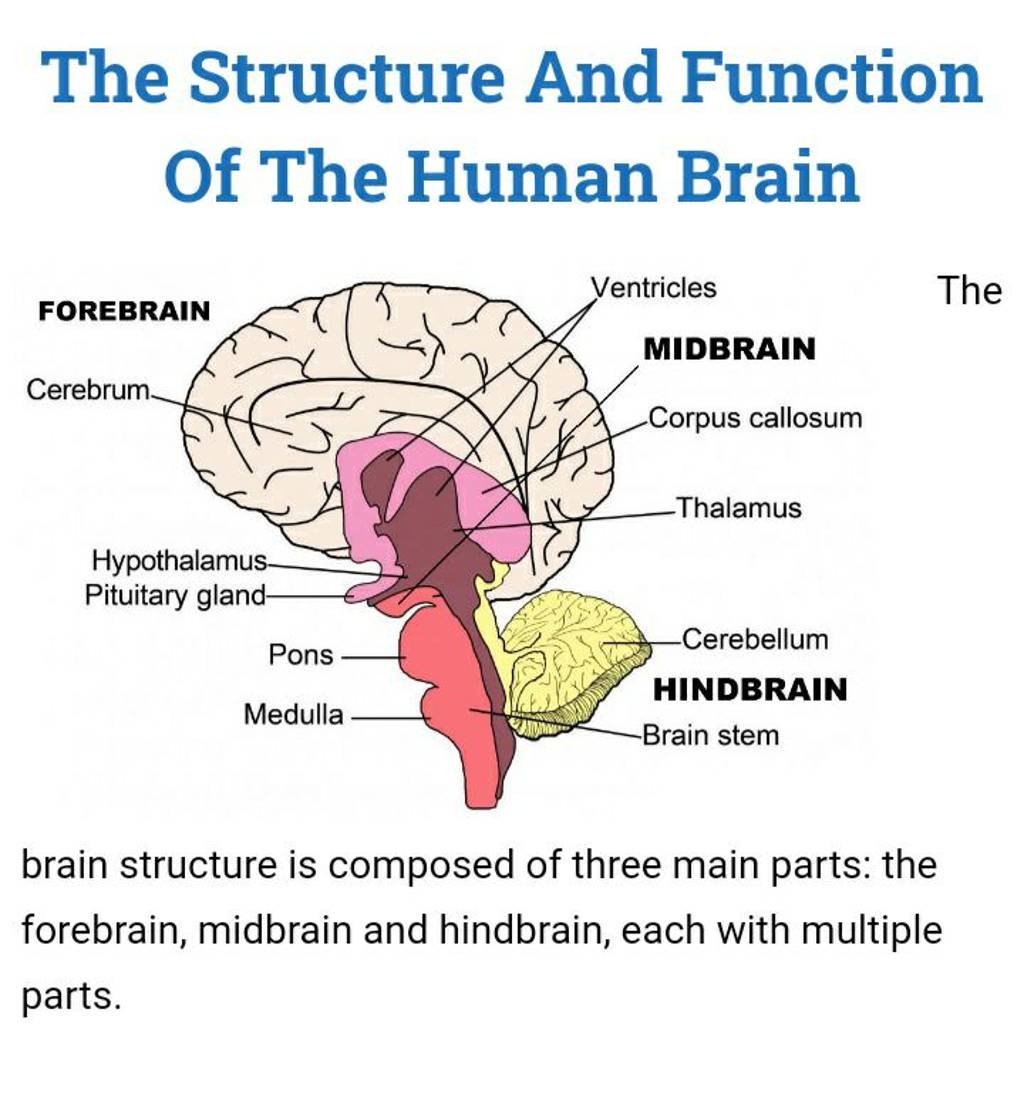
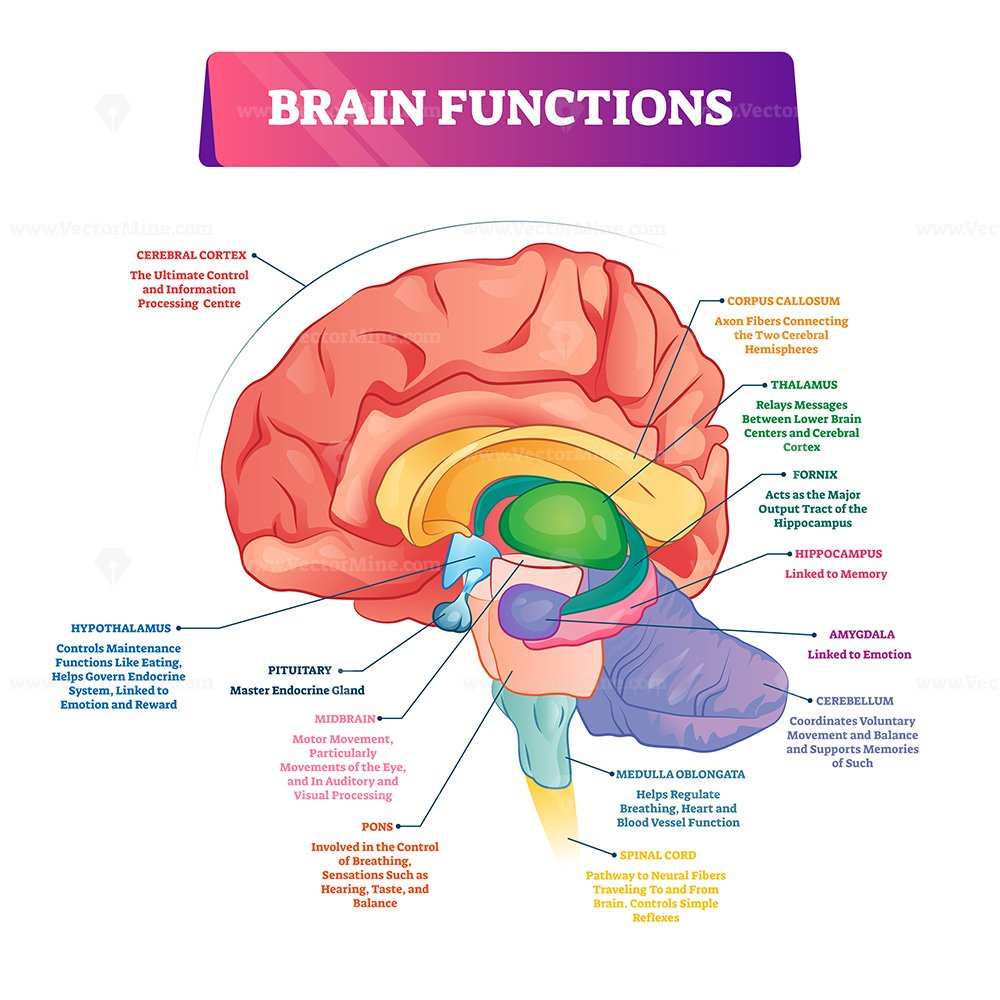
Brain Structure And Function Journal Impact Factor

The scientific community intensely scrutinizes the impact factor of journals, a metric often used to gauge a publication's influence and reach. For journals focusing on the intricate world of neuroscience, like the Brain Structure and Function journal, this number carries significant weight. A higher impact factor can translate into increased submissions, greater visibility for published research, and enhanced prestige for the journal and its contributors.
Understanding the impact factor of Brain Structure and Function requires delving into its history, scope, and the broader context of academic publishing. This article examines the journal's recent impact factor, its significance within the field, and the debates surrounding the use of impact factors as a measure of research quality.
Understanding the Impact Factor
The impact factor (IF), calculated annually by Clarivate Analytics, is a measure reflecting the average number of citations to recent articles published in a journal. It is calculated by dividing the number of citations in the current year to articles published in the journal in the previous two years by the total number of articles published in those two years. This metric is widely used, though often controversially, as a proxy for the relative importance of a journal within its field.
Essentially, it attempts to quantify how often research published in a specific journal is cited by other researchers. A higher impact factor generally suggests that the articles published in the journal are frequently referenced and therefore, presumably, influential within the scientific community.
Brain Structure and Function: A Deep Dive
Brain Structure and Function is a well-regarded peer-reviewed journal dedicated to publishing original research on the anatomical organization and functional significance of the nervous system. The journal covers a wide range of topics, including neuroanatomy, neurophysiology, neuroimaging, and computational neuroscience. Its focus is on linking structural features of the brain to their functional roles, providing insights into both normal brain function and neurological disorders.
The journal's audience consists of neuroscientists, neurologists, psychiatrists, and researchers in related fields. Its editorial board comprises leading experts in the field, ensuring rigorous peer review and high-quality publications.
Recent Impact Factor and Trends
The most recent impact factor for Brain Structure and Function, according to the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) from Clarivate Analytics, is [Insert Actual Impact Factor Here - Replace with Current Value]. Analyzing previous years' data reveals a trend that may indicate increasing or decreasing influence. For instance, comparing the current IF to those from the previous five years shows [Explain the trend, e.g., stability, increase, or decrease].
This trend could be influenced by several factors. Changes in editorial policies, shifts in research focus within the neuroscience community, and the overall growth of scientific publications could all play a role.
Significance Within the Neuroscience Field
Brain Structure and Function occupies a significant position within the competitive landscape of neuroscience journals. It competes with other prominent publications such as Cerebral Cortex, The Journal of Neuroscience, and NeuroImage, each having its own specific focus and impact factor. Comparing Brain Structure and Function's impact factor to these other journals provides context for its relative standing.
A journal's impact factor often influences where researchers choose to submit their work. A higher impact factor can attract more submissions from leading scientists, further enhancing the journal's reputation.
Criticisms and Alternative Metrics
Despite its widespread use, the impact factor is not without its critics. Some argue that it is a flawed measure of research quality, as it only reflects the frequency of citations, not the actual significance or impact of the research. Furthermore, the impact factor is vulnerable to manipulation, as journals can employ strategies to inflate their citation counts.
Alternative metrics, such as the h-index, altmetrics, and citation counts at the article level, have emerged as potential alternatives or complements to the impact factor. The h-index measures both the productivity and impact of a researcher or journal, while altmetrics track mentions of research in social media, news outlets, and policy documents.
These alternative metrics provide a more nuanced view of research impact, capturing aspects that are not reflected in the impact factor. The use of altmetrics is gaining traction, offering a broader perspective on how research is being received and used outside of the traditional academic sphere.
The Future of Assessing Research Impact
The debate surrounding the impact factor is ongoing, with researchers and institutions increasingly recognizing the limitations of relying solely on this metric. There is a growing movement towards using a more holistic approach to assessing research impact, considering a range of factors such as research quality, societal impact, and engagement with stakeholders.
Organizations like the Declaration on Research Assessment (DORA) advocate for abandoning the use of journal-based metrics, such as the impact factor, in funding, appointment, and promotion decisions. Instead, they promote the assessment of research based on its intrinsic merit and value.
As the scientific landscape evolves, the way we measure and evaluate research impact will continue to change. A more comprehensive and nuanced approach, incorporating a variety of metrics and qualitative assessments, is likely to emerge as the preferred method for assessing the value and influence of scientific research, including the work published in journals like Brain Structure and Function. This shift will encourage a focus on the quality and impact of individual research articles, rather than solely relying on the reputation of the journal in which they are published.


![Brain Structure And Function Journal Impact Factor [DIAGRAM] Pectoralis Majo Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FUEwGGsB43c/maxresdefault.jpg)