A Hormone That Is Synergistic To Growth Hormone Is

Imagine a symphony orchestra. Each instrument, from the delicate flute to the booming timpani, plays its part, contributing to the overall richness and complexity of the music. Now, picture one instrument, a seemingly unassuming violin, whose presence subtly amplifies the beauty and power of the entire orchestra. In the world of hormones, a similar phenomenon is unfolding, with scientists increasingly recognizing the importance of a hormone that works synergistically with the well-known growth hormone.
This article explores the burgeoning understanding of IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1), a hormone that acts as a crucial mediator and amplifier of growth hormone's effects. While growth hormone often takes center stage, IGF-1's role in facilitating growth, repair, and overall metabolic health is proving to be indispensable, offering potential therapeutic avenues for growth disorders, aging-related decline, and beyond.
The Growth Hormone Axis: A Dynamic Duo
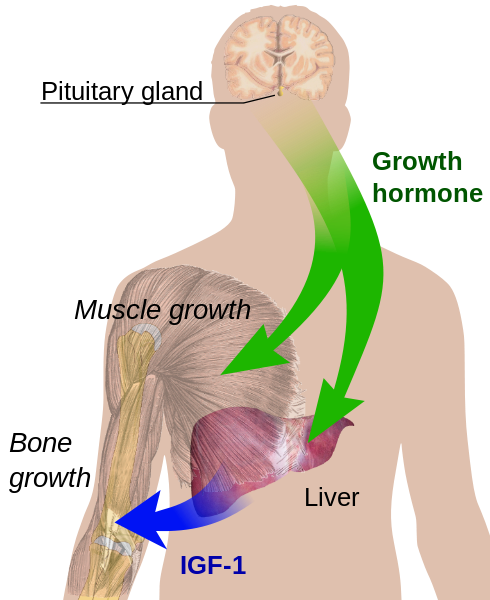
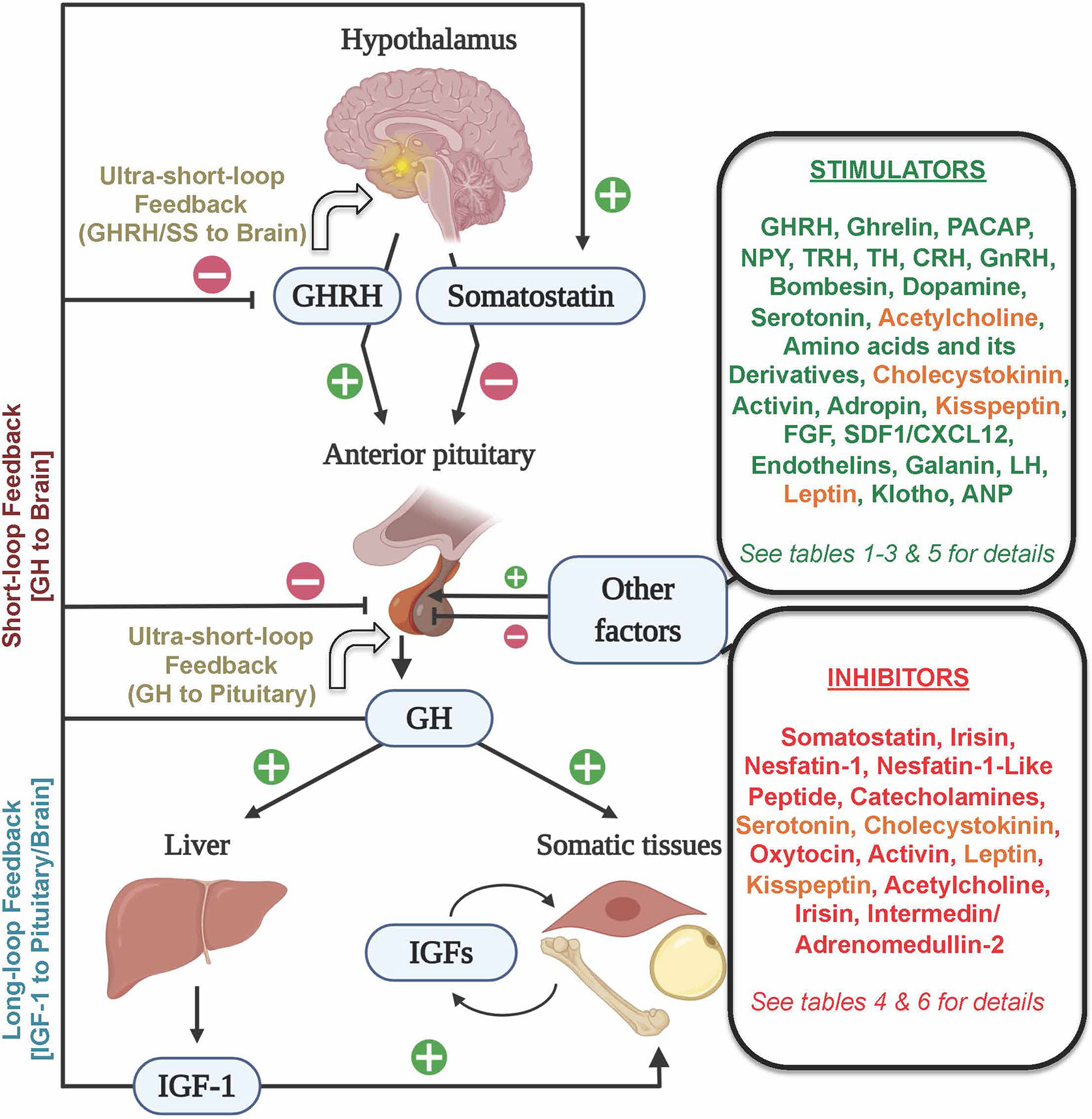
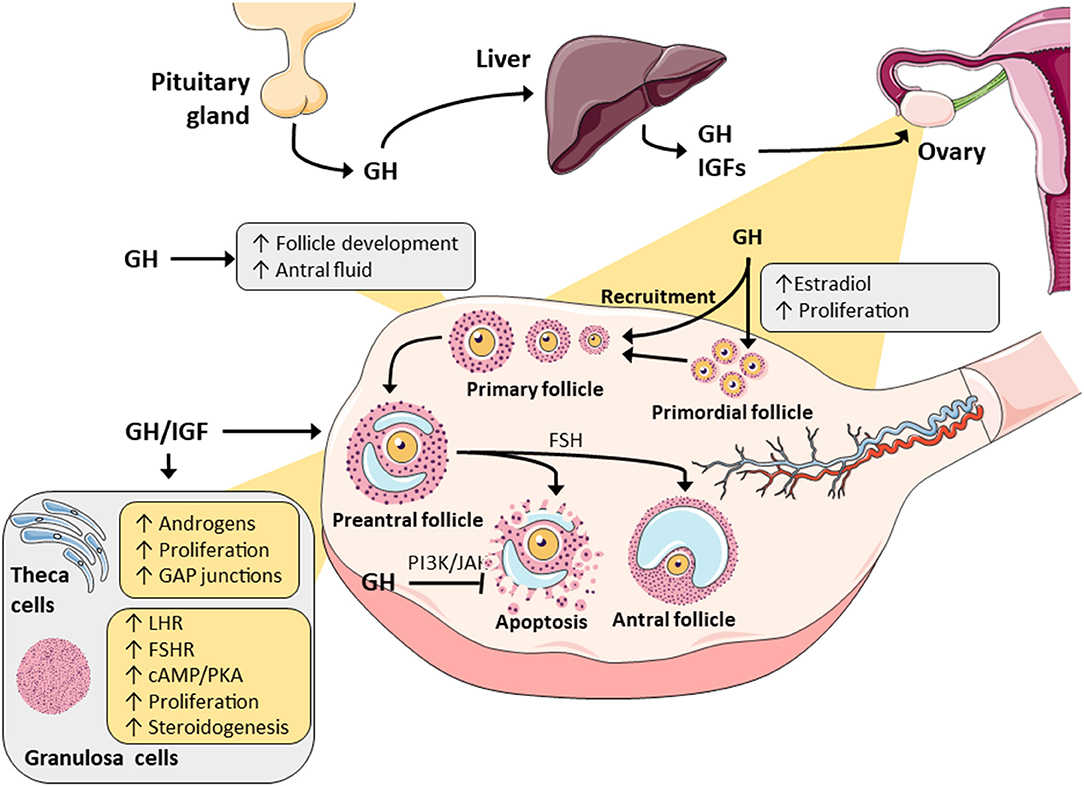
For decades, growth hormone (GH) has been recognized as a key player in childhood development, regulating bone growth, muscle mass, and body composition. However, the story doesn't end with GH alone. Scientists discovered that many of GH's effects are actually mediated by IGF-1, primarily produced in the liver in response to GH stimulation.
Think of GH as the conductor of our symphony. It signals the body to grow and repair, but IGF-1 is the instrument that translates the conductor's instructions into specific actions at the cellular level. Without IGF-1, GH's signals would be significantly muted.
This GH-IGF-1 relationship is often referred to as the growth hormone axis, a complex and tightly regulated system that ensures proper growth and development throughout life. Disruptions in this axis can lead to a range of health problems, highlighting the delicate balance required for optimal function.
IGF-1: More Than Just Growth
While IGF-1 is undoubtedly crucial for growth, its functions extend far beyond childhood development. It plays a vital role in maintaining tissue health, regulating metabolism, and even influencing cognitive function. These broader effects are becoming increasingly apparent as researchers delve deeper into IGF-1's mechanisms of action.
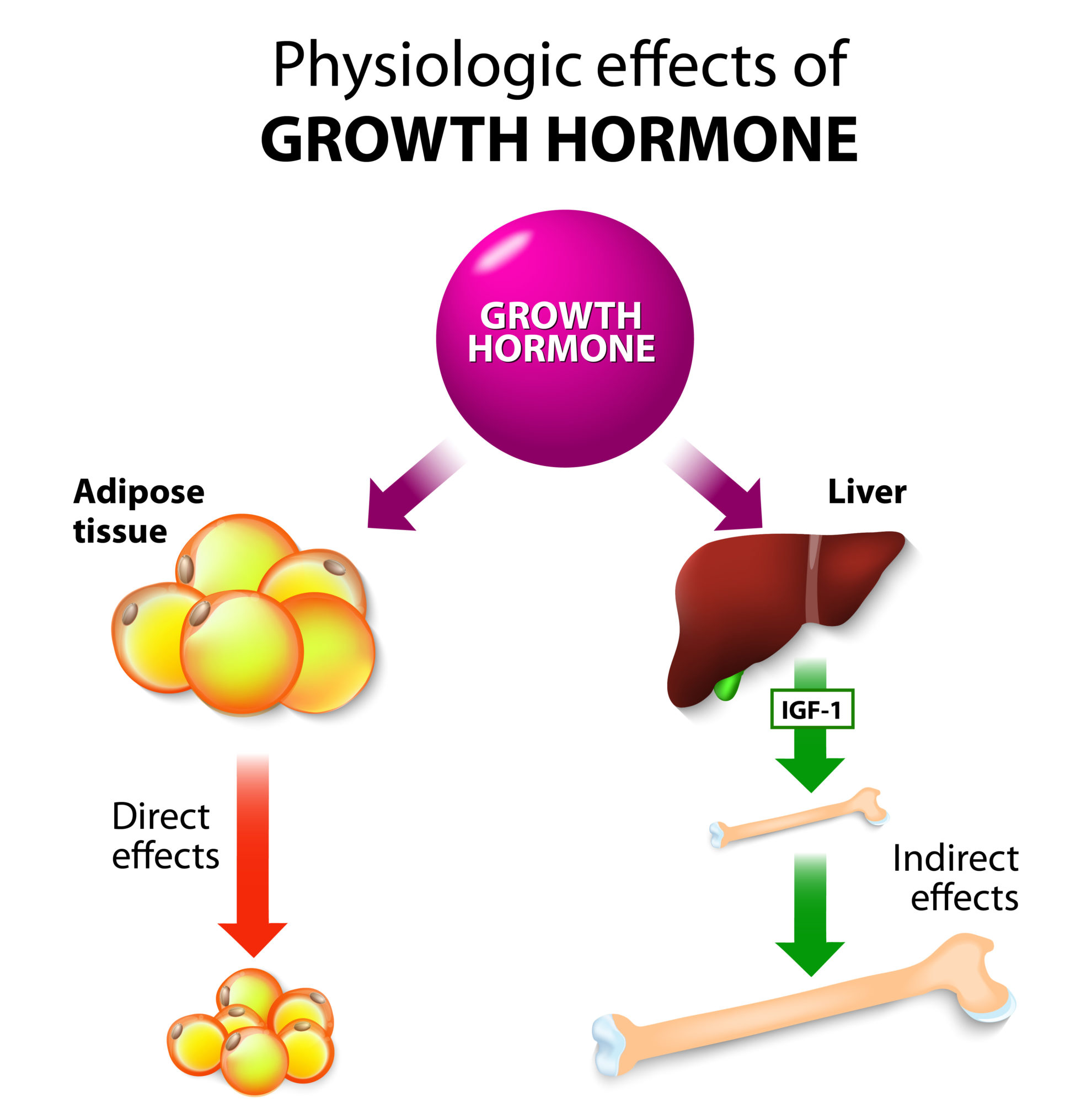
IGF-1 stimulates the uptake of glucose and amino acids into cells, providing the building blocks and energy necessary for growth and repair. This anabolic effect is particularly important for maintaining muscle mass and bone density, which tend to decline with age.
Studies have also linked IGF-1 to improved cognitive function, possibly through its neuroprotective effects and its ability to promote the growth and survival of brain cells. Research suggests that adequate IGF-1 levels may play a role in preventing age-related cognitive decline.
Implications for Health and Disease
The synergistic relationship between GH and IGF-1 has significant implications for understanding and treating a variety of health conditions. Deficiencies in either hormone can lead to growth disorders in children, while imbalances in adulthood can contribute to metabolic problems, muscle weakness, and increased risk of chronic diseases.
For example, children with growth hormone deficiency often benefit from GH therapy, which stimulates the liver to produce more IGF-1. However, in some cases, children may have a resistance to GH, meaning their bodies don't respond adequately to GH stimulation. In these situations, direct IGF-1 therapy may be considered.
On the other end of the spectrum, excessive GH and IGF-1 levels can lead to acromegaly, a condition characterized by abnormal growth of the hands, feet, and face. Understanding the complex interplay between these hormones is crucial for developing effective treatments for both deficiencies and excesses.
Aging and the GH-IGF-1 Axis
As we age, the production of both GH and IGF-1 naturally declines, contributing to the age-related loss of muscle mass, bone density, and overall vitality. This decline has fueled interest in exploring whether interventions that boost GH and IGF-1 levels could help to slow down the aging process.
While GH therapy has shown some promise in improving body composition and muscle strength in older adults, it also carries potential risks, including increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular problems. Therefore, researchers are exploring alternative strategies, such as lifestyle interventions and targeted therapies, to safely and effectively optimize IGF-1 levels.
For example, resistance exercise has been shown to stimulate GH and IGF-1 production, helping to maintain muscle mass and bone density as we age. Dietary modifications, such as ensuring adequate protein intake, can also support IGF-1 synthesis.
The Future of IGF-1 Research
The understanding of IGF-1's multifaceted role in human health is constantly evolving. Researchers are actively investigating its potential therapeutic applications in a wide range of conditions, from growth disorders and diabetes to neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.
One promising area of research is the development of IGF-1 analogs that can selectively target specific tissues and pathways, minimizing the risk of side effects. These analogs could potentially be used to treat muscle wasting diseases, promote wound healing, and even enhance cognitive function.
Furthermore, scientists are exploring the role of IGF-1 in regulating the lifespan. Studies in animal models have shown that reduced IGF-1 signaling can extend lifespan, suggesting that modulating IGF-1 activity may hold the key to slowing down the aging process.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading endocrinologist at the National Institutes of Health, emphasizes the importance of continued research in this area. "IGF-1 is a critical regulator of growth, metabolism, and aging," she explains. "By unraveling the complexities of the GH-IGF-1 axis, we can develop more effective strategies to prevent and treat a wide range of diseases and promote healthy aging."
A Symphony of Health
The story of IGF-1 is a testament to the intricate and interconnected nature of our bodies. It reminds us that even seemingly secondary players can have a profound impact on our overall health and well-being. By understanding the synergistic relationship between GH and IGF-1, we can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms that govern growth, repair, and aging.
As research continues to unravel the complexities of the GH-IGF-1 axis, we can anticipate exciting new developments in the prevention and treatment of a wide range of diseases. Ultimately, this knowledge will empower us to live healthier, longer, and more fulfilling lives.
Just as the violin's subtle contributions enhance the richness of a symphony, IGF-1 plays a critical role in amplifying the positive effects of growth hormone, ensuring the harmony of our internal systems and promoting a life of vitality.

+both+help+increase+volume+of+fluid+in+body..jpg)
+Adrenaline.+Increase+level+of+blood+glucose.+Mutual+effect+among+hormones+is+intensive+each+other..jpg)



.jpg)