Why Do Earplugs Hurt My Ears

Imagine this: You're nestled in bed, eager to escape the city's relentless hum. A set of freshly unwrapped earplugs promises blissful silence. But instead of drifting off to dreamland, a nagging pressure builds in your ears, quickly escalating into a throbbing ache. The supposed solution has become the problem, leaving you tossing and turning, even more frustrated than before.
The discomfort and even pain caused by earplugs is a common experience, and while the solution seems straightforward, the underlying reasons are multifaceted. This article delves into the surprising culprits behind earplug-induced ear pain, offering practical insights and solutions to help you achieve the peaceful rest you deserve, without the agony.
Understanding the Anatomy
To understand why earplugs can cause pain, it's helpful to understand the basic anatomy of the ear. The ear is divided into three parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
The outer ear includes the visible part of your ear (the auricle or pinna) and the ear canal, which leads to the eardrum. The middle ear contains tiny bones that amplify sound vibrations. Finally, the inner ear houses the cochlea, responsible for converting these vibrations into signals that the brain interprets as sound.
The ear canal is a sensitive area, lined with skin that contains nerve endings and glands that produce earwax (cerumen). It's also not perfectly straight, but rather an S-shaped curve. This curvature, along with the sensitivity of the skin, plays a crucial role in why earplugs can sometimes cause discomfort.
Common Culprits Behind Earplug Pain
Several factors can contribute to earplug-related pain. Here are some of the most common:
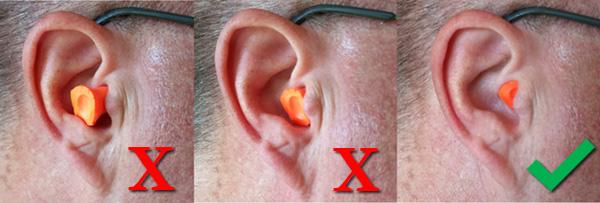
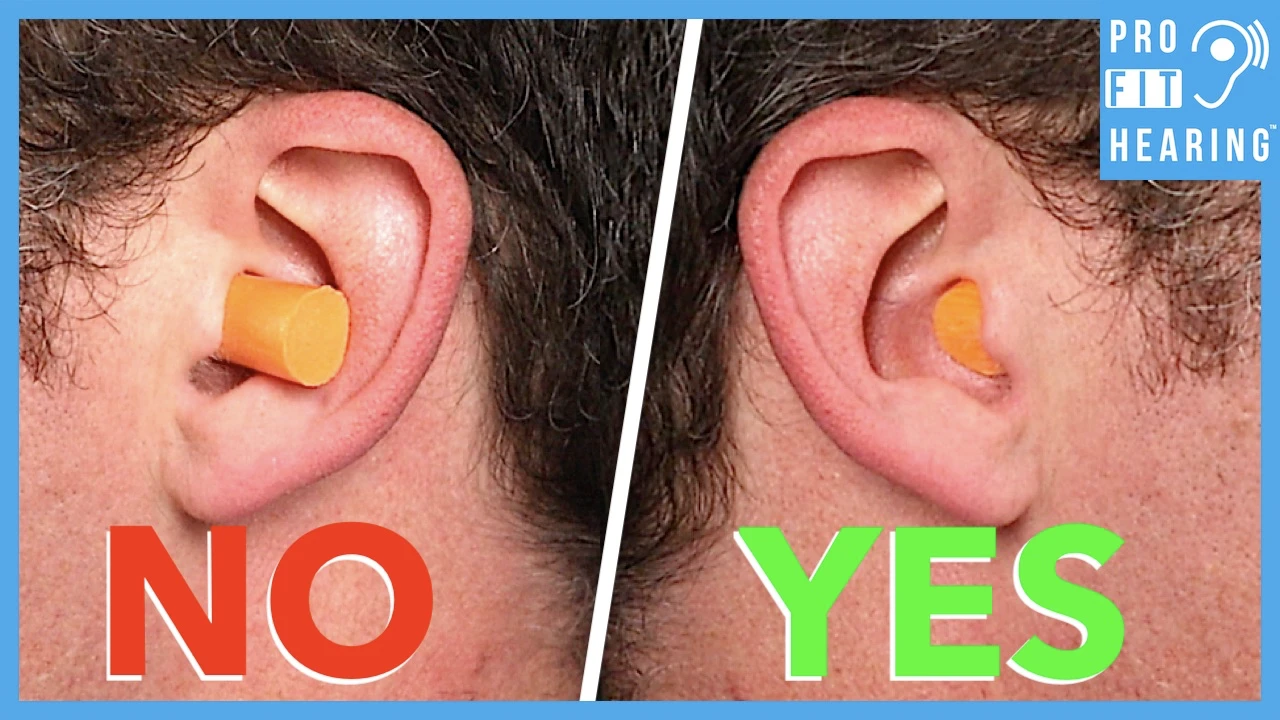
Improper Fit
Perhaps the most frequent offender is an improper fit. Ear canals vary in size and shape from person to person.
Using earplugs that are too large can exert excessive pressure on the ear canal walls, leading to pain and discomfort. Conversely, earplugs that are too small may not seal the canal properly, requiring you to push them in further, which can also cause pain.
Material Sensitivity
The material of the earplug itself can be a source of irritation for some individuals. Many disposable earplugs are made from foam, while reusable options often consist of silicone or other polymers.
Some people are sensitive or even allergic to these materials, resulting in itching, inflammation, and pain within the ear canal. According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology, contact dermatitis can occur from prolonged exposure to certain materials.
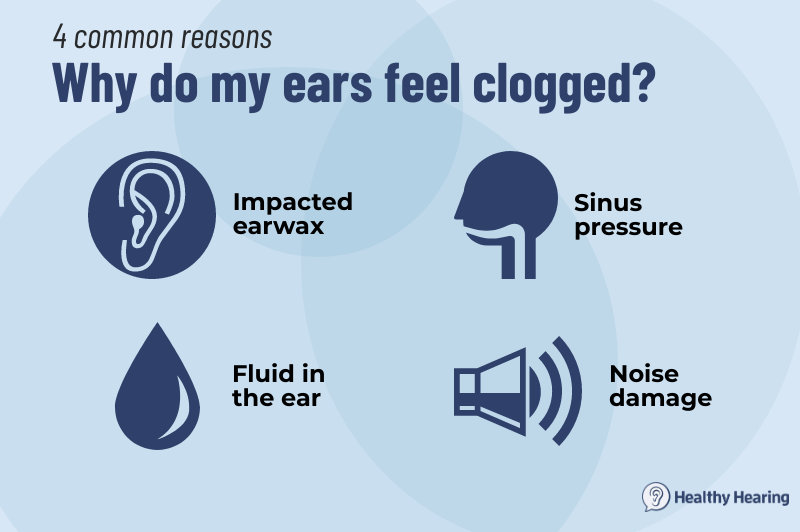
Pressure Imbalance
Earplugs can sometimes create a pressure imbalance between the outer and middle ear. This is especially true when flying or experiencing rapid altitude changes.
When the pressure outside the ear changes quickly, the Eustachian tube (which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat) may not be able to equalize the pressure quickly enough. This can lead to a feeling of fullness, pain, and even temporary hearing loss.
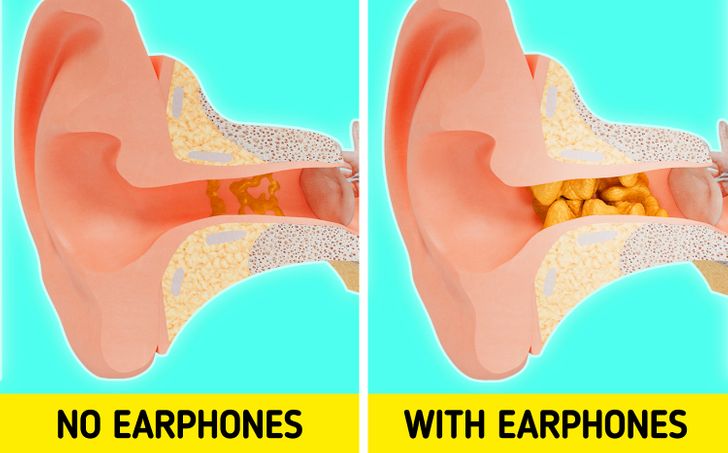
Earwax Buildup
Earwax is a natural and protective substance produced by the ear. However, excessive earwax buildup can become problematic, especially when combined with earplug use.
Earplugs can push earwax further into the ear canal, compacting it and potentially causing blockage. This blockage can lead to pressure, pain, and even infection.
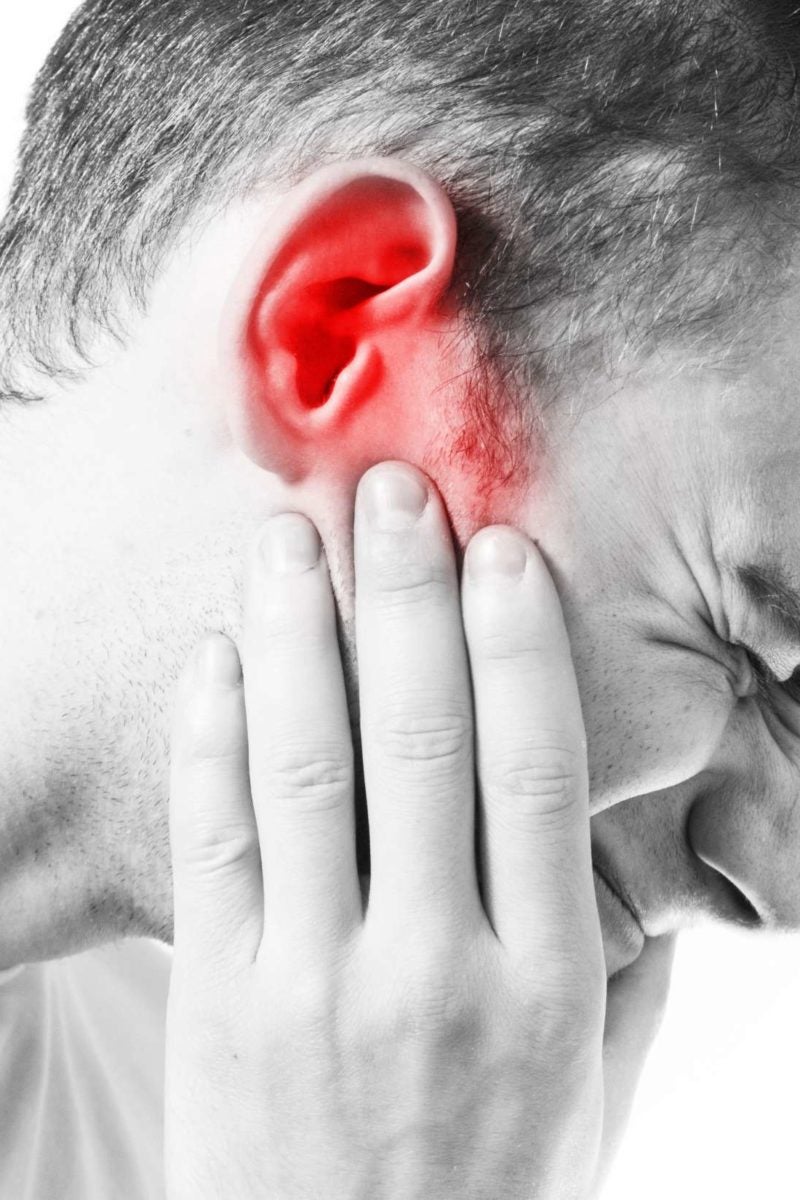
Infection or Inflammation
In some cases, earplug-related pain can be a sign of an underlying infection or inflammation. Using earplugs, especially if they are not clean, can introduce bacteria into the ear canal, increasing the risk of infection.
Pre-existing conditions like otitis externa (swimmer's ear) can also be aggravated by earplug use. Symptoms of infection include pain, redness, swelling, and discharge from the ear.
Solutions and Prevention
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to prevent and alleviate earplug-related pain:
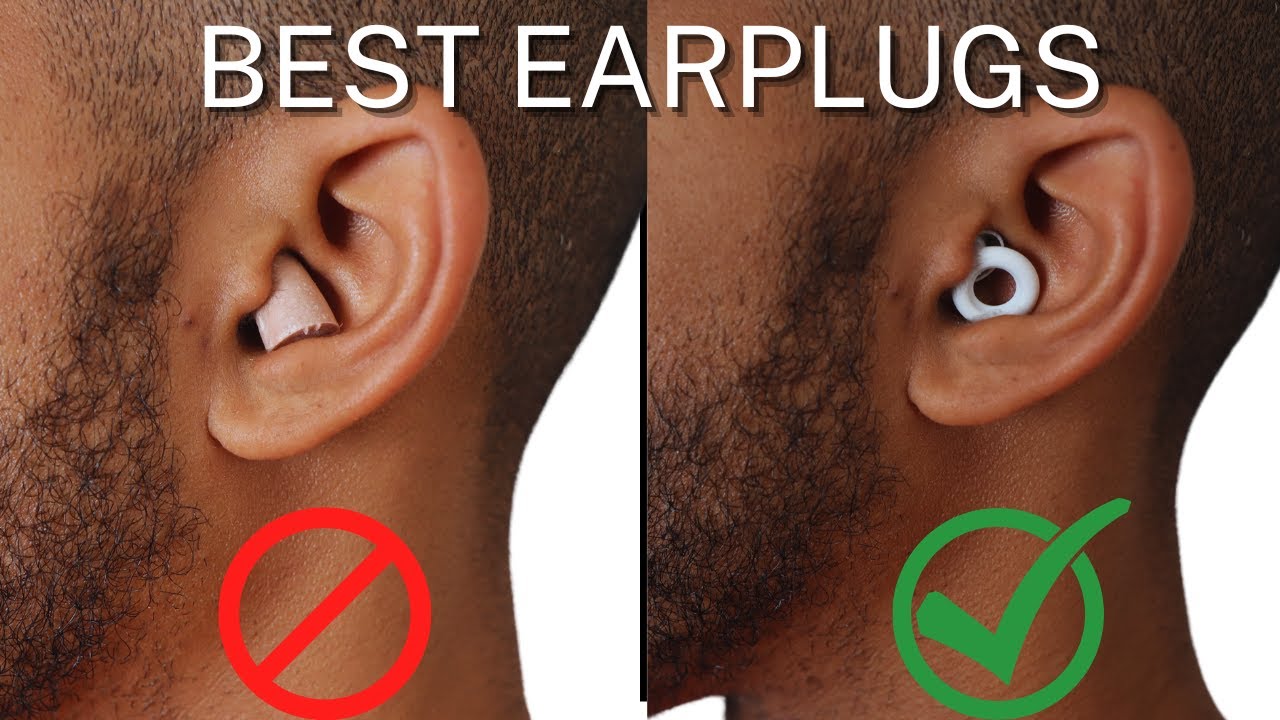
Choosing the Right Earplugs
Experimenting with different types and sizes of earplugs is crucial. Consider trying custom-molded earplugs, which are specifically designed to fit the unique contours of your ear canal.
These offer the best possible fit and can significantly reduce pressure and discomfort. Many audiologists offer custom earplug fitting services.
Proper Insertion and Removal
Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for inserting and removing earplugs. Rolling foam earplugs tightly between your fingers before insertion can help them compress and fit more comfortably.
When removing earplugs, do so slowly and gently to avoid creating a vacuum that can pull on the eardrum. Avoid yanking them out quickly.
Maintaining Hygiene
Clean your earplugs regularly with mild soap and water, especially reusable ones. Ensure they are completely dry before inserting them into your ears.
Avoid sharing earplugs with others to prevent the spread of bacteria. Replace disposable earplugs frequently.
Managing Earwax
If you are prone to earwax buildup, consider using over-the-counter earwax removal drops or visiting a healthcare professional for professional earwax removal. Avoid using cotton swabs to clean your ears, as they can push earwax further into the ear canal.
Addressing Pressure Imbalance
When flying or experiencing altitude changes, try yawning, swallowing, or chewing gum to help equalize pressure in your ears. Special earplugs designed to regulate pressure during flights are also available.
If you experience significant ear pain during flights, consult with your doctor before your next trip.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you experience persistent ear pain, discharge, or hearing loss, it's essential to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional. They can diagnose any underlying conditions and recommend appropriate treatment.
Don't attempt to self-treat ear infections or other ear problems, as this can potentially worsen the condition. Consult a doctor!
Beyond the Physical: The Psychological Impact
While the physical discomfort of earplug pain is undeniable, it's also important to acknowledge the psychological impact. The inability to find a comfortable and effective solution for noise reduction can lead to frustration, anxiety, and even sleep deprivation.
For individuals with noise sensitivities, such as those with misophonia or hyperacusis, the stakes are even higher. The promise of relief from disruptive sounds can quickly turn into a source of further distress when earplugs cause pain. This reinforces the need for personalized solutions and professional guidance.
The Future of Ear Protection
Innovation in ear protection is ongoing, with researchers and manufacturers constantly seeking to improve comfort and effectiveness. Advances in materials science are leading to the development of softer, more flexible earplugs that conform better to the ear canal.
Furthermore, advancements in noise-canceling technology are providing alternative solutions for individuals who find traditional earplugs uncomfortable. Noise-canceling headphones and earbuds can effectively reduce unwanted noise without the need for physical insertion into the ear canal.
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) continues to conduct research on hearing protection devices, aiming to improve their design and effectiveness in various environments.
A Path to Peaceful Sleep
Earplugs should be a tool for tranquility, not a source of torment. By understanding the potential causes of earplug-related pain and taking proactive steps to address them, you can transform your experience from one of discomfort to one of blissful silence.
Remember, finding the right earplugs and using them correctly is a journey of discovery. Don't be discouraged if your first attempt isn't perfect. Keep experimenting, seeking professional advice when needed, and prioritizing your comfort and well-being.
As you finally find the earplugs that fit just right, sinking into the quiet embrace of a peaceful night, you'll realize it was all worth it. Sweet dreams!

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/earpainfinal-01-5c86a4ba46e0fb00015f8fca.png)