All Of The Following Are True About Variable Products Except

The complexities surrounding variable financial products often leave investors vulnerable to misinformation, leading to potentially detrimental financial decisions. A thorough understanding of these instruments is crucial, yet misconceptions persist, blurring the lines between fact and fallacy.
This article aims to clarify the landscape of variable products, dissecting common assumptions and highlighting a key point: while variable products offer numerous features, not all claims about them hold true. Specifically, we will explore a fictional, albeit representative, multiple-choice question: "All of the following are true about variable products EXCEPT…" This examination serves as a framework to understand the nuances, risks, and potential rewards associated with these investment vehicles, enabling readers to make informed choices.
Understanding Variable Products
Variable products, such as variable annuities and variable life insurance, are investment vehicles where the value fluctuates based on the performance of underlying investment options, typically sub-accounts holding stocks, bonds, or other assets. This contrasts with fixed products, where returns are guaranteed at a specific rate.
These products combine insurance features, like death benefits, with investment opportunities, providing a dual benefit to the policyholder. The variable nature, however, introduces market risk, meaning the value can increase or decrease depending on market conditions.
Common Misconceptions: Examining the "EXCEPT"
Let's consider a hypothetical question: "All of the following are true about variable products EXCEPT: A) They offer potential for higher returns compared to fixed products; B) They provide a death benefit to beneficiaries; C) Investment gains are always tax-free; D) They involve market risk." The correct answer, and thus the exception, is likely C: investment gains are not always tax-free.
While variable products offer tax-deferred growth, meaning taxes are not paid until withdrawal, this doesn't equate to complete tax exemption. When funds are withdrawn during retirement, the gains are typically taxed as ordinary income.
This contrasts with municipal bonds, where interest income may be tax-exempt. Understanding the nuances of tax treatment is crucial for assessing the true value proposition of variable products.
Potential for Higher Returns
Option A, the potential for higher returns, is generally true. Because variable products are linked to the market, investors have the opportunity to participate in market upside.
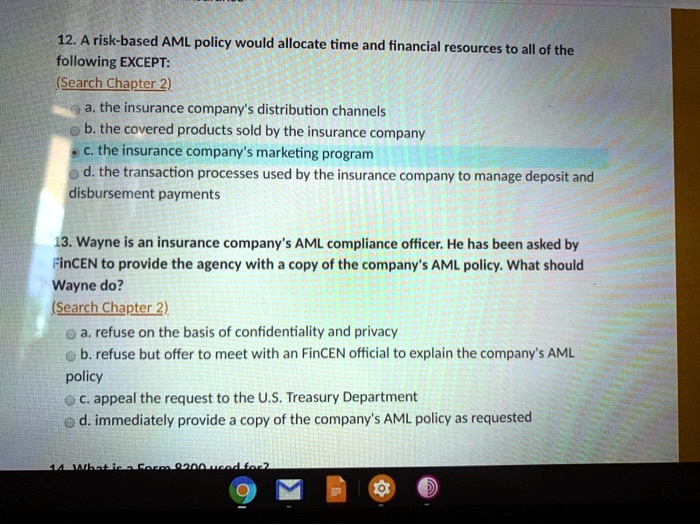
This potential for higher returns comes with increased risk. Market fluctuations can lead to significant losses, especially in volatile periods.
Diversification within the sub-accounts can mitigate some risk, but careful selection of investments is essential.
Death Benefit Provisions
Option B, the death benefit, is a core feature of both variable annuities and variable life insurance. The death benefit ensures that beneficiaries receive a payout upon the policyholder's death.
The amount of the death benefit may be based on the account value or a guaranteed minimum, whichever is higher. This feature provides financial security for loved ones.
However, the death benefit may be reduced by outstanding loans or withdrawals, highlighting the importance of understanding policy terms.
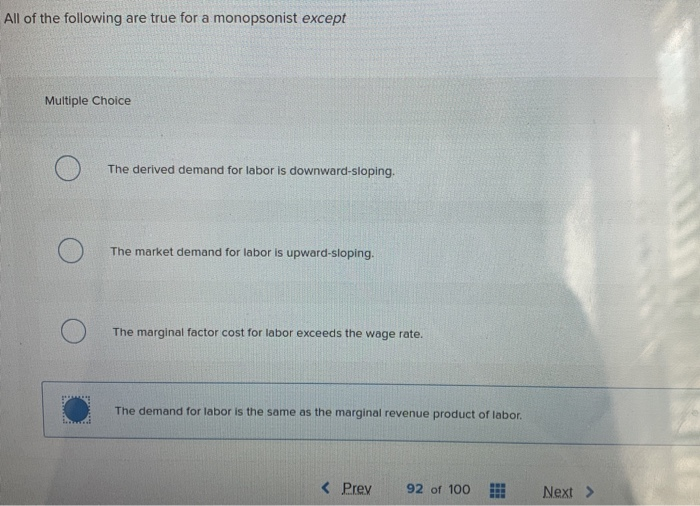
The Inherent Market Risk
Option D, the presence of market risk, is a fundamental characteristic of variable products. The value of the underlying investments can fluctuate based on market conditions, economic factors, and investor sentiment.
This risk is often higher than in fixed-income investments. Investors should have a long-term investment horizon to weather potential market downturns.
Risk tolerance and investment goals should be carefully considered before investing in variable products.
The Role of Fees and Expenses
Variable products often come with a range of fees and expenses, including mortality and expense (M&E) risk charges, administrative fees, and investment management fees. These fees can significantly impact returns.
It’s vital to understand the fee structure before investing. Compare the fees of different products to ensure you are getting a competitive rate.
High fees can erode potential gains, making it difficult to achieve investment goals.
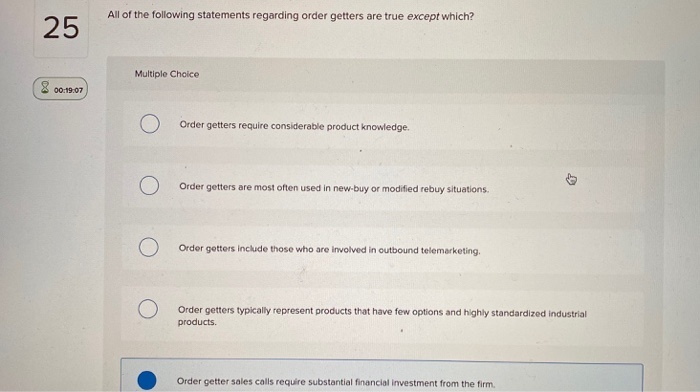
Suitability and Investor Considerations
Variable products are not suitable for all investors. They are generally more appropriate for individuals with a long-term investment horizon and a moderate to high risk tolerance.
Financial advisors play a crucial role in assessing suitability. They can help investors understand the complexities of variable products and determine if they align with their financial goals and risk profile.
Investors should carefully review the prospectus before investing. The prospectus contains detailed information about the product's features, risks, and fees.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Variable Products
The variable product landscape is continually evolving. New products and features are being developed to meet changing investor needs.
Regulatory changes and market conditions also influence the industry. Staying informed about these developments is essential for investors and financial professionals alike.
As the demand for retirement income solutions grows, variable products will likely continue to play a significant role in helping individuals achieve their financial goals, provided that investors approach them with a clear understanding of their benefits and limitations.


![All Of The Following Are True About Variable Products Except [Solved]: All of the following are an example of a](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/dd3/dd3d78d4-26dc-4d26-89c3-d52a9658a75d/image.jpg)