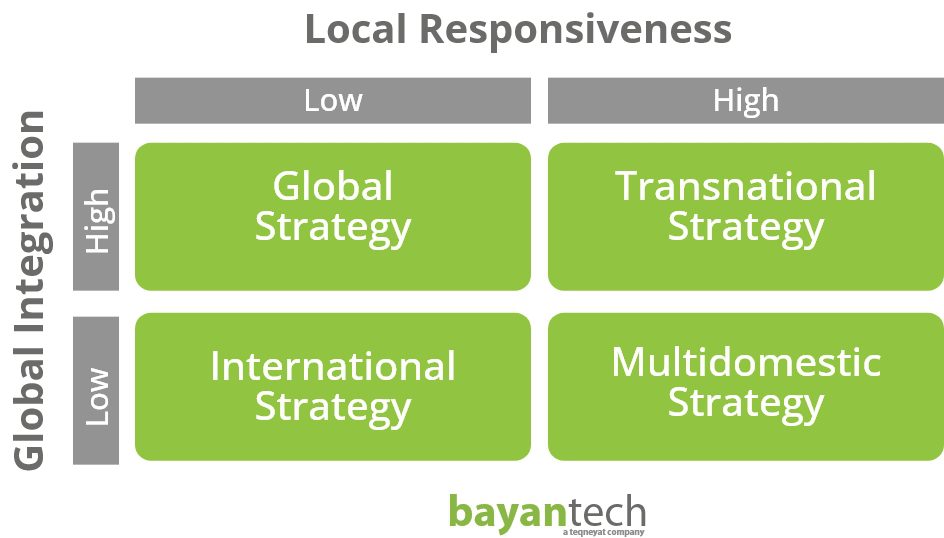
Which Type Of Internationalization Strategy Should We Pursue
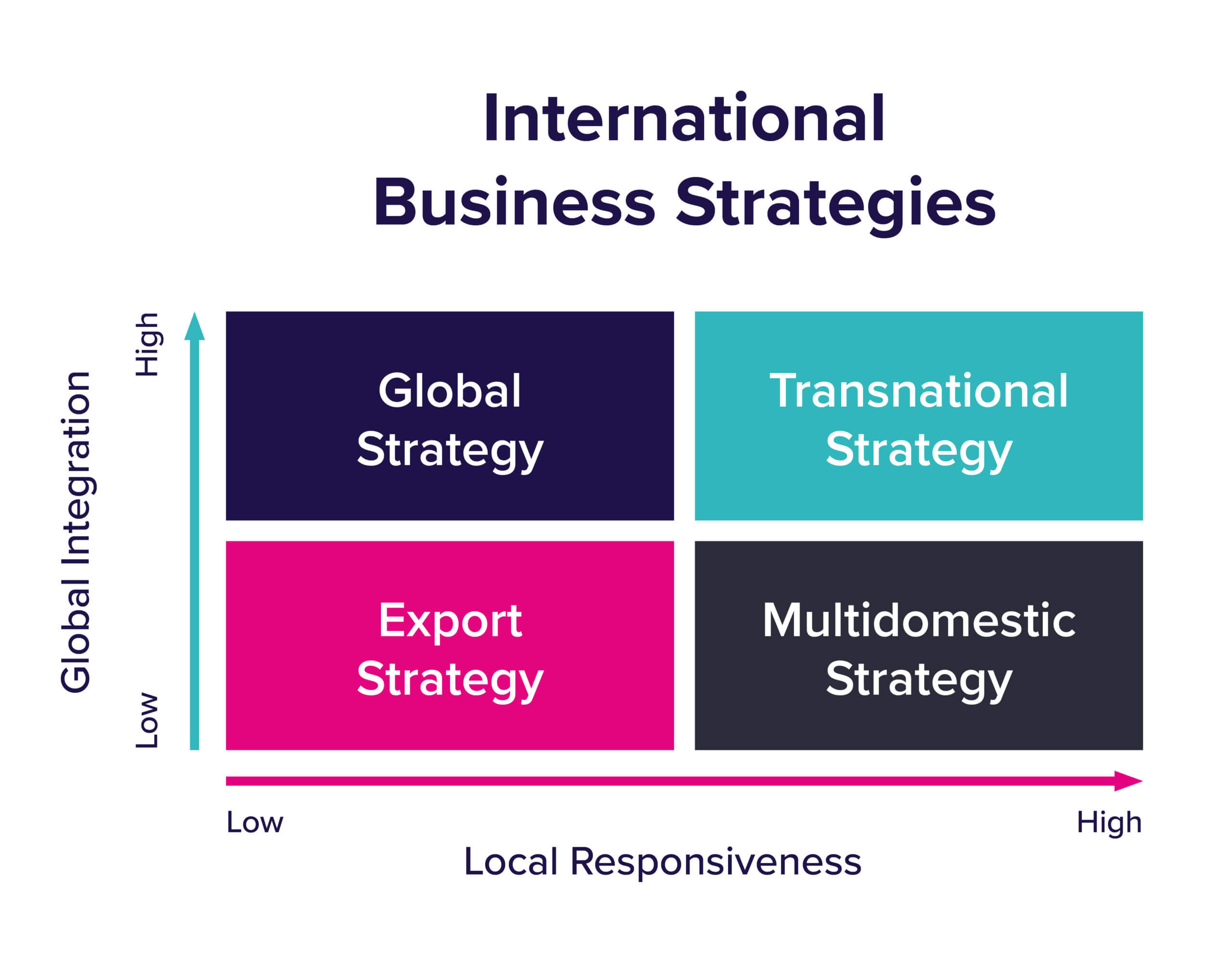
The global marketplace is a tempting, yet treacherous, landscape for businesses seeking growth. Expanding beyond domestic borders presents immense opportunities for increased revenue and brand recognition, but the path to international success is rarely straightforward. Companies face a critical decision: which internationalization strategy best suits their specific circumstances, resources, and ambitions? The wrong choice can lead to costly failures, while the right one can unlock unprecedented levels of prosperity.
Navigating the complexities of international expansion requires careful consideration of various strategies. This article delves into the primary options available to businesses venturing abroad, examining their advantages, disadvantages, and ideal applications. We'll explore the spectrum from exporting and licensing to foreign direct investment (FDI), providing a framework for informed decision-making in a rapidly evolving global economy. Ultimately, the most effective strategy hinges on a company's unique profile and the specific characteristics of its target markets.
Exporting: A Low-Risk Entry Point
Exporting, often the simplest entry strategy, involves producing goods or services in one country and selling them in another. It offers a relatively low-risk and low-cost way to test international waters. Companies can leverage existing production capabilities and avoid significant upfront investments in foreign infrastructure.
Indirect exporting involves selling through intermediaries, such as export management companies or distributors. This approach minimizes direct involvement and allows companies to focus on their core competencies. Direct exporting, on the other hand, requires building an internal export department or establishing a foreign sales office.
However, exporting can be limited by tariffs, transportation costs, and exchange rate fluctuations. Companies also have less control over marketing and distribution in foreign markets. As Professor Anya Sharma of the London School of Economics notes, "Exporting is a good starting point, but it may not be sustainable for long-term growth in all industries."
Licensing and Franchising: Leveraging Intellectual Property
Licensing grants a foreign company the right to use a firm's intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or technology, in exchange for royalties or fees. Franchising is a specific type of licensing where the franchisor provides a complete business system, including branding, operating procedures, and marketing support, to the franchisee.
These strategies offer a way to expand internationally without significant capital investment. Companies can generate revenue from their intellectual property while avoiding the complexities of direct operations. Licensing and franchising are particularly attractive for businesses with strong brands or proprietary technologies.
However, licensing and franchising entail a loss of control over quality and brand image. There is also a risk that the licensee or franchisee may become a competitor in the future. Careful selection and monitoring of partners are crucial for success.
Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures: Collaborative Approaches
Strategic alliances involve cooperative agreements between two or more firms to achieve shared strategic goals. Joint ventures are a specific type of strategic alliance where two or more companies create a new, jointly owned entity.
These strategies allow companies to share resources, expertise, and risks. They can also provide access to new markets, technologies, or distribution channels. Strategic alliances and joint ventures are often used when entering complex or politically sensitive markets.
However, these collaborations can be challenging to manage due to differences in organizational culture, management styles, and strategic objectives. Clear communication, mutual trust, and well-defined roles and responsibilities are essential for success. According to a 2022 report by McKinsey, "Over 70% of strategic alliances fail to meet expectations, often due to poor governance and lack of alignment."
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): A High-Commitment Strategy
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) involves establishing a physical presence in a foreign country through the acquisition of existing businesses or the creation of new facilities. This is the most complex and capital-intensive internationalization strategy.
FDI offers the highest level of control over operations and allows companies to tailor their products and services to local market needs. It can also provide access to lower labor costs, natural resources, or strategic locations. FDI signals a long-term commitment to the foreign market.
However, FDI involves significant financial risks and requires a deep understanding of the local business environment. Political instability, regulatory hurdles, and cultural differences can pose significant challenges. The World Bank emphasizes the importance of conducting thorough due diligence before making FDI decisions.
Factors Influencing Strategy Selection
Numerous factors influence the choice of internationalization strategy. These include the size and resources of the company, the nature of its products or services, the characteristics of the target market, and the competitive landscape.
Risk tolerance also plays a crucial role. Companies with a low-risk appetite may prefer exporting or licensing, while those with a higher risk tolerance may be more willing to invest in FDI.
The level of control a company desires is another key consideration. FDI offers the highest level of control, while exporting and licensing offer less control.
Emerging Trends in Internationalization
The rise of e-commerce and digital technologies has created new opportunities for international expansion. Companies can now reach global customers more easily and cost-effectively through online channels.
The growing importance of emerging markets is also shaping internationalization strategies. Companies are increasingly focusing on countries like China, India, and Brazil, which offer significant growth potential.
Sustainability and social responsibility are becoming increasingly important considerations for international businesses. Consumers are demanding ethically sourced products and environmentally friendly practices.
Conclusion: A Tailored Approach
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to internationalization. The optimal strategy depends on a company's unique circumstances and objectives. Companies must carefully evaluate their options and develop a tailored plan that aligns with their overall business strategy.
A phased approach, starting with lower-risk strategies like exporting and gradually moving towards more complex strategies like FDI, can be a prudent way to mitigate risk and learn from experience. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are essential for long-term success in the global marketplace.
Ultimately, successful internationalization requires a combination of strategic planning, operational excellence, and a deep understanding of the cultural and economic nuances of the target market. By carefully considering the options and adapting to the evolving global landscape, businesses can unlock the immense potential of international expansion and achieve sustainable growth.