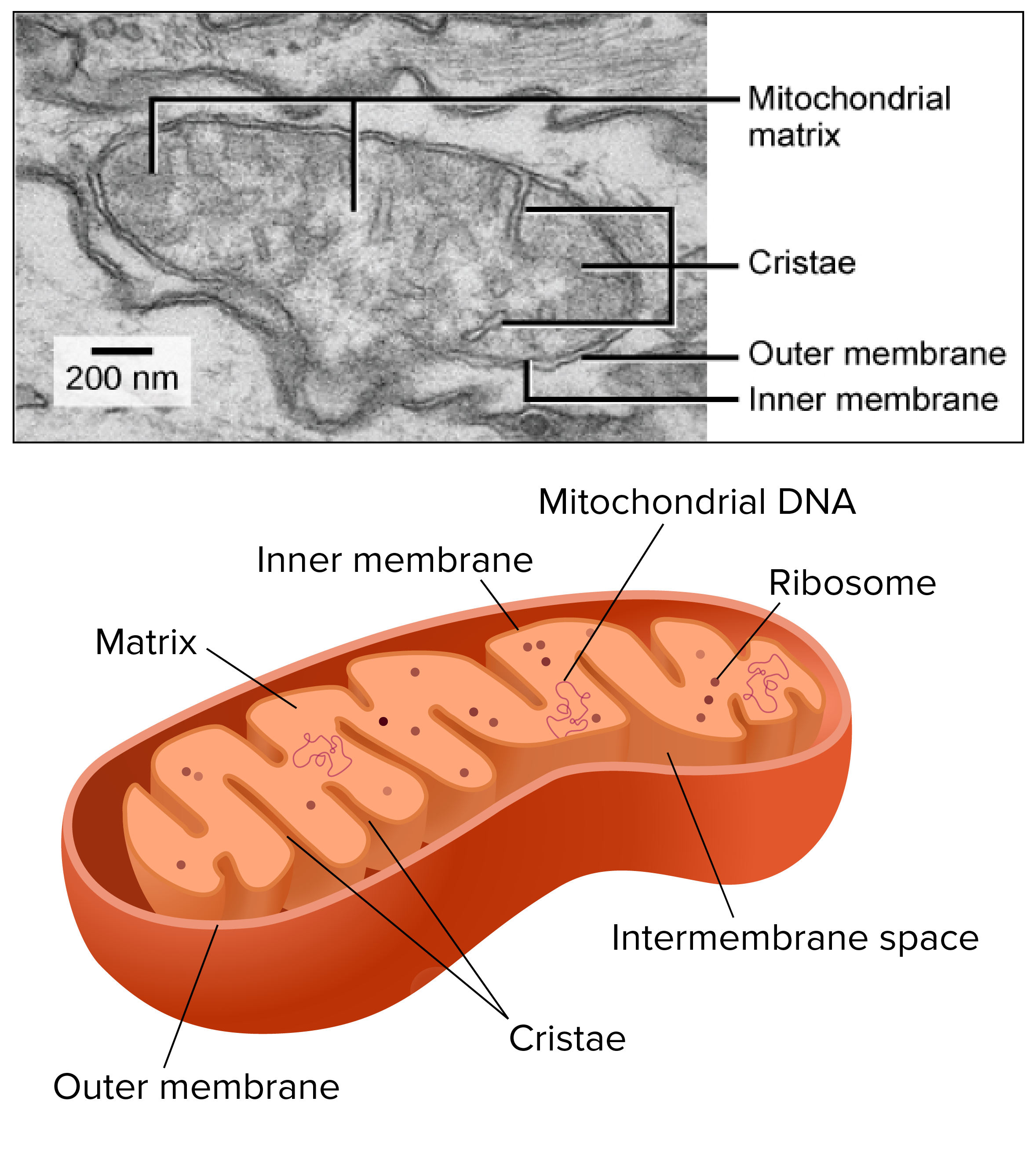
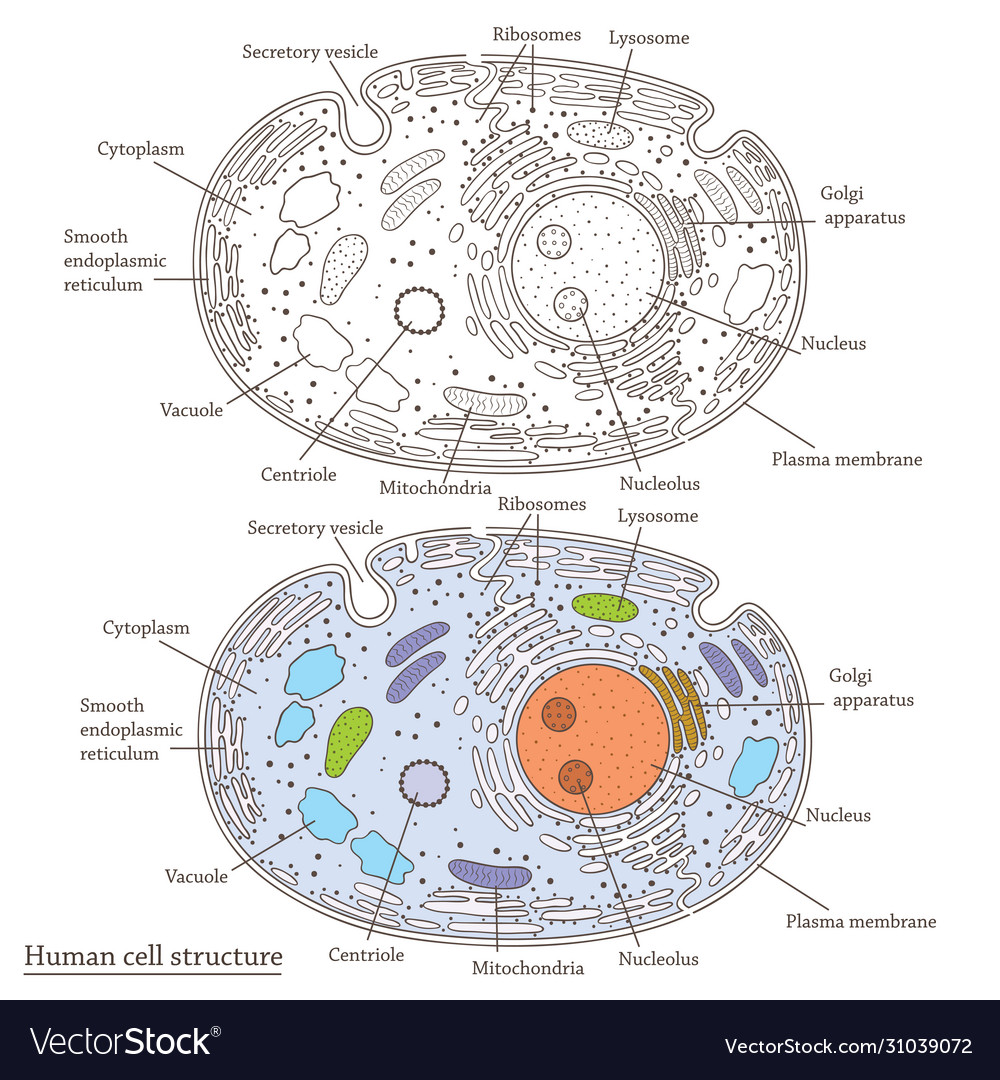
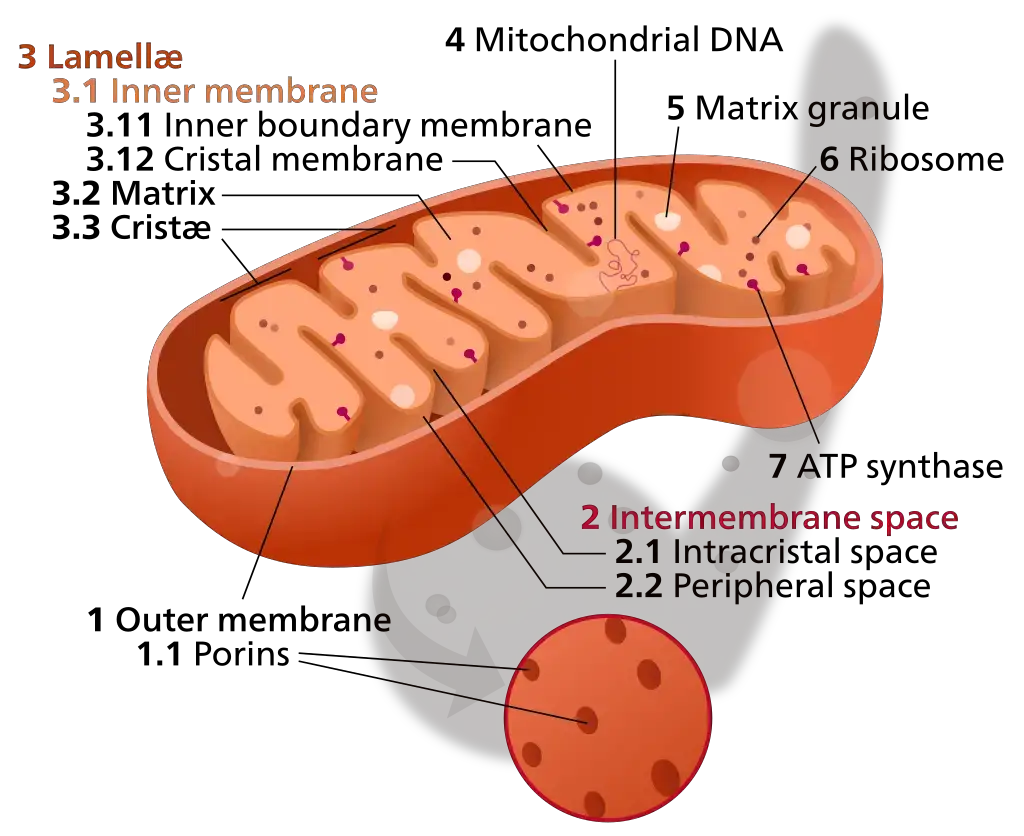
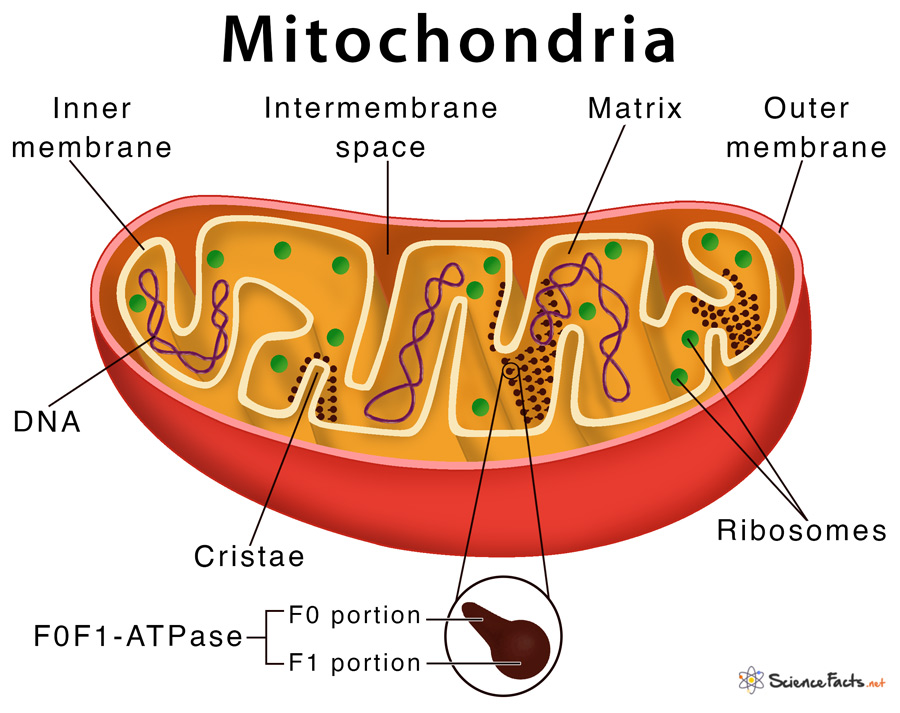
Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. Chemical energy is produced by the mitochondria in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
ATP is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. While the "powerhouse" analogy is apt, it simplifies the organelle's complex and varied functions.
Key Functions Beyond Energy Production
Mitochondria are involved in a range of crucial cellular processes. These include signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth.
They are also involved in synthesizing certain amino acids and heme, an essential component of hemoglobin. Furthermore, they play a role in regulating calcium levels within the cell.
Mitochondrial DNA and Inheritance
One of the most distinctive features of mitochondria is their own DNA (mtDNA), separate from the nuclear DNA found in the cell's nucleus. This mtDNA is circular and contains genes that code for some of the proteins and RNA molecules needed for mitochondrial function.
Unlike nuclear DNA, which is inherited from both parents, mtDNA is typically inherited solely from the mother. This maternal inheritance pattern makes mtDNA a valuable tool for studying human evolution and tracing maternal lineages.
Mutations in mtDNA can lead to a variety of mitochondrial diseases, affecting organs and tissues with high energy demands, such as the brain, heart, and muscles.
The Correct Statement: A Holistic View
So, which statement about mitochondria inside the human body holds true? It's not a single statement, but rather a comprehensive understanding of their interconnected roles.
A scientifically accurate statement would encompass the following: Mitochondria are essential organelles present in most human cells, responsible for generating ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, but they also participate in crucial cellular processes like signaling, cell differentiation, apoptosis, and the regulation of calcium homeostasis. They contain their own maternally inherited DNA and play a critical role in overall cellular health and function.
Simplifying this to a single, universally "true" statement can be misleading. For instance, stating "Mitochondria only produce energy" is demonstrably false, as is "Mitochondria are only found in muscle cells."
Impact on Health and Disease
Dysfunctional mitochondria are implicated in a wide range of human diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Understanding the specific mitochondrial defects associated with these diseases is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
Researchers are actively exploring therapeutic strategies that aim to improve mitochondrial function. These range from dietary interventions and exercise to gene therapies and pharmacological approaches.
"Mitochondrial dysfunction is increasingly recognized as a central factor in many age-related diseases," explains Dr. Emily Carter, a leading researcher in mitochondrial biology at the National Institutes of Health. "Therefore, targeting mitochondria offers promising avenues for preventing and treating these conditions."
The development of mitochondrial-targeted therapies faces significant challenges, including delivering drugs specifically to mitochondria and overcoming the blood-brain barrier. However, the potential benefits are substantial, driving ongoing research and innovation in this field.
Looking Ahead
The study of mitochondria continues to evolve, revealing new insights into their intricate functions and their profound impact on human health. Advanced imaging techniques, genetic analysis, and biochemical assays are providing unprecedented detail about these vital organelles.
Future research will likely focus on unraveling the complex interplay between mitochondria and other cellular components. This includes the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and other organelles, and investigating the role of mitochondria in aging and age-related diseases.
A deeper understanding of mitochondrial biology will undoubtedly lead to more effective strategies for preventing and treating a wide range of human diseases, ultimately improving the quality of life for millions of people.