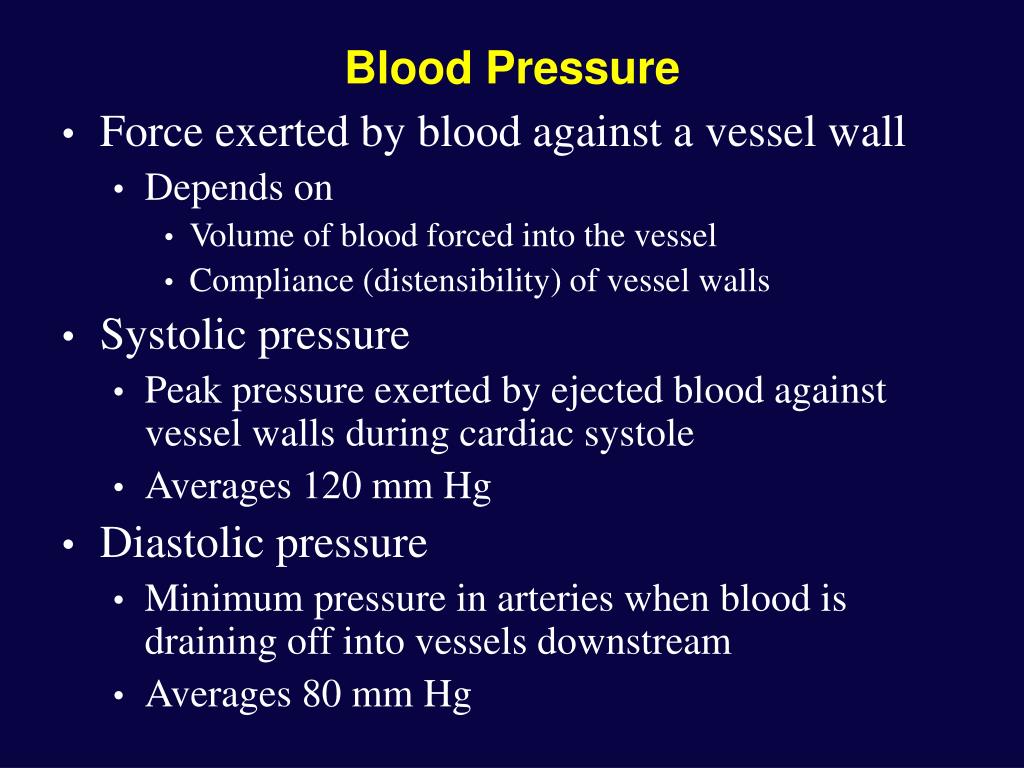
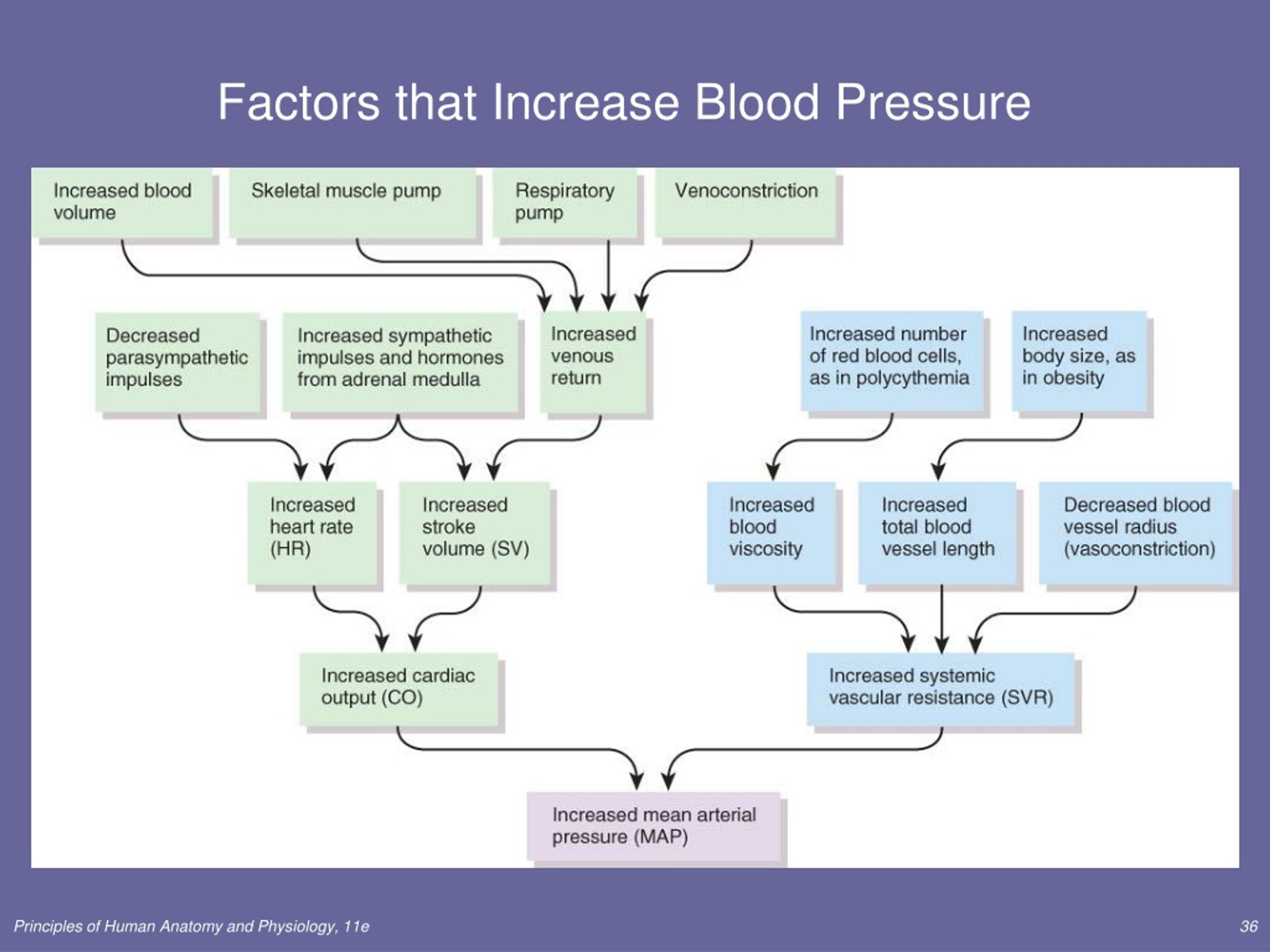
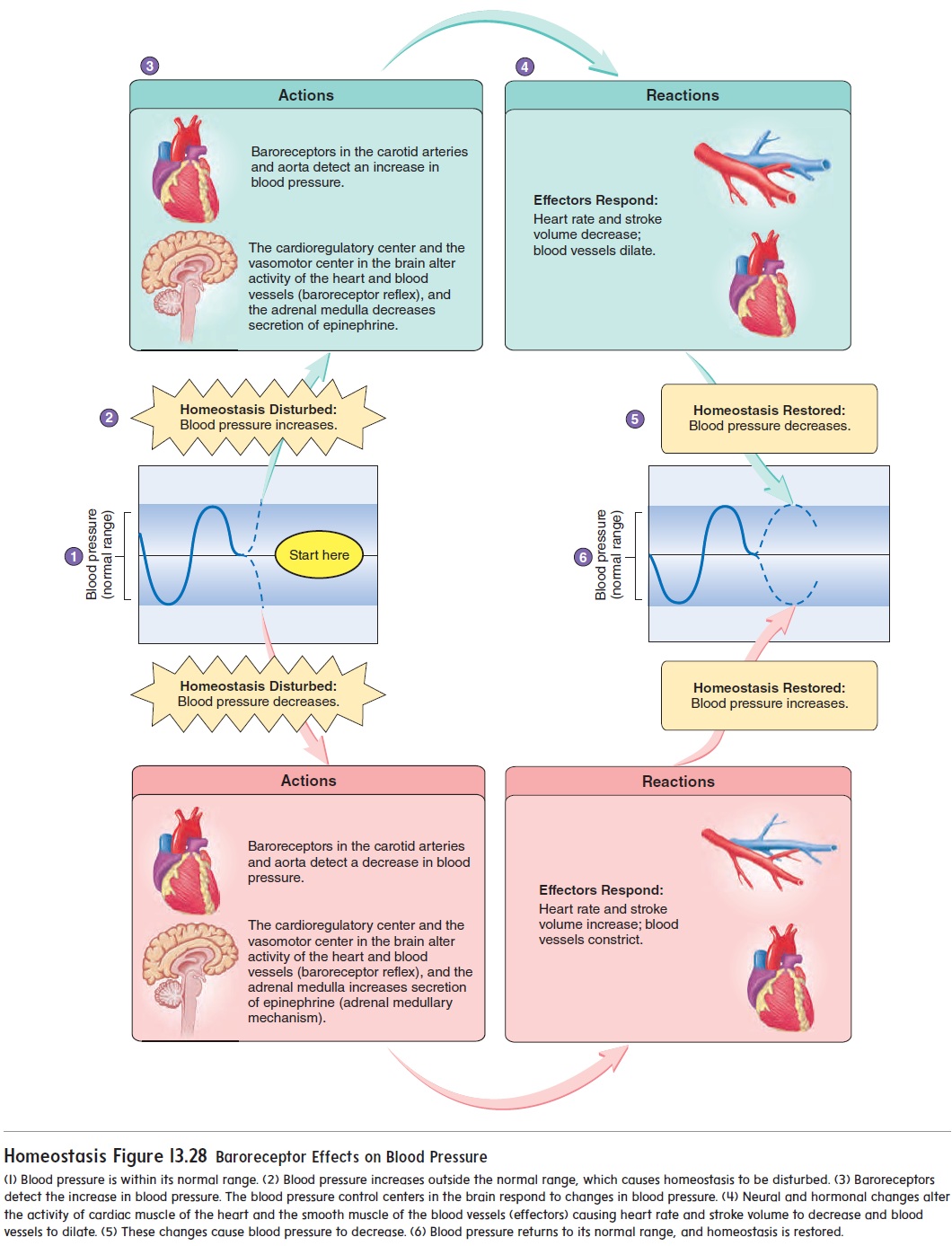
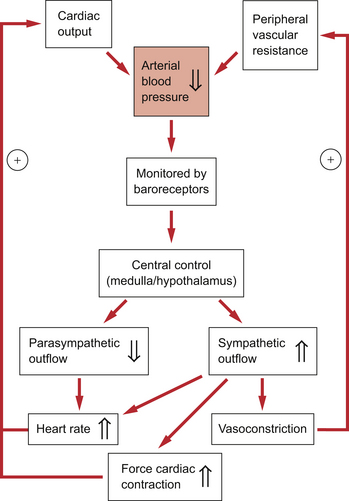
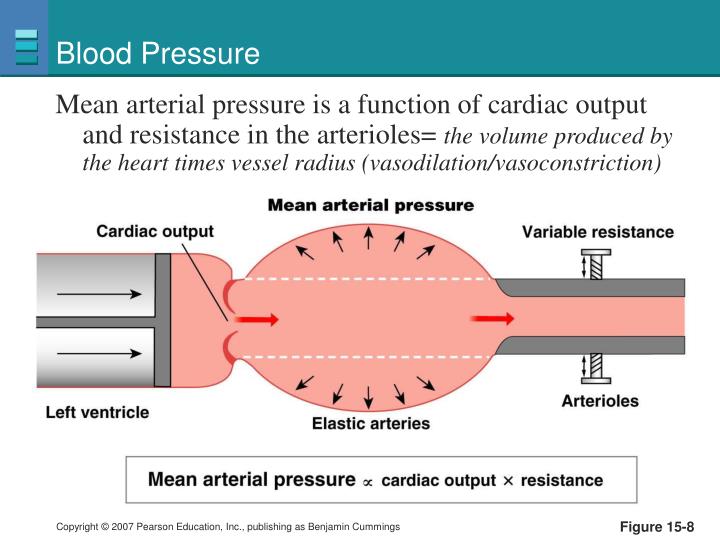
Blood Pressure Increases With Sustained Increased Resistance Because
Urgent health alert: New research confirms a direct link between sustained increased resistance and elevated blood pressure, posing significant risks for individuals engaging in prolonged strenuous activities or with specific underlying conditions. The findings underscore the critical need for proactive monitoring and management of resistance levels to mitigate potential cardiovascular complications.
This article breaks down the science and what it means for your health.
The Core Discovery: Resistance and Blood Pressure
A groundbreaking study published in the "Journal of Applied Physiology" reveals a definitive correlation: sustained increased resistance directly leads to increases in blood pressure.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) conducted the study, monitoring a cohort of 250 participants over a 12-month period. The results showed a statistically significant increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in individuals consistently exposed to elevated resistance levels.
The study focused on diverse demographics, aged 30-65, across various physical activity levels, ensuring broad applicability of the findings.
Understanding Resistance: What it Means
In this context, resistance refers to any factor impeding blood flow. This includes constricted blood vessels, increased blood viscosity, or external pressures affecting circulation.
Activities such as heavy weightlifting, chronic stress, and certain medical conditions can all contribute to increased resistance.
Even prolonged sitting can impact resistance, indirectly affecting blood pressure.
The Physiological Mechanism: How it Happens
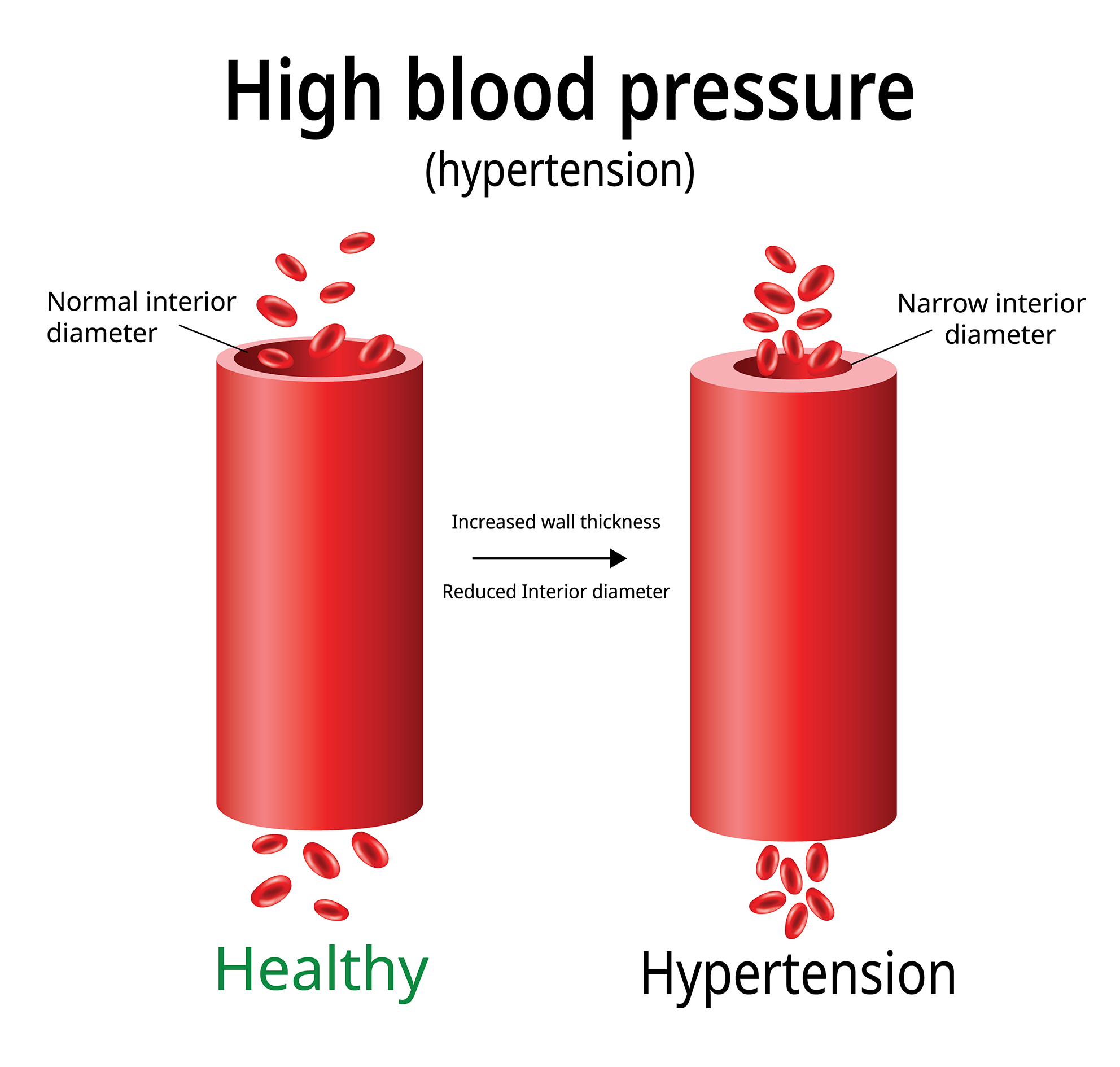
When the body encounters increased resistance, it compensates by increasing the force of heart contractions to maintain adequate blood flow. This elevated force translates to higher blood pressure readings.
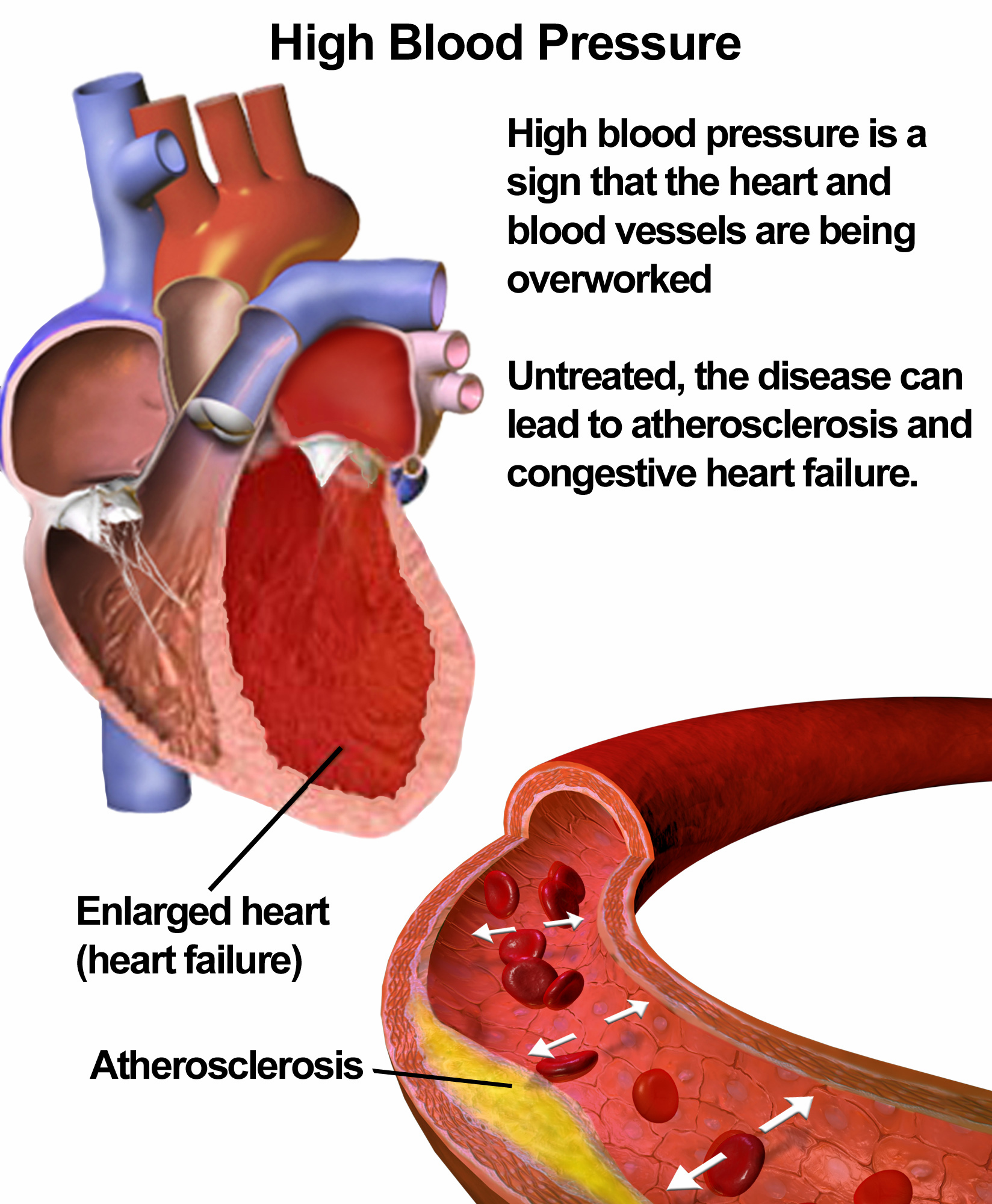
Over time, chronic exposure to heightened resistance can lead to structural changes in blood vessels, making them less elastic and further exacerbating hypertension.
Hormonal responses, such as the release of adrenaline and cortisol under stressful conditions, also play a significant role in raising blood pressure when resistance is present.
Who is Most at Risk?
Individuals with pre-existing conditions like atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), kidney disease, and diabetes are particularly vulnerable.
Those engaging in intense physical activities without proper conditioning or medical supervision also face increased risk.
Furthermore, individuals with a family history of hypertension should be especially vigilant in monitoring their blood pressure and resistance levels.
Practical Implications and Recommendations
Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for early detection of potential problems.
Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, regular exercise (emphasizing cardiovascular health), and stress management techniques, can help mitigate the effects of increased resistance.
Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized guidance and potential medical interventions, especially for individuals with identified risk factors.
Expert Commentary
Dr. Emily Carter, lead researcher on the NIH study, emphasized the importance of these findings: "Our research provides compelling evidence that sustained increased resistance is a significant contributor to hypertension."
"We urge individuals, particularly those at risk, to prioritize blood pressure monitoring and adopt proactive strategies to manage resistance factors," Dr. Carter added.
"Ignoring this connection can have severe long-term cardiovascular consequences," warned Dr. Carter.
Ongoing Research and Next Steps
The NIH is currently conducting further research to explore the specific molecular pathways linking resistance and blood pressure.
Researchers are also investigating the effectiveness of targeted interventions, such as medication and lifestyle changes, in reducing resistance and preventing hypertension.
The goal is to develop personalized strategies for managing resistance and improving cardiovascular health for individuals at risk.