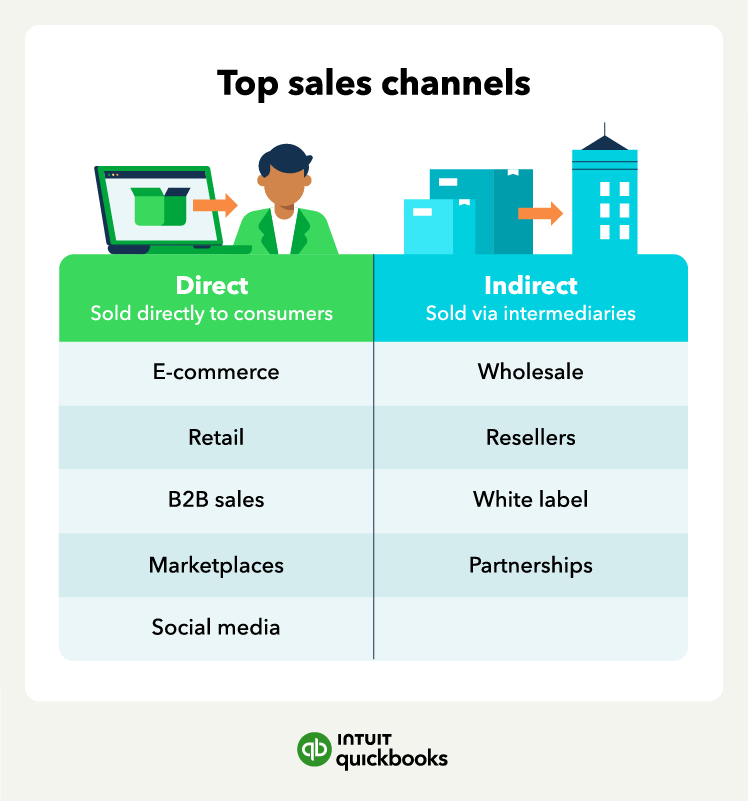
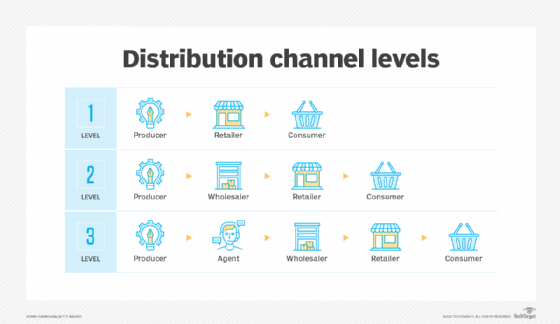
Which Two Channels Are Examples Of Physical Sales Channels

The retail landscape is constantly evolving, yet physical sales channels remain a vital component for many businesses. Understanding these channels is crucial for companies seeking to reach their target audience effectively.
This article will examine two prominent examples of physical sales channels: brick-and-mortar stores and direct sales. These channels offer unique advantages and cater to distinct consumer preferences, contributing significantly to the overall economy.
Brick-and-Mortar Stores: The Traditional Retail Powerhouse
Brick-and-mortar stores represent the most traditional and recognizable form of physical sales. These are physical retail locations where customers can browse, interact with products, and make purchases in person.
They range from small, independent boutiques to large department stores and supermarkets. According to the National Retail Federation (NRF), while e-commerce continues to grow, the vast majority of retail sales still occur in physical stores.
Key Characteristics and Advantages
One of the primary advantages of brick-and-mortar stores is the ability for customers to physically examine products before buying. This tactile experience is especially important for items like clothing, furniture, and food.
Customers can try on clothes, test electronics, or sample food, leading to a higher level of confidence in their purchase. In-store purchases also offer immediate gratification; customers can take their purchases home immediately, avoiding shipping delays.
Furthermore, brick-and-mortar stores provide opportunities for personalized customer service. Sales associates can answer questions, offer product recommendations, and assist with returns or exchanges, creating a more engaging and satisfying shopping experience.
However, brick-and-mortar stores also face challenges. They often require significant investment in rent, utilities, and staffing, leading to higher operating costs. Competition from online retailers and changing consumer preferences also necessitate constant adaptation and innovation.
Direct Sales: Personal Connection and Personalized Service
Direct sales involve selling products or services directly to consumers, often in a non-retail environment. This channel relies heavily on personal interaction and relationship-building.
Examples of direct sales include door-to-door sales, party plan sales (like Tupperware parties), and network marketing (also known as multi-level marketing or MLM). The Direct Selling Association (DSA) reported billions in retail sales through direct selling channels.
Key Characteristics and Advantages
A key advantage of direct sales is the personalized service and attention that customers receive. Sales representatives can tailor their approach to individual needs and preferences, providing customized product demonstrations and recommendations.
This personal connection can be particularly valuable for products that require explanation or demonstration, such as cosmetics, nutritional supplements, or home goods. Direct sales also offer flexibility and convenience for customers.
Sales representatives can meet customers in their homes, at work, or at social gatherings, eliminating the need for customers to travel to a store. For sales representatives, direct selling offers the opportunity to be their own boss and set their own hours.
However, direct sales also has its challenges. Recruiting and retaining sales representatives can be difficult, and the industry has faced scrutiny regarding ethical practices, particularly in the context of multi-level marketing schemes. Building trust and maintaining a positive reputation are crucial for success in this channel.
The Evolving Landscape of Physical Sales
While e-commerce continues its ascent, physical sales channels remain essential for many businesses. Companies are increasingly adopting omnichannel strategies, integrating online and offline experiences to cater to diverse consumer preferences.
Brick-and-mortar stores are evolving to offer enhanced experiences, such as interactive displays, personalized recommendations, and convenient services like in-store pickup of online orders. Direct sales companies are leveraging technology to streamline operations and reach a wider audience.
For example, they are providing online ordering platforms for sales representatives and customers. To maintain their appeal, both channels must adapt to changing consumer behavior and embrace new technologies.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Physical Presence
Both brick-and-mortar stores and direct sales represent significant physical sales channels, each with its unique strengths and weaknesses. They both offer consumers the opportunity to engage with products and services in a tangible and personal way.
These channels also allow for companies to create lasting connections with their customers. As the retail landscape continues to evolve, understanding the dynamics of these physical channels is crucial for businesses seeking to thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
Ultimately, the future of retail likely lies in a hybrid approach, where physical and digital channels work together to provide a seamless and personalized shopping experience for consumers.
![Which Two Channels Are Examples Of Physical Sales Channels Place: Distribution Channels | Introduction to Business [Deprecated]](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/903/2016/02/23230705/Marketing-channel-graphic.png)