Why Is Water Important For Metabolic Reactions

Imagine a bustling city, its streets teeming with activity, deliveries being made, and energy constantly being exchanged. Now, picture that city without its intricate network of roads and rivers; chaos would ensue, wouldn't it? Similarly, within our bodies, a silent, vital metropolis thrives, powered by countless metabolic reactions. But what is the lifeblood that keeps this inner city functioning smoothly? It's water, the unassuming yet indispensable element we often take for granted.
At the heart of it, water plays a crucial role in sustaining metabolic reactions. It’s more than just a thirst quencher; it’s the very foundation upon which life’s intricate chemical processes are built. Without sufficient water, our bodies simply can’t perform the necessary chemical reactions to convert food into energy, build and repair tissues, and eliminate waste products. Water is indispensable for survival.
The Universal Solvent: Setting the Stage for Reactions
Water's unique properties make it an exceptional solvent. Its polarity – the slight electrical charge difference within the molecule – allows it to dissolve a vast array of substances, including the nutrients, enzymes, and chemicals necessary for metabolic reactions. This dissolving ability is paramount, as it allows molecules to move freely and interact with each other within our cells.
Think of a crowded dance floor. It's hard to move and interact when everyone is packed tightly. Water provides the space needed for molecules to "dance" and react, facilitating the countless chemical transformations essential for life.
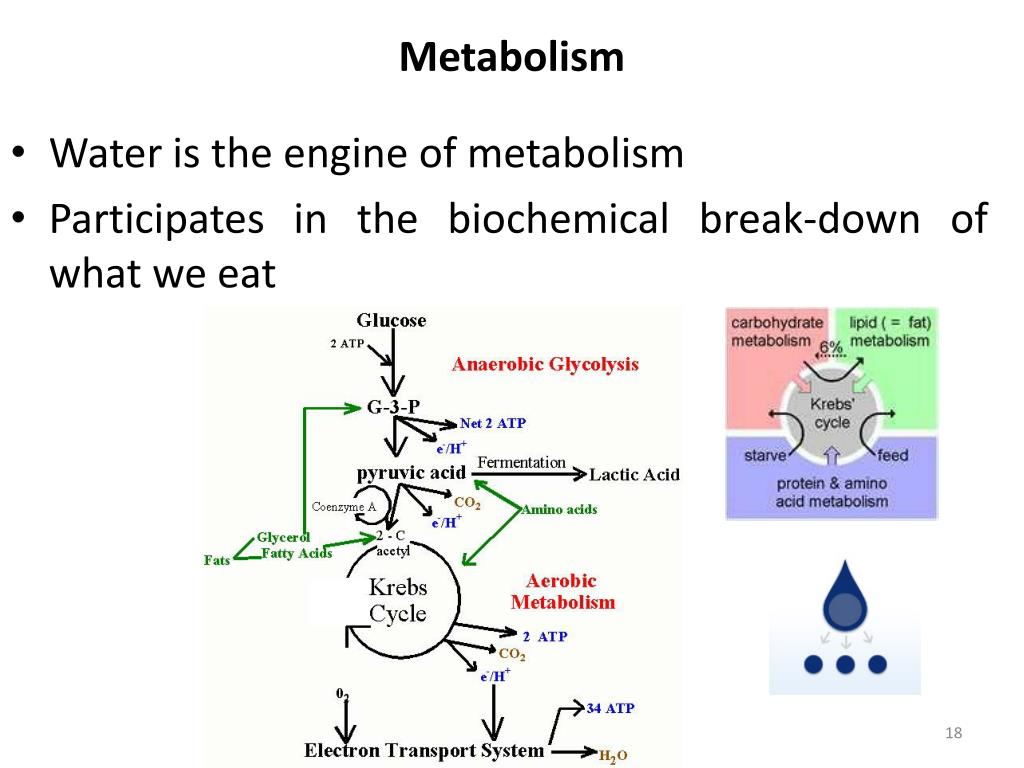
Hydrolysis and Dehydration: The Water-Driven Dance of Molecules
Many metabolic reactions hinge on the presence or absence of water. Two key processes, hydrolysis and dehydration, demonstrate water's pivotal involvement. Hydrolysis literally means "water splitting." This is when a water molecule is used to break down a larger molecule into smaller components.
For instance, the digestion of food relies heavily on hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are broken down into simpler sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids, respectively, through the addition of water. These smaller molecules can then be absorbed and used by the body for energy and building blocks.
Conversely, dehydration synthesis, also known as condensation reaction, involves the removal of a water molecule to join smaller molecules together to form larger ones. This process is crucial for building proteins, complex carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
Consider building a brick wall: bricks (smaller molecules) are joined together with mortar (dehydration reaction) to create a strong, stable structure (larger molecule). Without this process, our bodies couldn't build the complex molecules needed for growth, repair, and countless other functions.
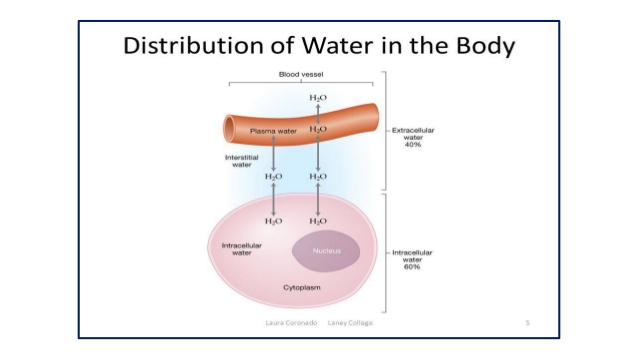
Water as a Transport Medium: Delivering the Goods
Beyond its direct involvement in chemical reactions, water serves as a vital transport medium within the body. Blood, which is primarily water, carries nutrients, oxygen, and hormones to cells and tissues throughout the body. Similarly, water transports waste products away from cells to be eliminated through urine and sweat.
Without adequate water, this transportation system becomes sluggish and inefficient. Nutrient delivery is hampered, waste removal is compromised, and overall cellular function suffers. This can lead to a cascade of negative health consequences, including fatigue, digestive issues, and impaired cognitive function, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Temperature Regulation: Maintaining the Optimal Environment
Water's high heat capacity plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature. It can absorb a significant amount of heat without undergoing drastic temperature changes itself. This helps to buffer our bodies against external temperature fluctuations and maintain a stable internal environment.
When we get too hot, we sweat. The evaporation of sweat from our skin draws heat away from the body, cooling us down. Without sufficient water, our ability to sweat effectively is diminished, increasing the risk of overheating.
The Risks of Dehydration: A Metabolic Slowdown
Dehydration, the state of not having enough water in the body, can significantly impair metabolic function. According to a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, even mild dehydration can reduce metabolic rate, making it harder to burn calories and maintain a healthy weight.
Dehydration can also lead to a buildup of toxins in the body, as the kidneys require water to effectively filter waste products from the blood. This can put extra stress on the liver and other organs involved in detoxification.
Symptoms of dehydration can range from mild fatigue and headache to more severe issues such as dizziness, confusion, and even organ failure. It is, therefore, essential to maintain adequate hydration levels by drinking enough water throughout the day.
How Much Water Do We Need? A Balancing Act
The amount of water needed varies from person to person, depending on factors such as activity level, climate, and overall health. However, a general guideline is to aim for about eight glasses of water per day, as recommended by the U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
Listen to your body's thirst cues and drink water throughout the day, even when you don't feel thirsty. Eating water-rich fruits and vegetables, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and spinach, can also contribute to your overall hydration levels.
It's also important to note that certain beverages, such as sugary drinks and alcohol, can actually contribute to dehydration. Opt for water, herbal teas, or infused water to stay properly hydrated.
A Deeper Appreciation for Water: A Call to Action
Water is an unsung hero of our inner world. It's a solvent, a reactant, a transport medium, and a temperature regulator – all essential for the smooth functioning of our metabolism. By understanding its importance, we can make conscious choices to prioritize hydration and support our overall health and well-being.
Perhaps the next time you reach for a glass of water, take a moment to appreciate the vital role it plays in keeping you alive and thriving. It's a simple act with profound consequences for the intricate metabolic processes that sustain us all. Remember to hydrate!
In a world increasingly focused on complex solutions, it’s easy to overlook the simple, yet profound power of water. By appreciating its significance and prioritizing hydration, we can unlock the full potential of our bodies and live healthier, more vibrant lives. It's a powerful reminder that sometimes, the most important things are the ones we often take for granted. So, drink up, and let the life-giving flow of water nourish you from the inside out.