Are Naps Good For Muscle Growth

In the relentless pursuit of muscle hypertrophy, athletes and fitness enthusiasts tirelessly explore every avenue for optimization. From meticulously crafted diets to rigorously planned workout routines, no stone is left unturned. But what about the simple act of napping? Can a midday snooze truly contribute to building a stronger physique, or is it merely a blissful indulgence with no tangible benefits for muscle growth?
The question of whether naps aid muscle growth is more complex than it appears, demanding a nuanced understanding of sleep's impact on hormonal regulation, protein synthesis, and overall recovery. While intense training breaks down muscle fibers, the body's repair and rebuilding processes are largely orchestrated during periods of rest, primarily during sleep. This article delves into the science behind sleep and muscle growth, examining the potential benefits of napping, exploring conflicting research findings, and offering practical guidance for those seeking to integrate naps into their muscle-building strategies. We'll dissect the roles of key hormones like testosterone and growth hormone, analyze the impact of sleep deprivation on muscle protein synthesis, and consider the individual factors that influence the effectiveness of napping.
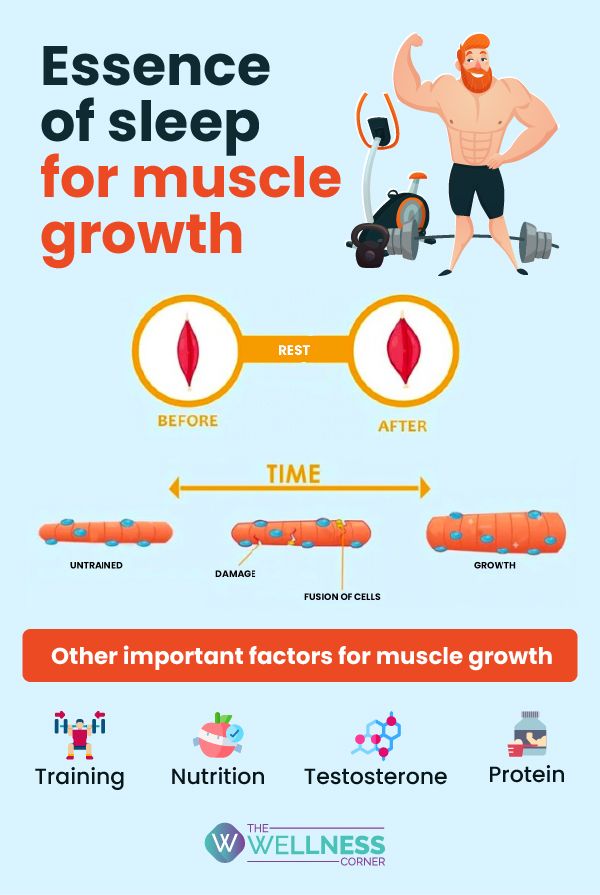
The Science of Sleep and Muscle Growth
Sleep is not merely a period of inactivity; it's a highly active state crucial for numerous physiological processes. During sleep, the body releases hormones essential for muscle repair and growth, most notably growth hormone (GH). GH stimulates the production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which plays a vital role in muscle protein synthesis.
Testosterone, another key hormone, also plays a pivotal role. Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal testosterone levels, which are essential for muscle development and overall physical performance. Studies have shown that sleep deprivation can significantly reduce testosterone levels, potentially hindering muscle growth and recovery.
Napping and Hormonal Response
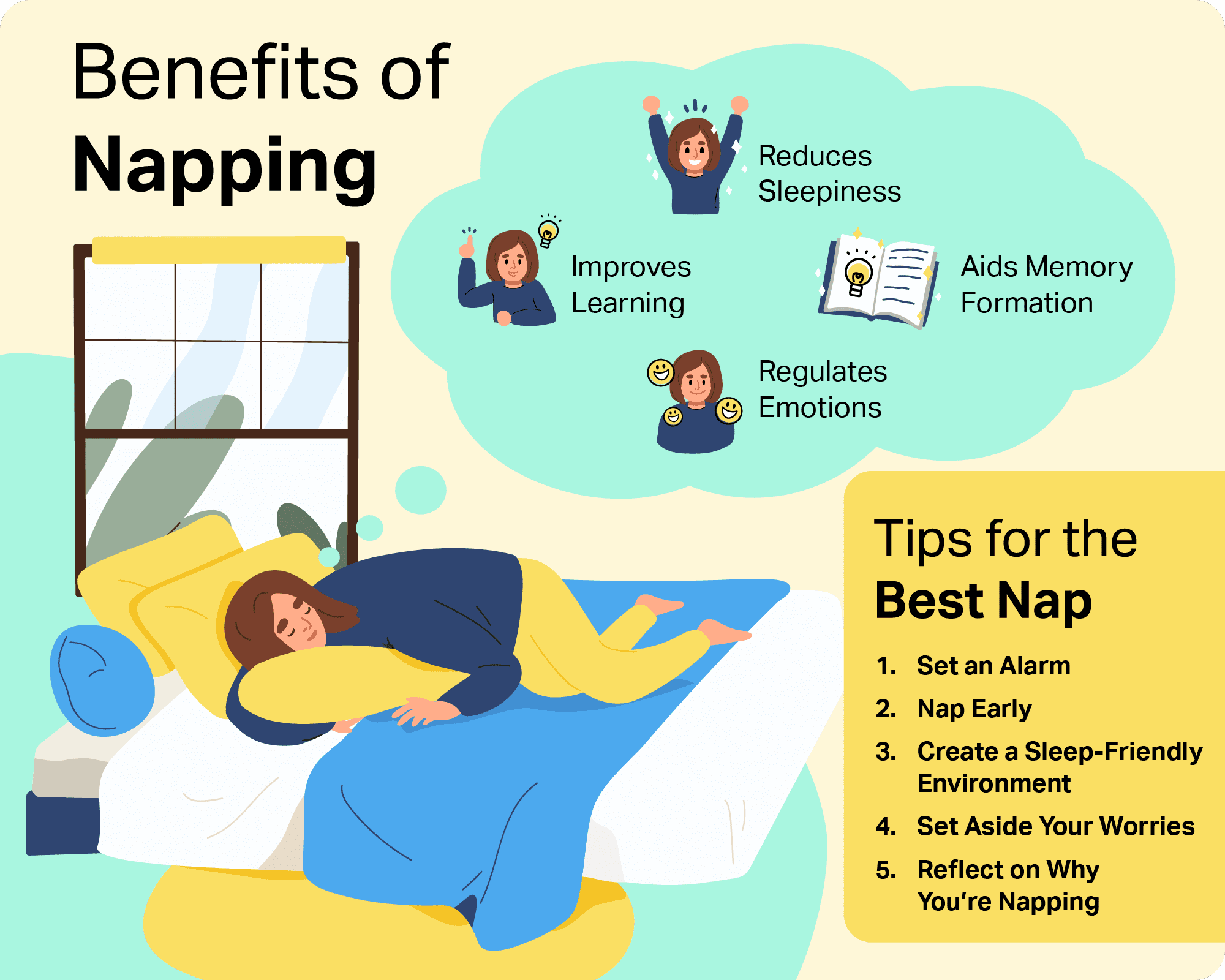
Naps, especially those lasting longer than 30 minutes, can potentially trigger the release of growth hormone. A short nap can provide a boost to the endocrine system, supporting muscle recovery and growth. The extent of the hormonal response depends on factors such as the timing, duration, and individual sleep patterns.
However, the hormonal benefits of napping are not universally consistent. Some studies suggest that the impact of naps on GH release is less pronounced compared to nighttime sleep. The body's circadian rhythm also plays a significant role, influencing hormone release patterns throughout the day.
Muscle Protein Synthesis and Recovery
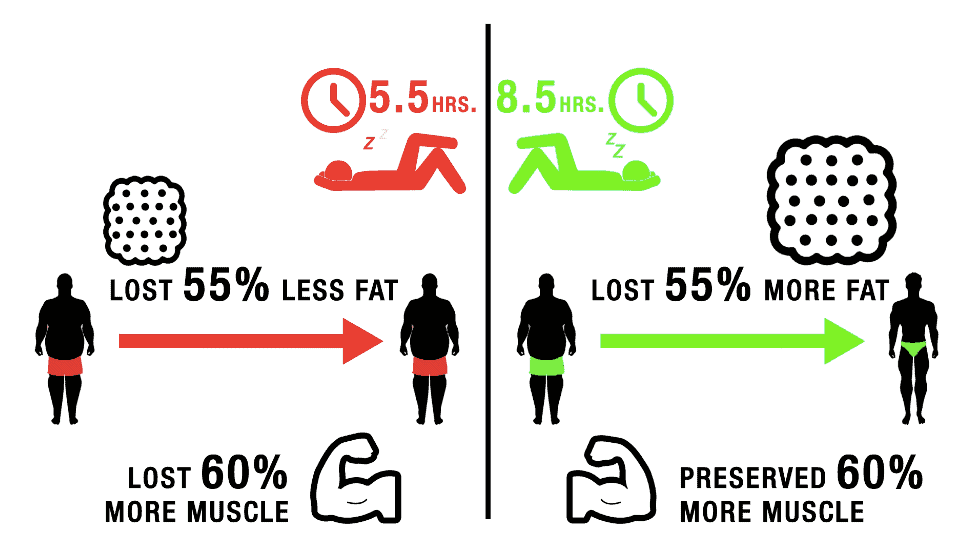
Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is the process by which the body repairs and rebuilds muscle tissue after exercise. Sleep deprivation can impair MPS, making it harder for muscles to recover and grow. Naps, by providing additional rest, can potentially counteract the negative effects of sleep deprivation on MPS.
A 2011 study published in the journal "Sleep" indicated that sleep restriction can impair muscle recovery and increase muscle protein breakdown. This highlights the importance of adequate sleep, whether through nighttime sleep or naps, for optimizing muscle growth.
Recovery is another critical aspect of muscle growth. Naps can help reduce muscle soreness, improve energy levels, and enhance overall physical performance. Improved recovery allows for more intense and frequent training sessions, ultimately contributing to greater muscle gains.
Conflicting Research and Individual Variability
While some studies suggest a positive correlation between napping and muscle growth, other research findings are less conclusive. The impact of napping can vary significantly depending on individual factors such as age, sleep quality, training intensity, and dietary habits.
Some individuals may experience improved muscle growth and recovery with regular naps, while others may not see significant benefits. Factors like sleep inertia (the grogginess experienced after waking up) can also negate the potential benefits of napping. The timing and duration of naps are also critical; excessively long or poorly timed naps can disrupt nighttime sleep.
"There's no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to napping and muscle growth,"says Dr. Emily Carter, a sports medicine physician at the National Institute of Sports Medicine.
"Individual responses can vary widely, and it's essential to consider the overall context of an individual's training, diet, and sleep patterns."
Practical Considerations for Napping
If you're considering incorporating naps into your muscle-building strategy, there are several factors to keep in mind. First, keep naps short, typically 20-30 minutes, to avoid sleep inertia. Second, time your naps strategically, ideally in the early afternoon, to minimize disruption to nighttime sleep.
Create a conducive environment for napping, ensuring a dark, quiet, and cool space. Experiment with different nap durations and timings to find what works best for your individual needs and preferences. Listen to your body and adjust your napping habits accordingly.
The Future of Sleep Research and Muscle Growth
Future research should focus on further elucidating the mechanisms by which sleep, including napping, influences muscle protein synthesis and hormonal regulation. More studies are needed to investigate the optimal nap duration, timing, and frequency for maximizing muscle growth benefits. Understanding the individual factors that influence the effectiveness of napping will also be crucial.
Advances in sleep monitoring technology may allow for more precise tracking of sleep stages and hormonal responses during naps. This could lead to personalized recommendations for napping based on individual sleep profiles and training goals.
Ultimately, napping can be a valuable tool in the arsenal of anyone striving to optimize muscle growth. However, it should be viewed as one component of a holistic approach that includes adequate nighttime sleep, a well-balanced diet, and a properly structured training program. By understanding the science behind sleep and muscle growth, and by tailoring napping strategies to individual needs, athletes and fitness enthusiasts can potentially unlock new levels of physical performance and muscle development.