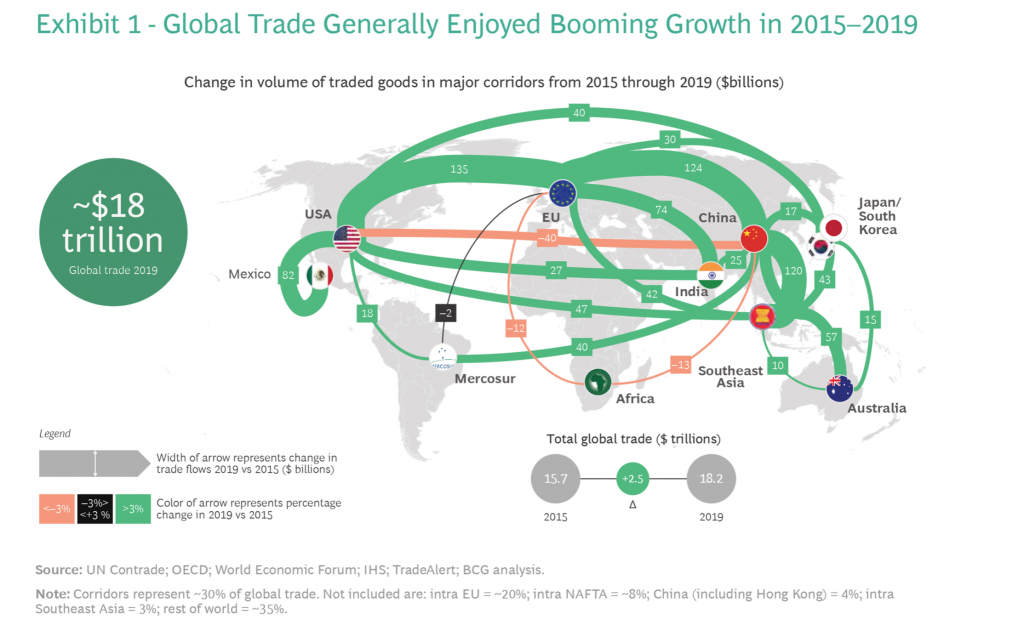
Among The Changes Resulting From Increased Global Trade Is

The interconnected tapestry of global commerce has been relentlessly rewoven in recent decades, its threads drawn tighter by technological advancements and policy shifts. This intensification of international trade has yielded undeniable economic benefits, yet it has also sown seeds of profound societal transformation. From shifting labor markets to the homogenization of consumer culture, the ripples of increased global trade are reshaping lives and landscapes across the world.
This article delves into the multifaceted consequences of escalating global trade, focusing particularly on the less heralded, yet deeply impactful, changes that are reshaping societies. We will explore how this interconnectedness is altering employment patterns, influencing cultural identities, and impacting environmental sustainability, drawing on data from organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and academic research to paint a comprehensive picture. Ultimately, we seek to understand not just the economic gains, but the broader societal costs and opportunities that arise from an increasingly interconnected world economy.
Shifting Sands: The Restructuring of Labor Markets
One of the most significant consequences of increased global trade is the profound restructuring of labor markets. The ease with which goods and services can now cross borders has led to a redistribution of jobs, often from developed to developing nations.
This phenomenon, commonly referred to as outsourcing or offshoring, has resulted in job losses in certain sectors in industrialized countries, particularly in manufacturing. Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates a steady decline in manufacturing employment in the United States over the past several decades, a trend often linked to increased competition from lower-wage countries.
Conversely, developing nations have experienced significant job growth in export-oriented industries. Countries like China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh have become major hubs for manufacturing and assembly, providing employment opportunities for millions. However, these jobs often come with concerns about labor standards, working conditions, and wages.
Cultural Convergence and the Rise of Global Brands
Beyond the economic realm, increased global trade is also fostering a convergence of cultures. The proliferation of international brands and products is shaping consumer preferences and homogenizing lifestyles across national boundaries.
This cultural diffusion is largely driven by multinational corporations who are able to promote their products and services on a global scale. The rise of global brands like McDonald's, Nike, and Coca-Cola is a testament to this phenomenon, representing more than just products, they are symbols of a globalized consumer culture.
However, the spread of global brands can also lead to concerns about the erosion of local traditions and cultural identities. Critics argue that the dominance of Western culture through global brands can marginalize local businesses and dilute unique cultural expressions. There is a growing movement promoting the consumption of local products and the preservation of cultural heritage in response to this homogenizing trend.
The Environmental Cost: A Balancing Act
The expansion of global trade has also raised significant environmental concerns. The increased production and transportation of goods contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, pollution, and resource depletion.
The WTO has acknowledged the importance of addressing the environmental challenges associated with trade. The increased transportation of goods across long distances requires substantial consumption of fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions and air pollution. Deforestation to create agricultural land for export crops can also exacerbate environmental damage and biodiversity loss.
Some argue that trade can also promote environmental sustainability by facilitating the diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies and practices. Countries with stricter environmental regulations can encourage companies to adopt cleaner production methods, which can then be disseminated through global supply chains. The challenge lies in creating a system that incentivizes sustainable practices and penalizes environmentally harmful ones.
Navigating the Future: Opportunities and Challenges
As global trade continues to evolve, it is crucial to address the challenges and harness the opportunities that arise. This requires a multi-faceted approach that considers the economic, social, and environmental dimensions of trade.
Policies aimed at mitigating the negative impacts of trade on labor markets are essential. Investing in education and retraining programs can help workers adapt to changing job demands. Strengthening social safety nets, like unemployment insurance and worker support programs, can provide a buffer for those displaced by trade-related job losses.
Promoting sustainable trade practices is also vital. This includes incentivizing the adoption of cleaner production technologies, enforcing environmental regulations, and supporting fair trade initiatives. Consumers also play a role by making informed choices about the products they purchase and supporting companies that prioritize sustainability.
Ultimately, the goal should be to create a more inclusive and sustainable global trade system that benefits all stakeholders. This requires international cooperation, responsible corporate behavior, and a commitment to addressing the social and environmental consequences of trade.
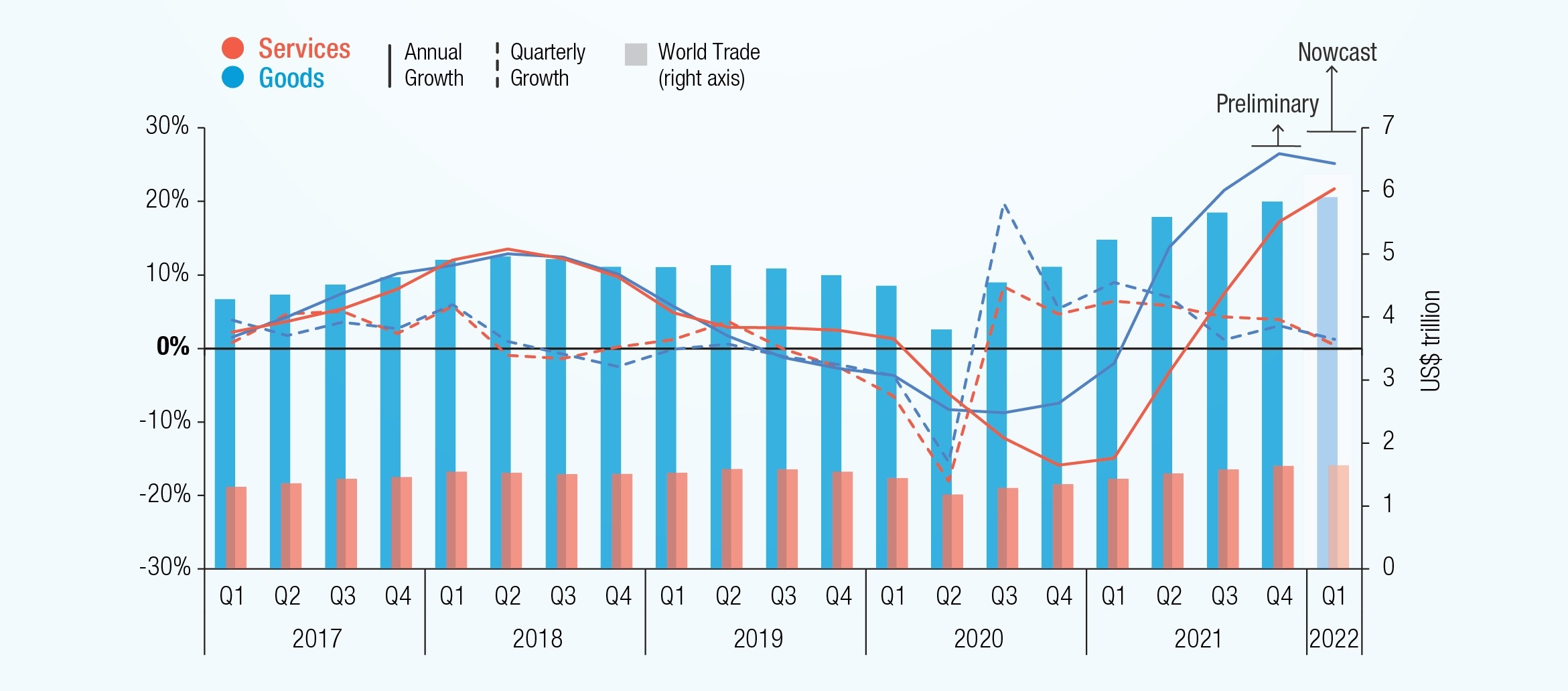
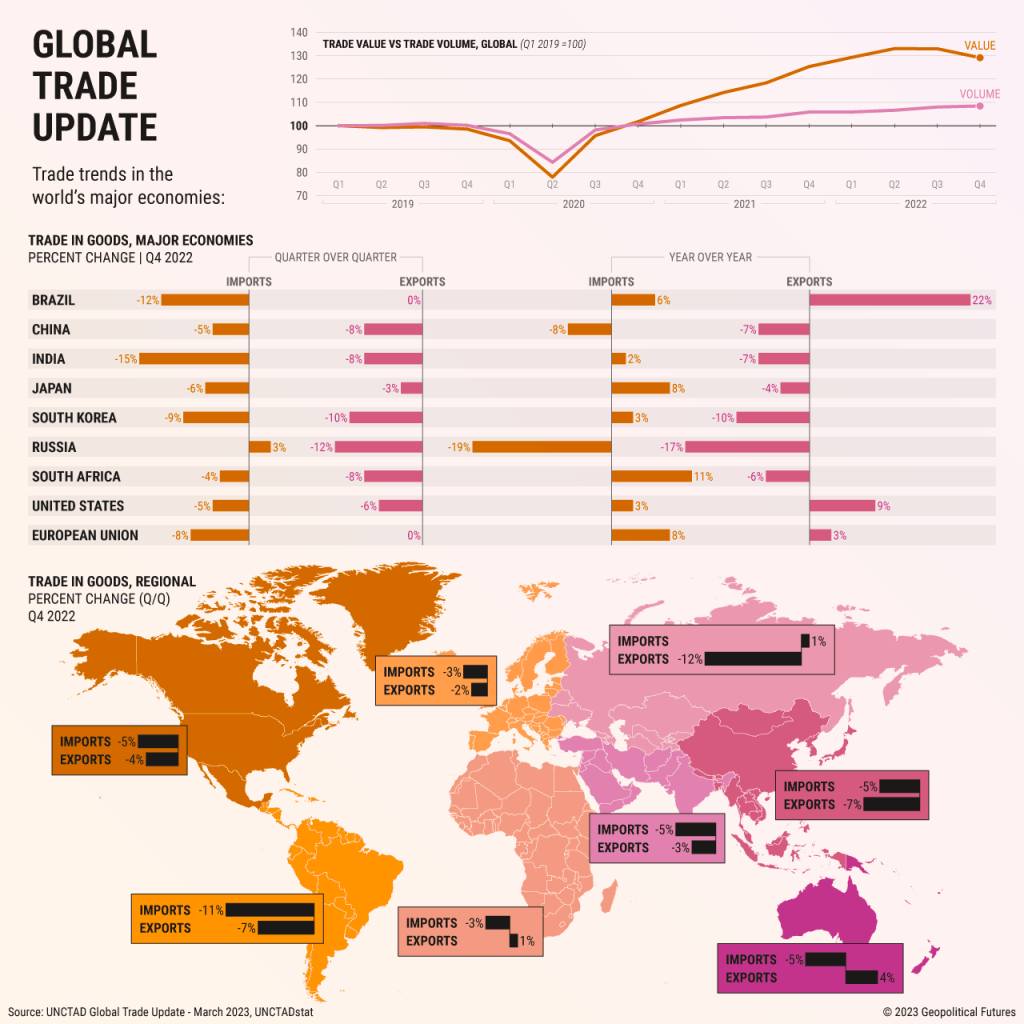








+-+comprised+of+Western+European+countries+to+promote+free+trade+among+members+–.jpg)