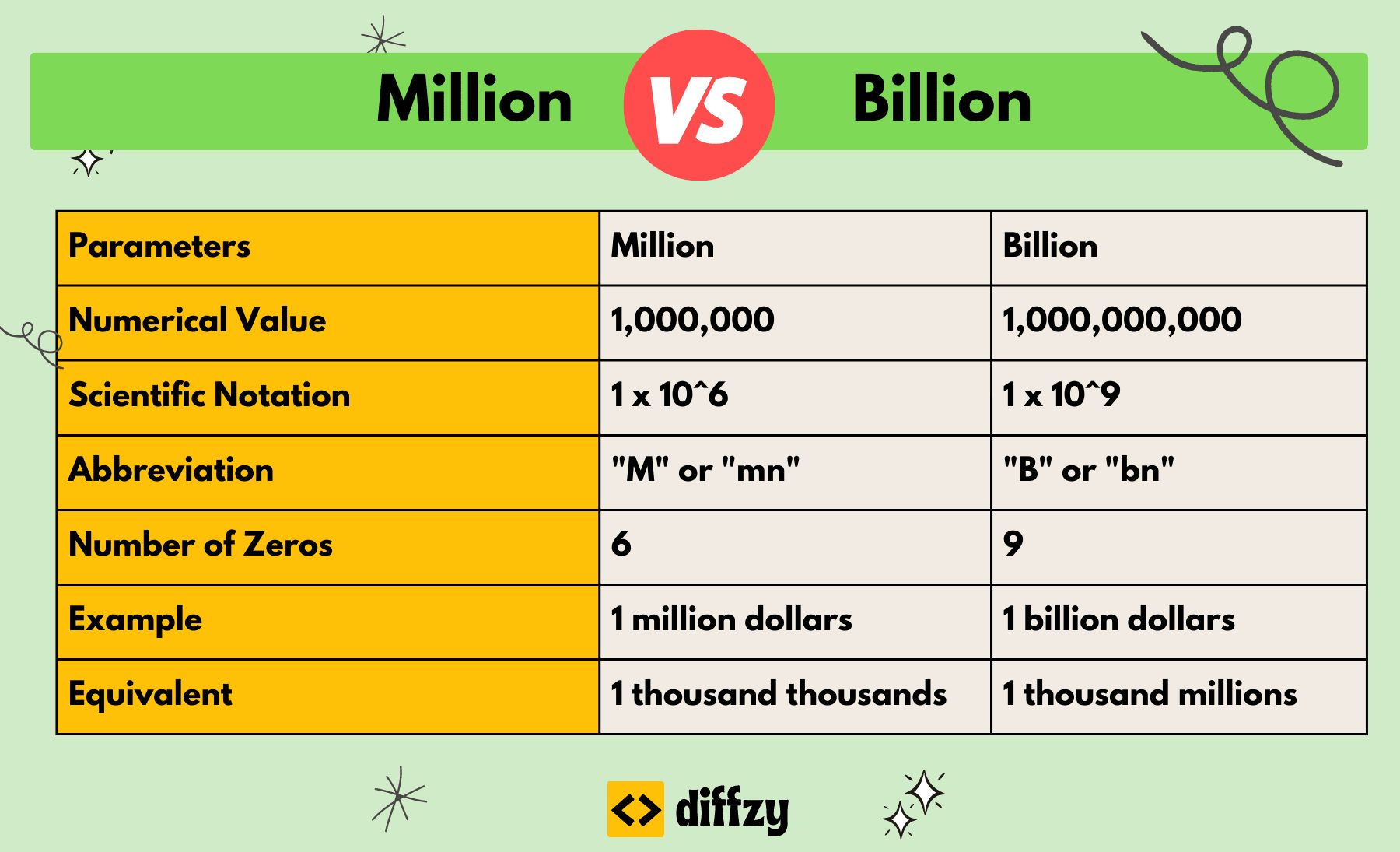
8 Billion Divided By 8 Million

The global population recently surpassed 8 billion, a milestone prompting both celebration of human progress and concern about resource distribution. Simultaneously, the number of millionaires worldwide is estimated to be around 59.4 million, creating a striking divide. This article explores the implications of this disparity, examining its potential impact on global stability and future policies.
The rapid population increase, coupled with the concentration of wealth, presents a complex challenge. Understanding the factors contributing to this imbalance and its potential consequences is crucial for informed policy-making and sustainable development strategies.
Global Population Surpasses 8 Billion
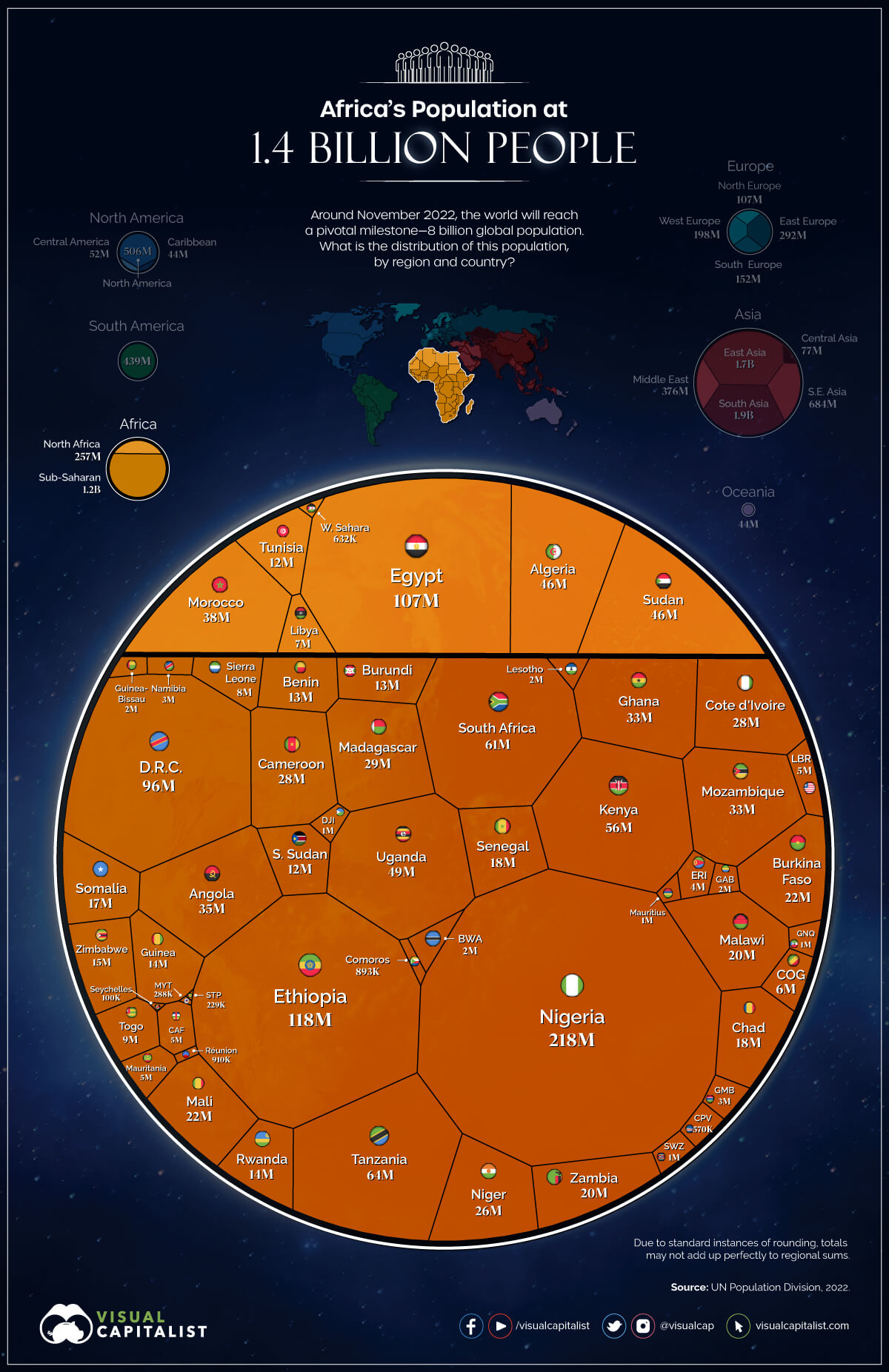
In November 2022, the United Nations announced that the world population had reached 8 billion. This significant increase has occurred in a relatively short period. It took roughly twelve years to grow from 7 billion to 8 billion.
According to the UN, much of this growth has been concentrated in developing countries, particularly in Africa and Asia. Increased life expectancy and declining child mortality rates have contributed significantly to this population boom.
Key Drivers of Population Growth
Several factors contribute to the continued growth of the global population. Improvements in healthcare and sanitation have led to longer lifespans. Increased access to food and resources, though unevenly distributed, has also played a role.
The UN projects that the world population will continue to grow. Projections estimate reaching 9 billion in about 2037 and 10 billion in 2058. This growth will place further strain on existing resources and infrastructure.
Wealth Concentration: The Rise of Millionaires
While the global population has surged, wealth has become increasingly concentrated in the hands of a few. Reports from organizations like Credit Suisse and UBS indicate a significant increase in the number of millionaires worldwide.
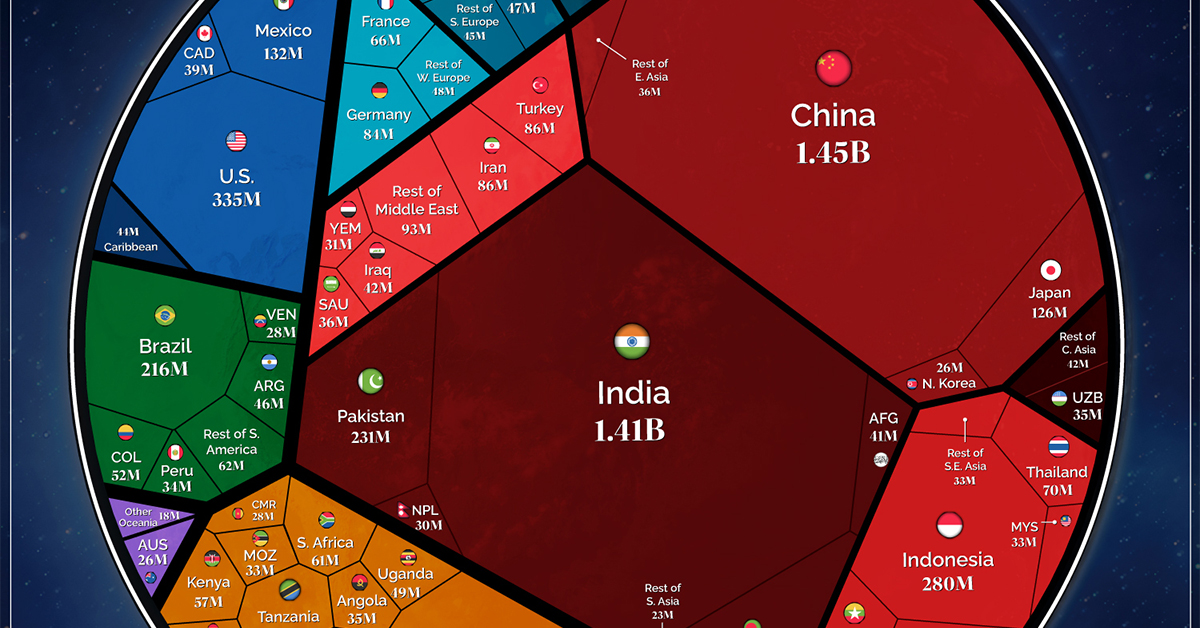
As of 2023, it is estimated that there are around 59.4 million millionaires globally. This figure represents a substantial portion of the world's wealth controlled by a relatively small percentage of the population.
North America and Europe continue to house a significant number of millionaires. However, wealth is also growing rapidly in emerging economies such as China and India.
Factors Contributing to Wealth Inequality
Several factors have contributed to the increasing concentration of wealth. Globalization and technological advancements have created new opportunities for wealth creation.
Capital gains, inheritance, and favorable tax policies have also played a role. These factors exacerbate existing inequalities and make it more difficult for individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds to accumulate wealth.
"Wealth inequality is not just an economic issue; it's a social and political one that can undermine social cohesion and democratic institutions," - Oxfam International
The Divide: 8 Billion Divided by Millions
The stark contrast between the global population and the number of millionaires highlights the issue of wealth inequality. The implications of this divide are far-reaching, affecting everything from access to resources to political stability.
The concentration of wealth in the hands of a few can lead to social unrest and political instability. Those who feel left behind may become disillusioned with the existing system. They might demand greater economic justice.
The distribution of resources, such as food, water, and healthcare, is also affected. Unequal access to these essential resources can lead to humanitarian crises and exacerbate existing inequalities.
Potential Impacts and Policy Considerations
Addressing wealth inequality requires a multifaceted approach. Progressive taxation, investment in education and healthcare, and policies that promote fair wages and working conditions are essential.
International cooperation is also crucial. Addressing global challenges such as climate change and poverty requires coordinated efforts across borders.
Promoting sustainable development that benefits all segments of society is vital. This requires a shift away from purely economic growth towards a more inclusive and equitable model.
Technological advancements can play a role in addressing inequality. Increased access to education and resources is possible through technology.
Human Interest Angle
Maria Rodriguez, a single mother in Guatemala, struggles to provide for her family. Her daily life reflects the challenges faced by billions living in poverty. Access to basic necessities, such as clean water and adequate nutrition, remains a constant struggle.
Contrast this with John Smith, a successful entrepreneur. He benefits from a globalized economy and ample resources. His lifestyle is vastly different, highlighting the stark divide that exists in the world.
Stories like these underscore the human impact of wealth inequality. It reminds us of the urgent need for solutions that address the root causes of poverty and promote greater economic justice.
The global community must confront the challenges posed by population growth and wealth concentration. By working together, it is possible to create a more just and sustainable future for all.