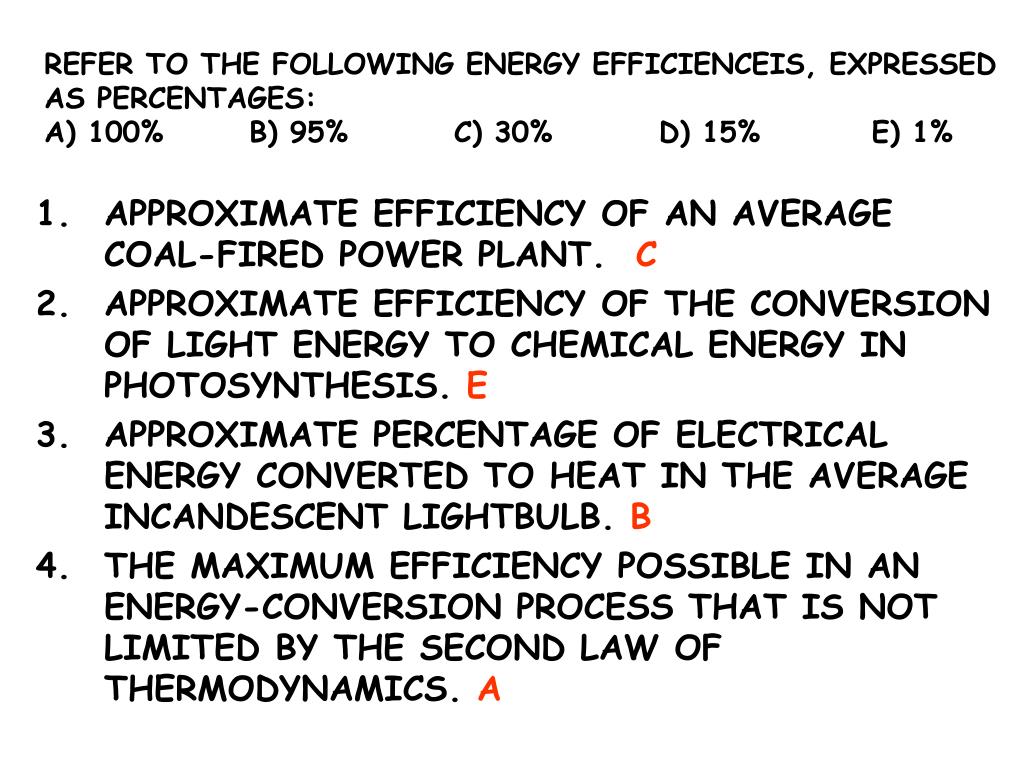
Approximate Efficiency Of An Average Coal Fired Power Plant
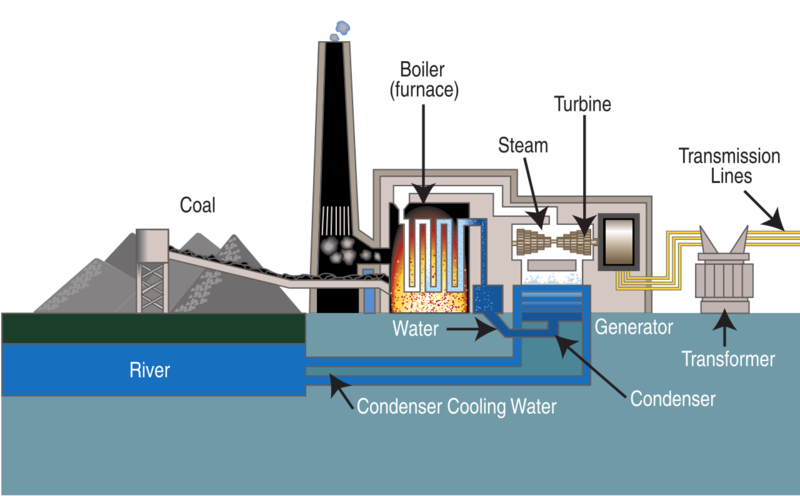
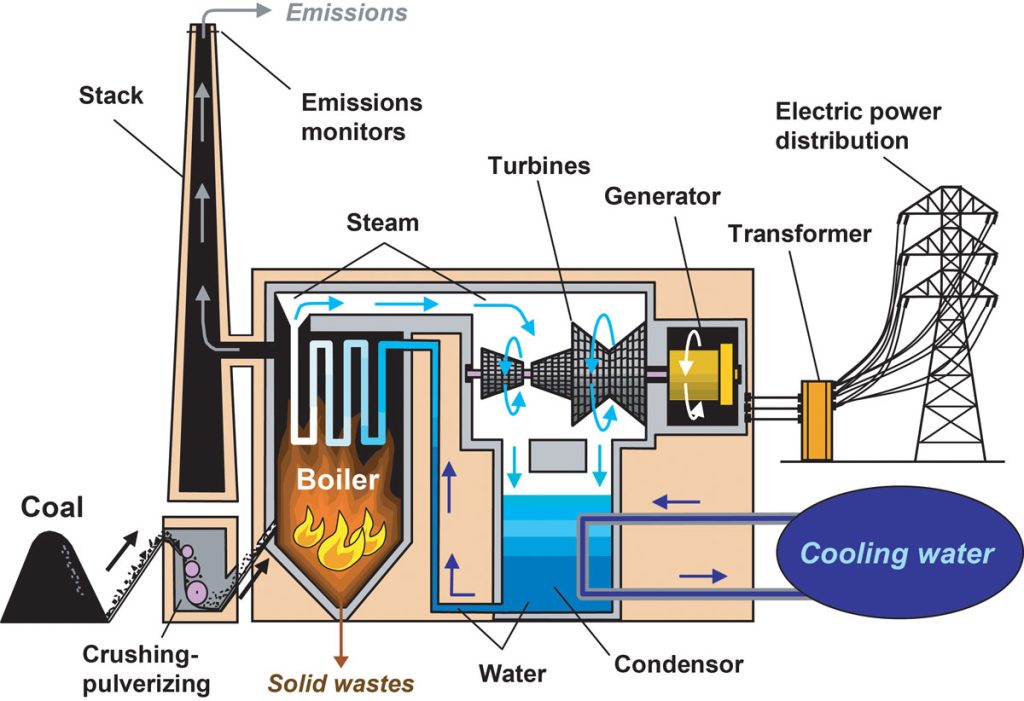
Imagine standing in the shadow of a colossal structure, steam billowing into the sky like a dragon's breath. This is the heart of a coal-fired power plant, a place where the ancient energy of the earth is unleashed to power our modern lives. But how much of that ancient energy is actually converted into the electricity that lights our homes and charges our devices?
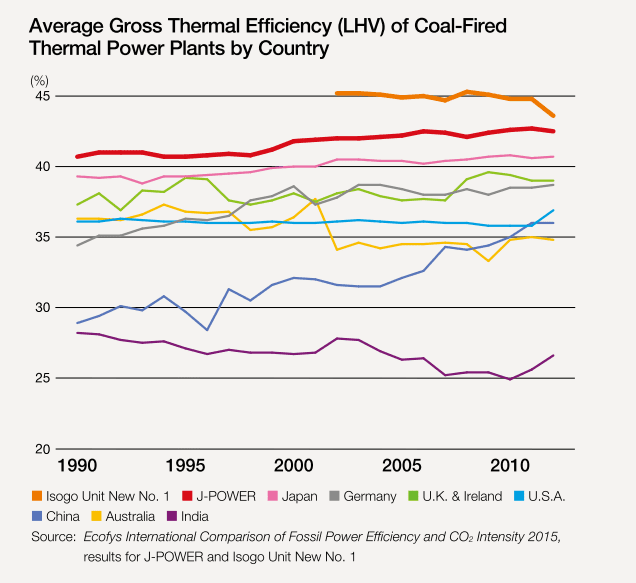
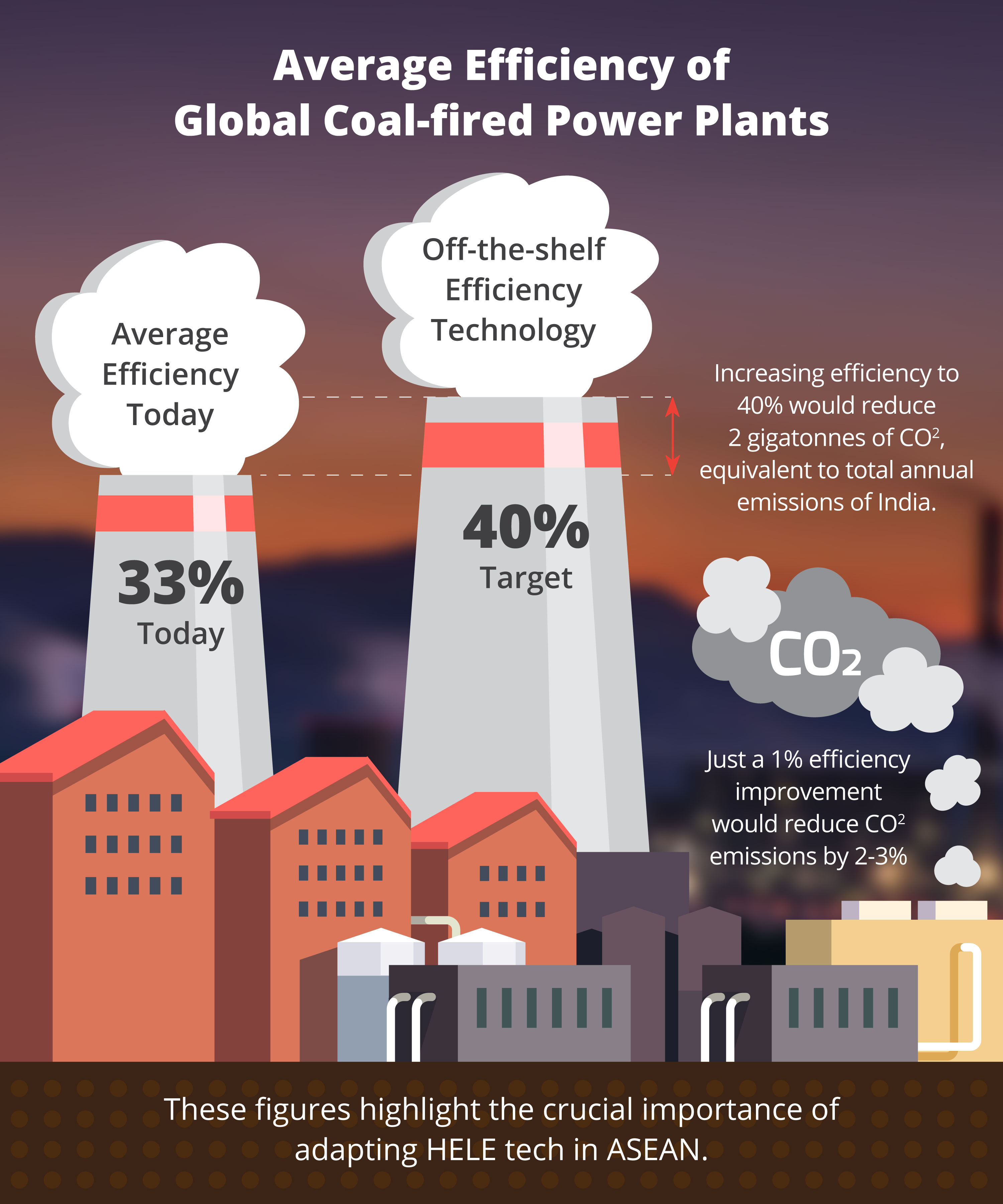
The answer to that question lies in a crucial metric: efficiency. And when it comes to the average coal-fired power plant, the efficiency hovers around 33%. This means that for every unit of energy contained in the coal burned, only about a third is transformed into usable electricity.
Understanding Efficiency in Coal Power
Delving into the world of coal-fired power plants requires understanding what "efficiency" truly signifies. It represents the ratio of electrical energy produced to the thermal energy contained within the coal.
In simpler terms, it's about how well a plant converts the heat from burning coal into electricity. A higher efficiency rating signifies less wasted energy and reduced environmental impact.
The Energy Journey: From Coal to Kilowatts
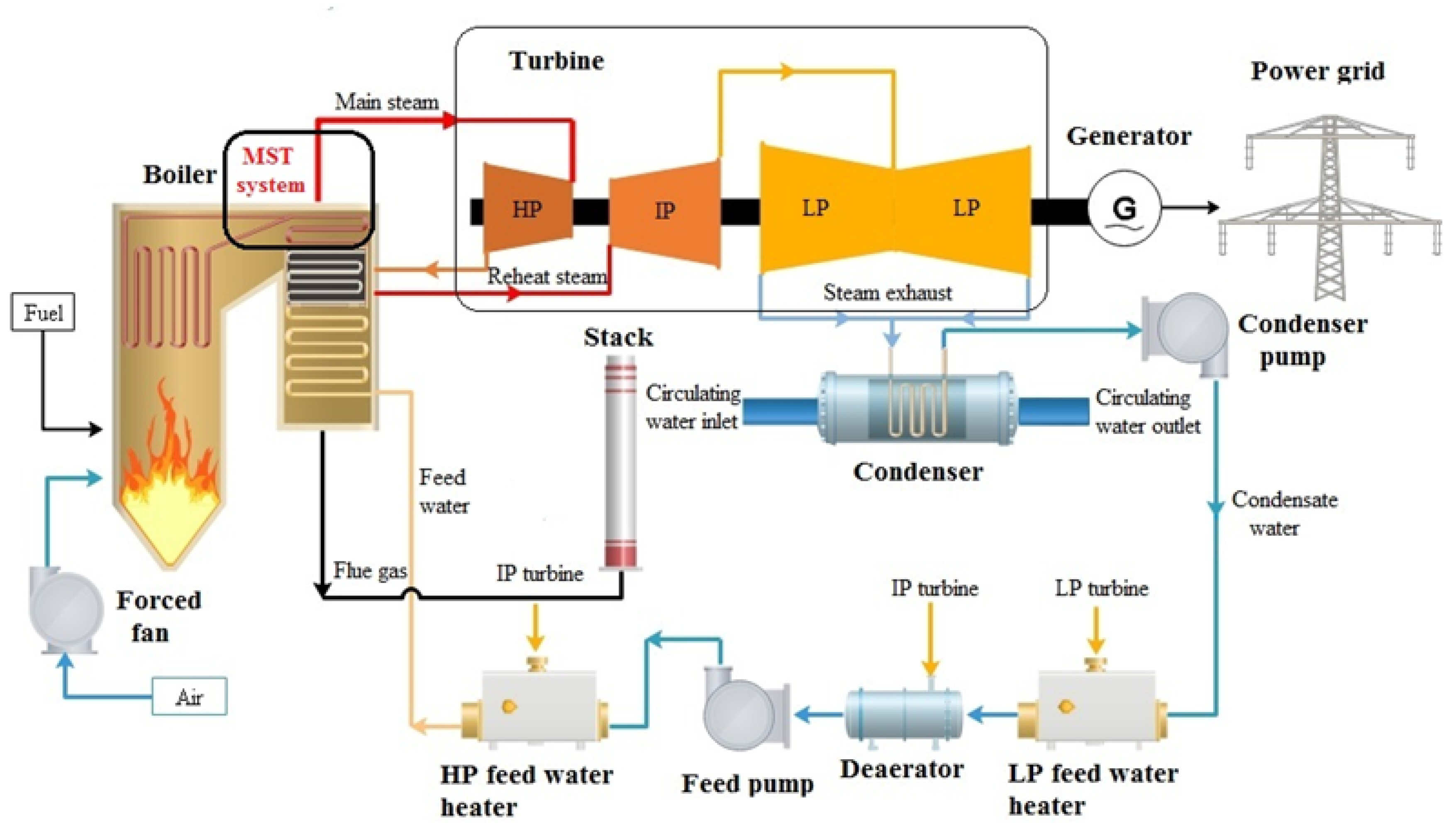
The process begins with burning coal, releasing heat that boils water. This creates high-pressure steam, which then spins a turbine connected to a generator. The generator, in turn, produces electricity.
However, energy is lost at each stage of this process. Some heat escapes up the smokestack, some is lost due to friction in the machinery, and some is inherent in the thermodynamic limitations of the process itself.
Factors Influencing Efficiency
Several factors affect the efficiency of a coal-fired power plant. The age of the plant is a significant one; older plants typically operate at lower efficiencies due to outdated technology.
The type of coal used also matters. Some coals have higher energy content and burn more efficiently than others. Bituminous coal, for example, generally yields better results than lignite.
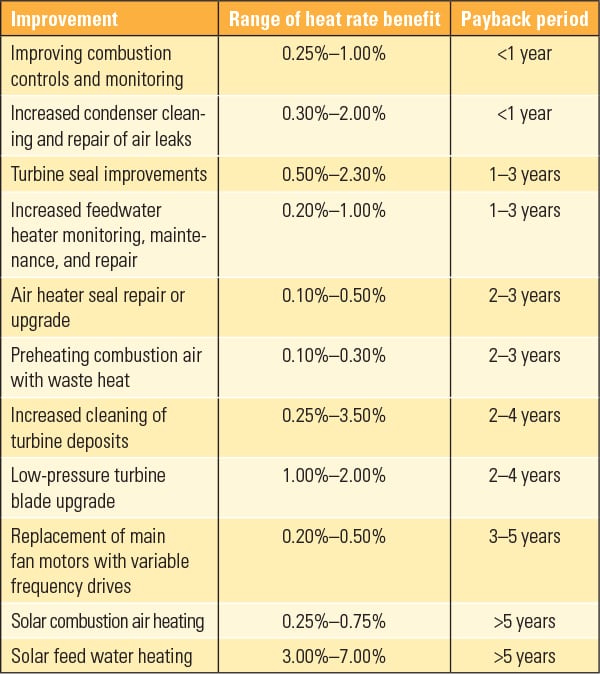
Furthermore, the design and maintenance of the plant play crucial roles. Modern supercritical and ultra-supercritical plants, with their higher operating temperatures and pressures, can achieve efficiencies closer to 40%, showcasing the impact of technological advancements.
The Significance of Efficiency
Why is efficiency so important? The answer is multi-faceted, touching on both economic and environmental considerations.
From an economic standpoint, higher efficiency translates to lower fuel costs. A more efficient plant requires less coal to produce the same amount of electricity, saving money and reducing the strain on coal resources.
Environmentally, increased efficiency leads to reduced emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants. Burning less coal means releasing less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.
"Improving the efficiency of coal-fired power plants is a critical step towards a more sustainable energy future," stated a recent report from the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Many countries are investing in upgrading their existing coal plants or building new, more efficient ones. This includes incorporating technologies like carbon capture and storage (CCS) to further reduce emissions.
Looking Ahead
While coal-fired power plants still play a significant role in global energy production, their future is intertwined with the pursuit of greater efficiency and cleaner technologies.
The development and deployment of advanced technologies, coupled with policies that incentivize efficiency improvements, will be crucial in minimizing the environmental impact of coal power.
As the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy mix, the lessons learned from optimizing coal-fired power plants can inform the development of other energy sources, ensuring a more efficient and environmentally responsible energy future for all.