Why Are Cells Considered The Most Basic Unit Of Life
From the towering sequoia to the microscopic bacteria, all known life on Earth shares a fundamental building block: the cell. Understanding why cells hold this esteemed position as the most basic unit of life requires delving into their structure, function, and the historical context of their discovery.
The concept of the cell as the fundamental unit of life, often referred to as cell theory, is a cornerstone of modern biology. It dictates that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This article explores the significance of this theory and the reasons why cells are considered so fundamental.
The Foundations of Cell Theory
The journey towards understanding the cell began in the 17th century with the invention of the microscope. Robert Hooke, in 1665, using an early microscope, observed compartments in cork and coined the term "cellulae," meaning small rooms, due to their resemblance to monastery cells.
However, Hooke's observation was of dead plant cells. It wasn't until later that scientists began to appreciate the dynamic and living nature of cells.
Significant advancements came in the 19th century. Matthias Schleiden, a botanist, and Theodor Schwann, a zoologist, independently concluded that plants and animals are composed of cells, respectively.
Their work, along with contributions from others, led to the formulation of the first two tenets of cell theory in 1839. Later, Rudolf Virchow proposed the third tenet, "Omnis cellula e cellula" – all cells arise from pre-existing cells – solidifying the theory.
Why Cells are Fundamental
Cells are considered the most basic unit of life for several key reasons. First, they are the smallest units capable of performing all the functions necessary for life.
These functions include metabolism (chemical processes needed to survive), growth, reproduction, and response to stimuli. A cell can independently carry out these processes, whereas smaller components like organelles cannot.
Second, cells contain the genetic material, DNA, that is passed on from one generation to the next. This DNA provides the instructions for building and maintaining the organism.
The ability to replicate and transmit genetic information is crucial for inheritance and evolution. Without cells, there would be no mechanism for passing on traits or for life to persist.
Third, cells are the basic units of structure in all living organisms. Whether it's a single-celled bacterium or a complex multicellular organism like a human, all life is organized at the cellular level.
In multicellular organisms, cells are often specialized to perform specific tasks, such as muscle cells for movement or nerve cells for communication. This specialization allows for greater complexity and efficiency.
The Significance of Cell Structure
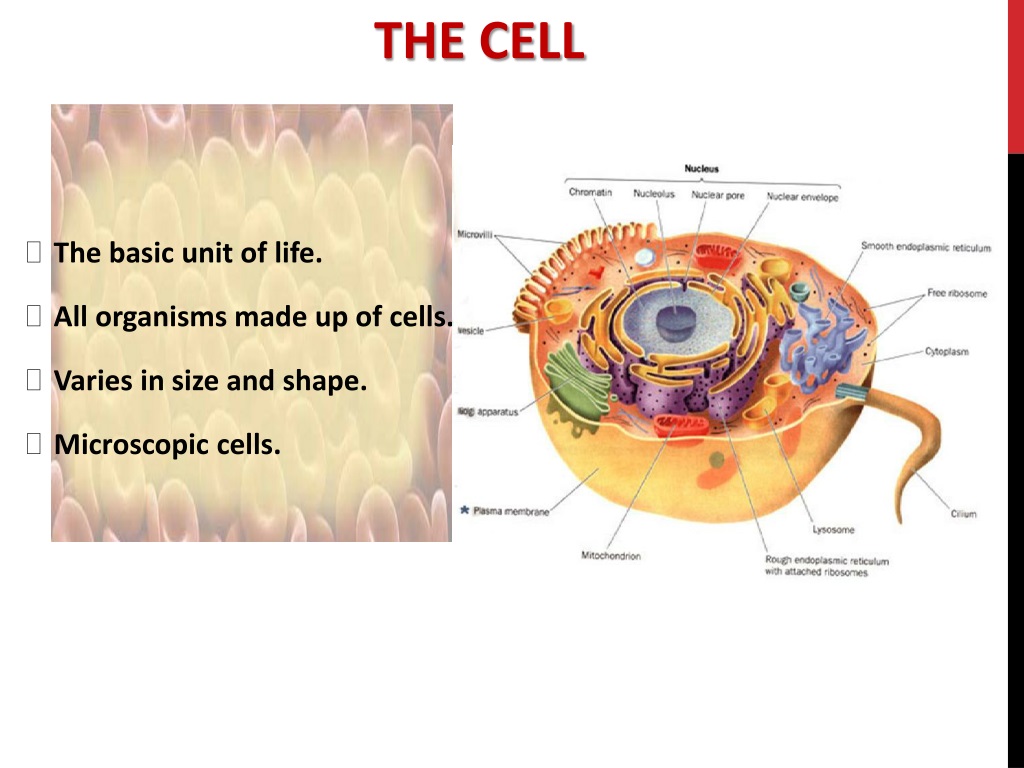
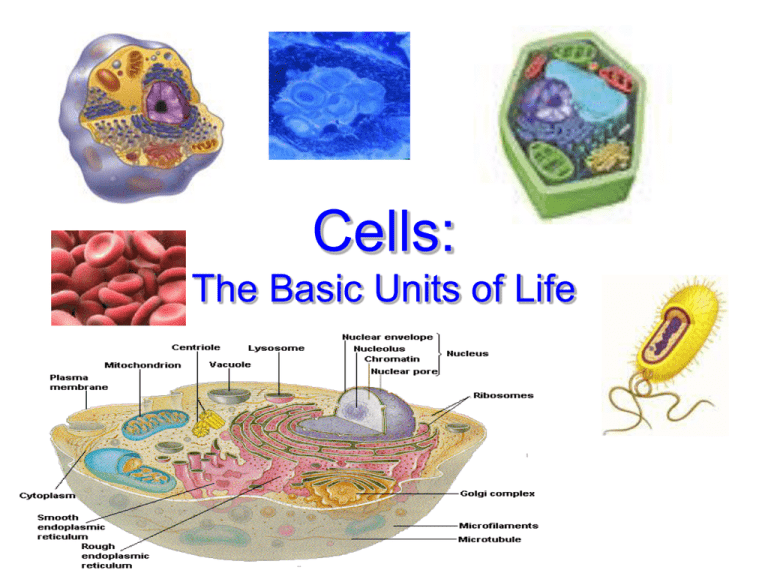
The structure of a cell is intimately linked to its function. All cells, whether prokaryotic (lacking a nucleus) or eukaryotic (possessing a nucleus), share basic components such as a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material.
The plasma membrane acts as a barrier, controlling what enters and exits the cell. The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance within the cell where various biochemical reactions occur.
The nucleus, found in eukaryotic cells, houses the DNA and controls cellular activities. Organelles like mitochondria (energy production) and ribosomes (protein synthesis) are crucial for cellular function.
Impact and Applications
Understanding the cell as the basic unit of life has profound implications for various fields. In medicine, it has led to the development of treatments for diseases like cancer, which is characterized by uncontrolled cell growth.
In biotechnology, cell culture techniques are used to produce pharmaceuticals and other valuable products. Furthermore, cell theory underpins our understanding of development, aging, and many other biological processes.
The ability to manipulate cells, through techniques like genetic engineering, has opened up new possibilities for treating genetic disorders and improving human health.
Looking Ahead
The study of cells continues to be a vibrant and rapidly evolving field. Advances in microscopy, genomics, and proteomics are providing new insights into cellular structure, function, and interactions.
Research on stem cells, which have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, holds great promise for regenerative medicine. Understanding how cells communicate with each other is also crucial for developing new therapies for diseases.
In conclusion, cells are considered the most basic unit of life because they are the smallest units capable of performing all the functions necessary for life, they contain the genetic material that is passed on from one generation to the next, and they are the basic units of structure in all living organisms. Their discovery and ongoing study have revolutionized our understanding of biology and medicine, and continue to hold immense potential for future advancements.







.PNG)






(141).jpg)