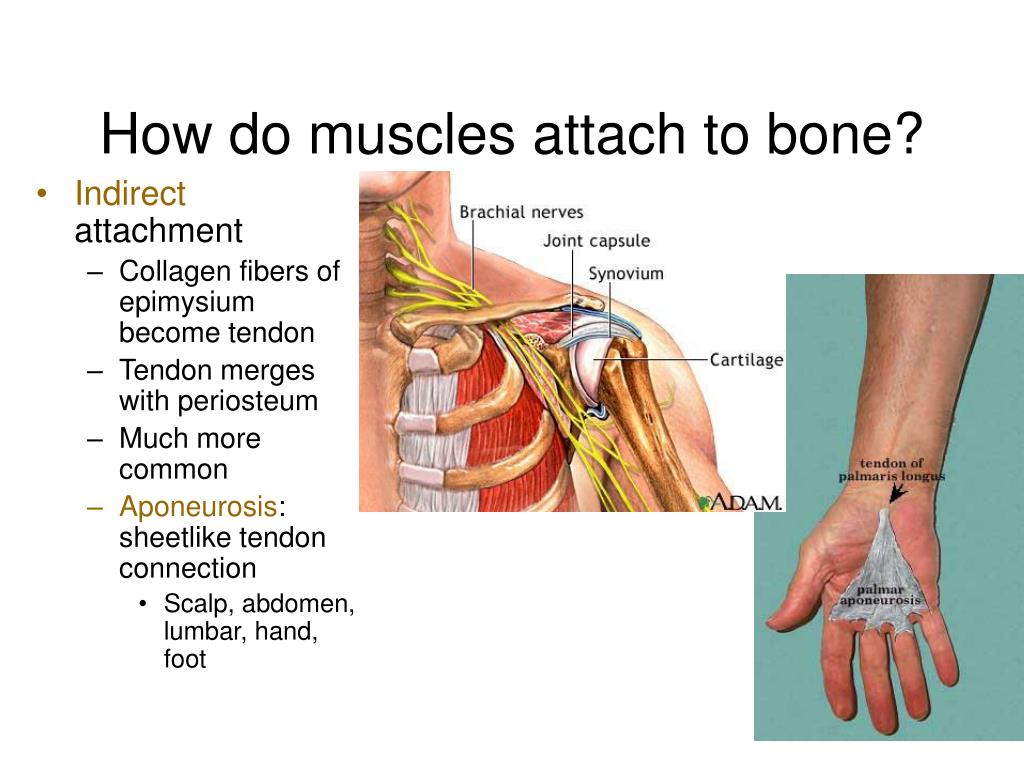
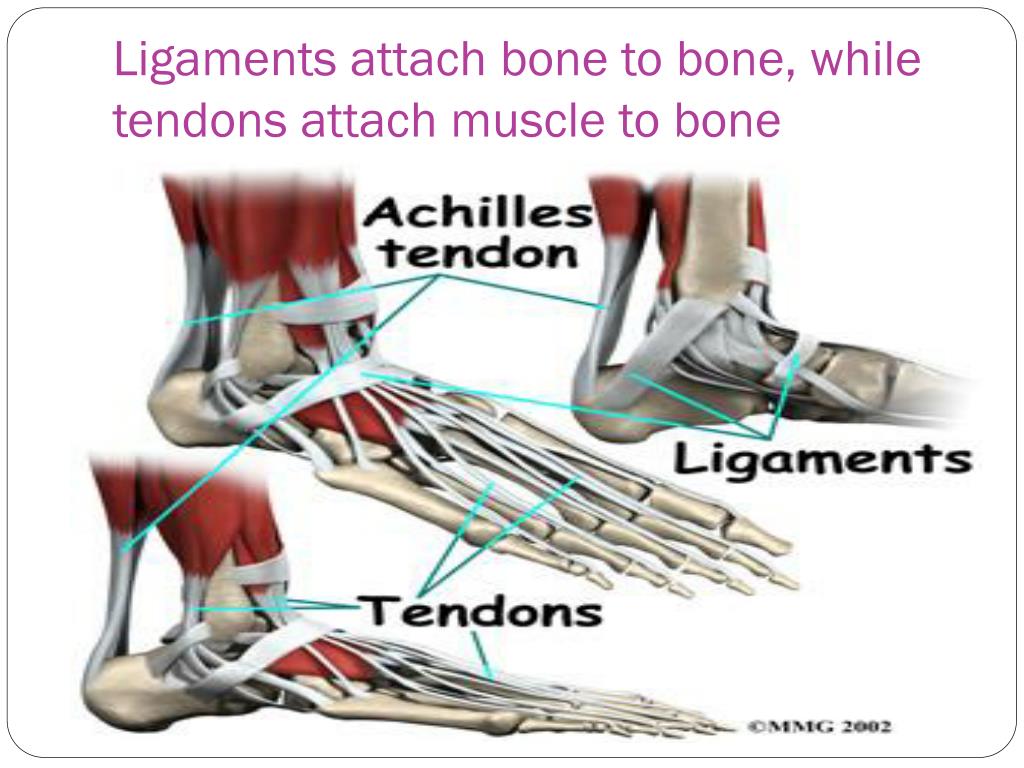
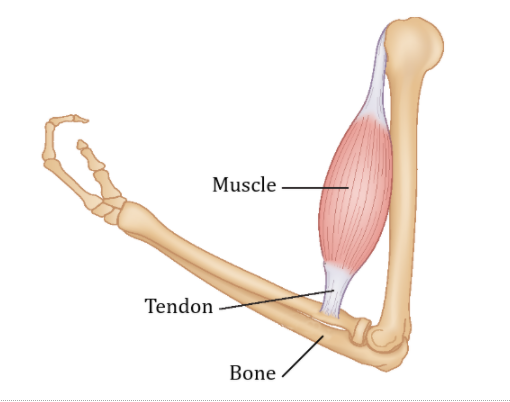
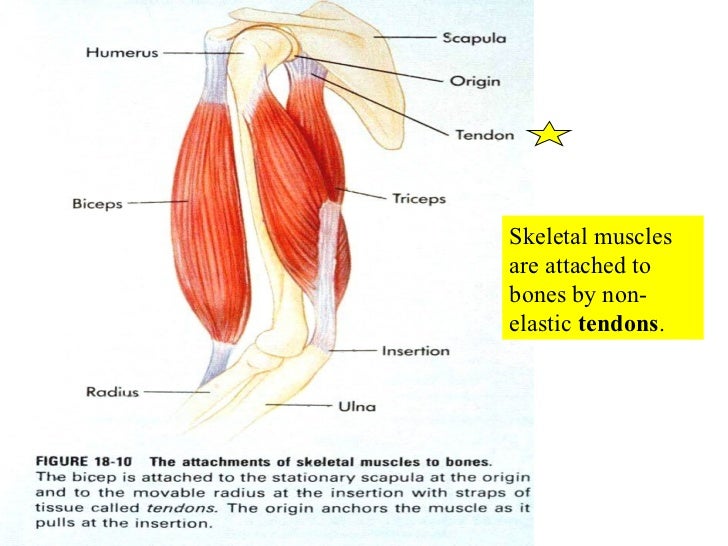
Attaches Bones To Bones And Muscles To Bones
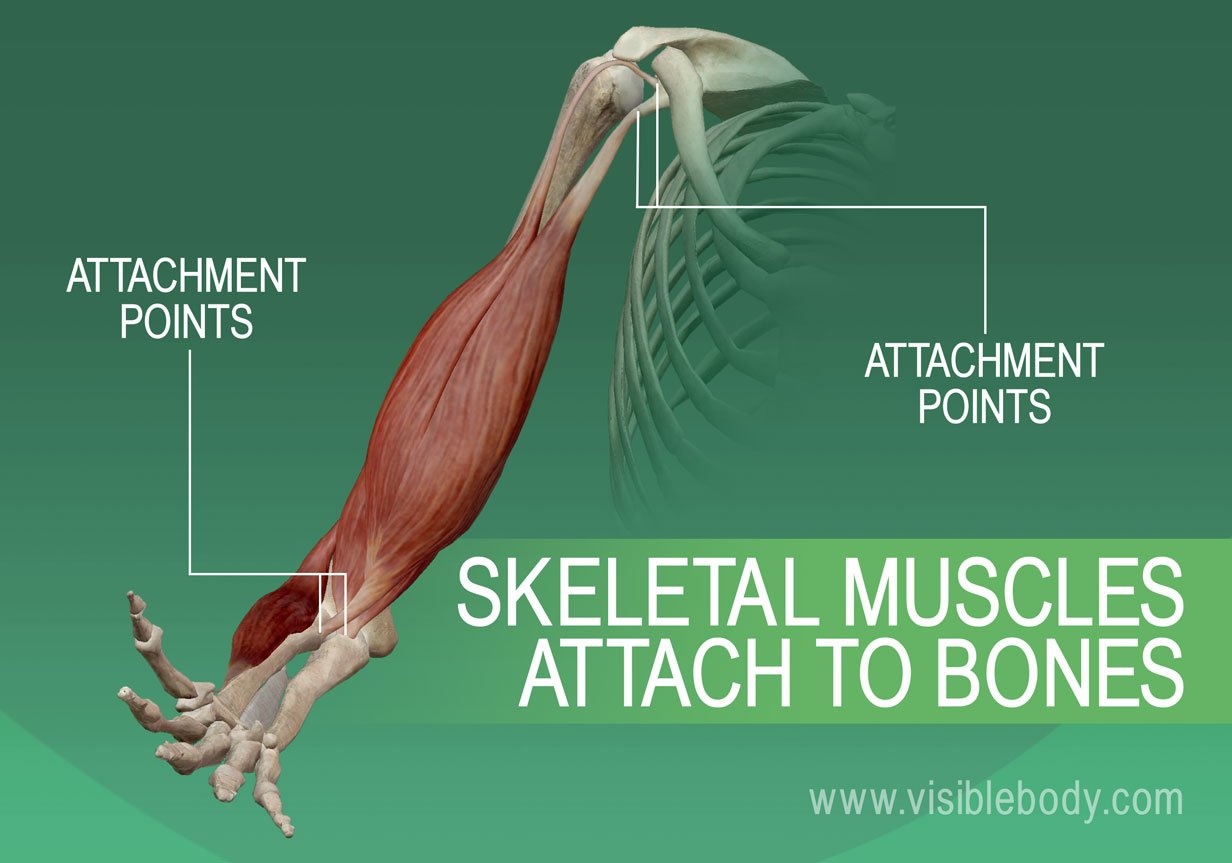
A medical breakthrough is revolutionizing reconstructive surgery. New bio-adhesive technology permanently bonds bone to bone and muscle to bone, offering unprecedented possibilities for trauma patients and those with degenerative conditions.
This groundbreaking method sidesteps the limitations of traditional screws and sutures. It is poised to transform orthopedic and reconstructive procedures.
The Revolutionary Adhesive
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have developed the adhesive. It is a biocompatible polymer with unique bonding properties.
The adhesive, code-named "OsteoFuse," mimics the natural bonding mechanisms. This occurs within the body at a molecular level.
How OsteoFuse Works
OsteoFuse is applied as a liquid. Then, it quickly hardens upon exposure to a specific wavelength of light, creating an incredibly strong bond.
It integrates with the existing bone and muscle tissue. This promotes natural healing and long-term stability.
The chemical makeup of OsteoFuse ensures that it is completely broken down and metabolized. There are no long-term toxic materials left in the body.
Successful Trials and Early Applications
Animal trials have demonstrated exceptional results. The bonded tissues are stronger and heal faster than with conventional methods.
Dr. Sarah Chen, lead researcher on the project, noted, "We observed a significant increase in bone density and muscle regeneration at the bonding site."
The adhesive has been used in a limited number of human trials. All of these trials were approved by the FDA.
Human Trial Outcomes
The initial human trials focused on patients with severe bone fractures. The traditional methods had failed to achieve proper healing.
OsteoFuse successfully bonded the fractured bones in all cases. Patients reported reduced pain and faster recovery times.
A separate trial involved patients with rotator cuff tears. Muscle-to-bone adhesion was achieved with significantly improved shoulder function.
Benefits Over Traditional Methods
Traditional methods of bone and muscle repair rely on screws, plates, and sutures. These can be invasive and cause complications.
OsteoFuse is less invasive. It minimizes trauma to surrounding tissues.
It also eliminates the need for secondary surgeries. This secondary surgery would remove hardware and can reduce the risk of infection.
Reduced Recovery Time
Patients treated with OsteoFuse experience significantly shorter recovery periods.
In some cases, recovery time has been reduced by as much as 50%. This allows patients to return to their normal activities sooner.
This quicker recovery rate translates to significant cost savings for healthcare providers and patients.
Widespread Availability and Future Research
The University of Pennsylvania has partnered with MedTech Innovations. This ensures the rapid manufacturing and distribution of OsteoFuse.
The adhesive is expected to be available to surgeons nationwide within the next six to twelve months.
Ongoing research is focused on expanding the applications of OsteoFuse. This would include spinal fusion and joint replacement procedures.
Ethical Considerations
The development of such powerful bio-adhesives raises ethical considerations. These relate to the potential for misuse and equitable access.
Researchers are working with ethicists and policymakers. This ensures responsible use and availability of the technology.
Dr. Chen emphasized the importance of ensuring that OsteoFuse benefits all patients in need. This is a priority for the development team.
Conclusion: A New Era in Reconstructive Surgery
OsteoFuse represents a paradigm shift in reconstructive surgery. It provides a superior alternative to traditional methods.
The FDA is expediting the approval process for broader applications. This promises a future where bone and muscle repair is faster, less invasive, and more effective.
Further clinical trials are planned to explore the long-term effects. The researchers are also looking at the optimal application methods of OsteoFuse.