Business Cycle Phases In Economics

Economic storm clouds are gathering as experts warn of a potential shift in the business cycle. Understanding these phases is now critical for businesses and individuals to navigate the turbulent waters ahead.
The business cycle, a recurring pattern of expansion and contraction in economic activity, directly impacts jobs, investments, and overall financial stability. Ignoring its ebbs and flows can have severe consequences for unprepared entities.
The Four Key Phases
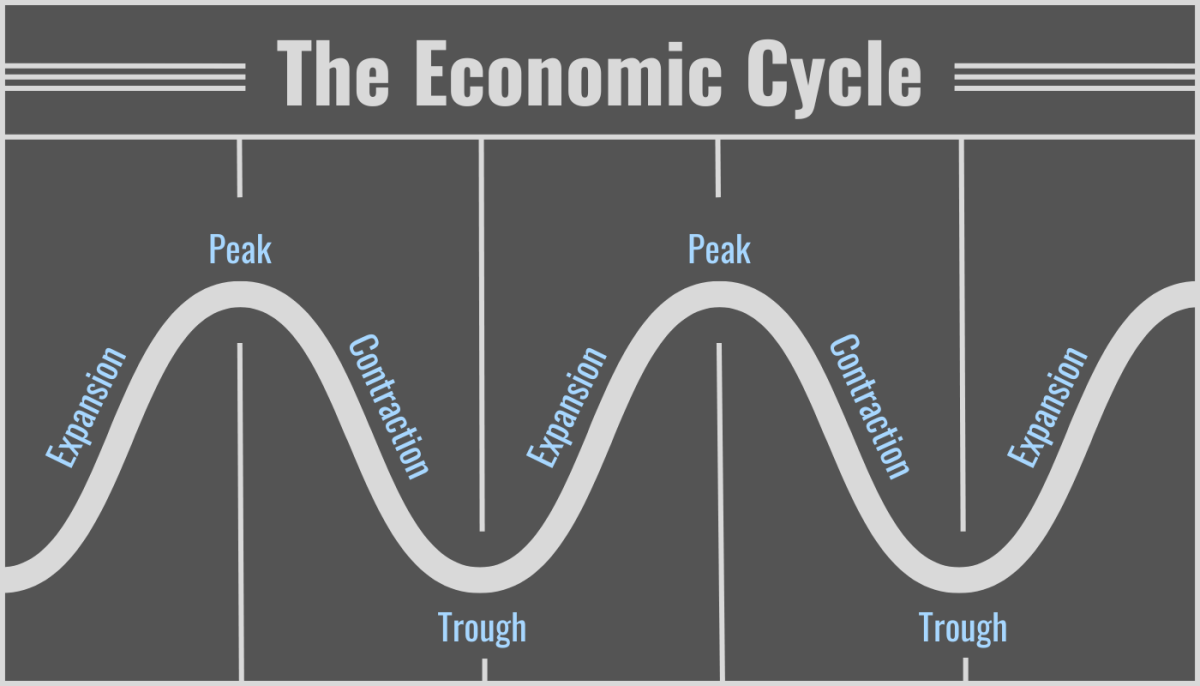
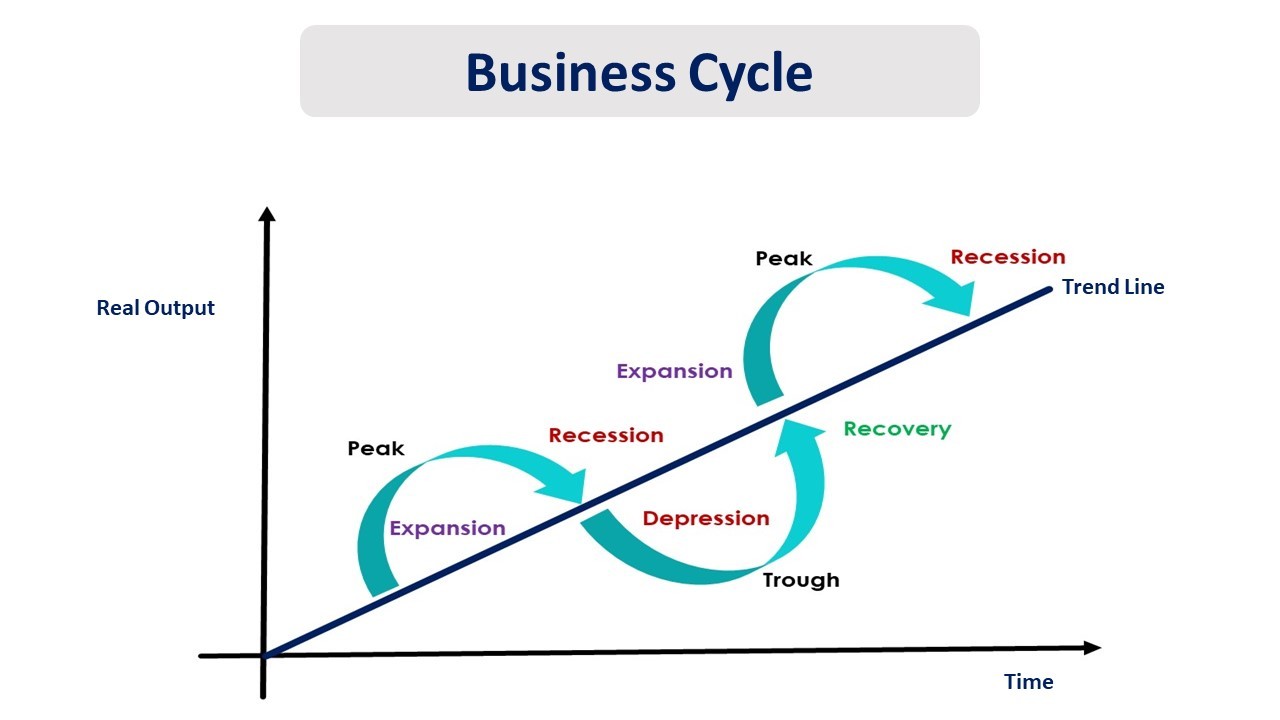
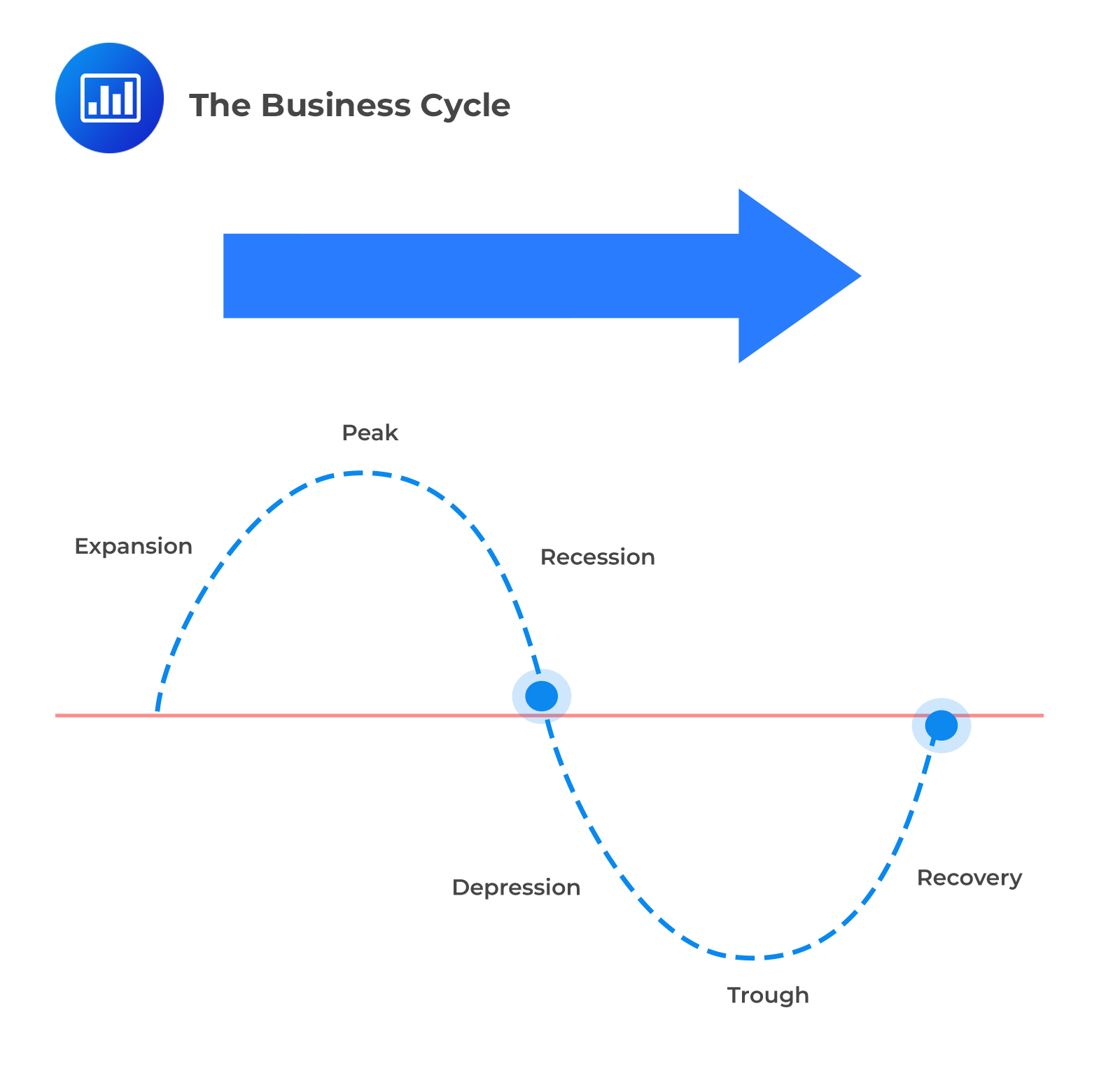
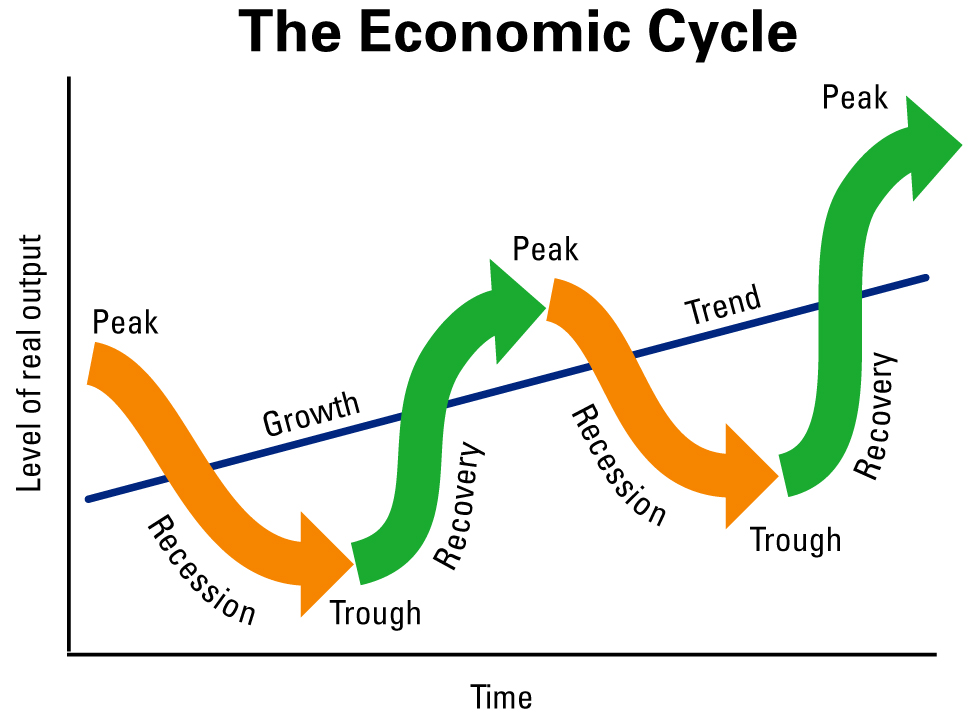
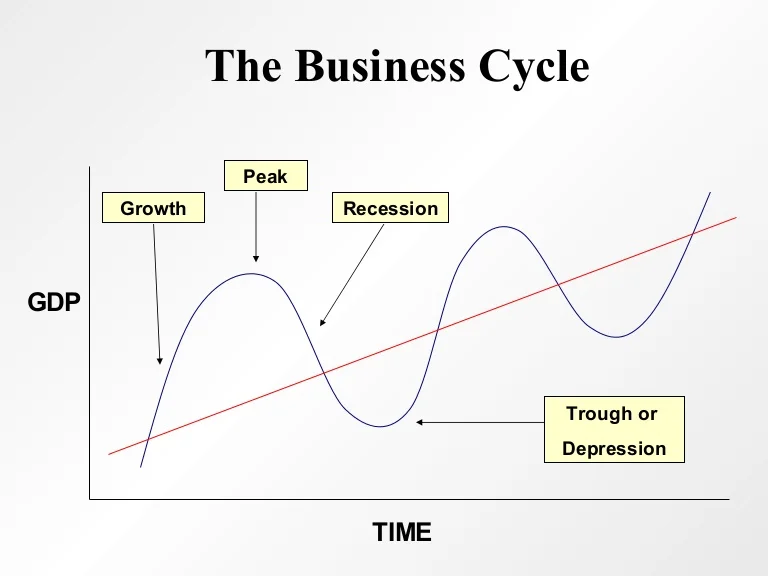
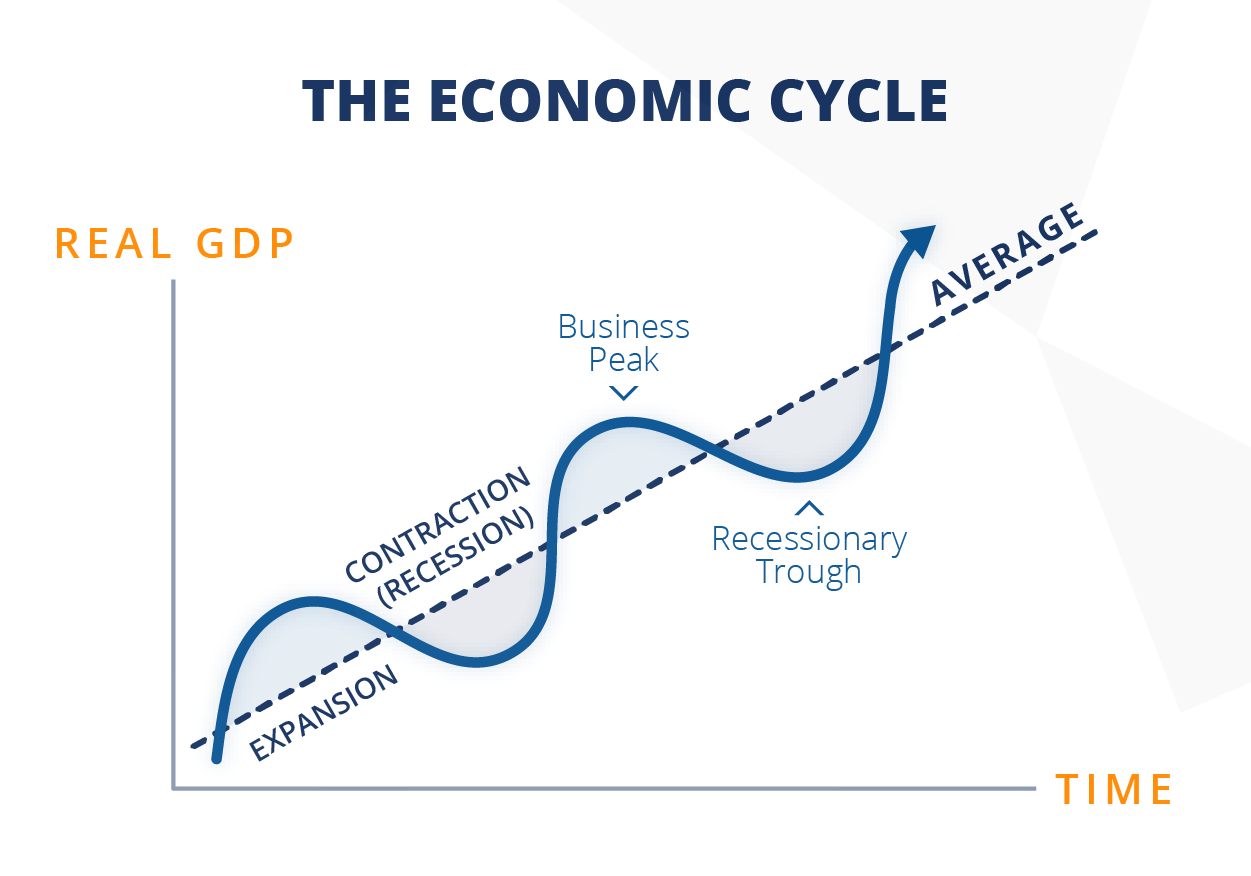
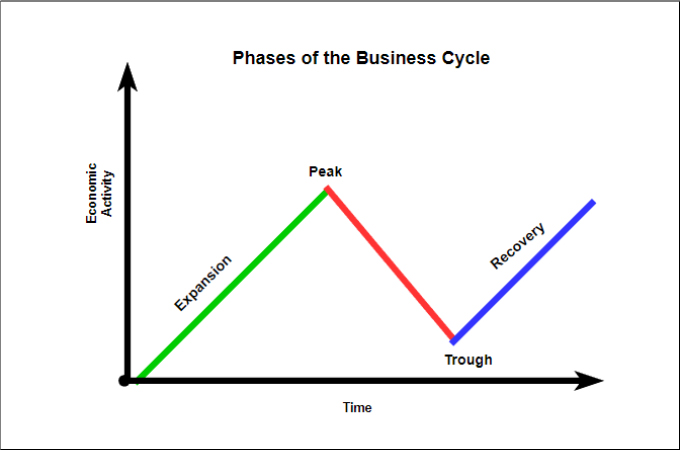
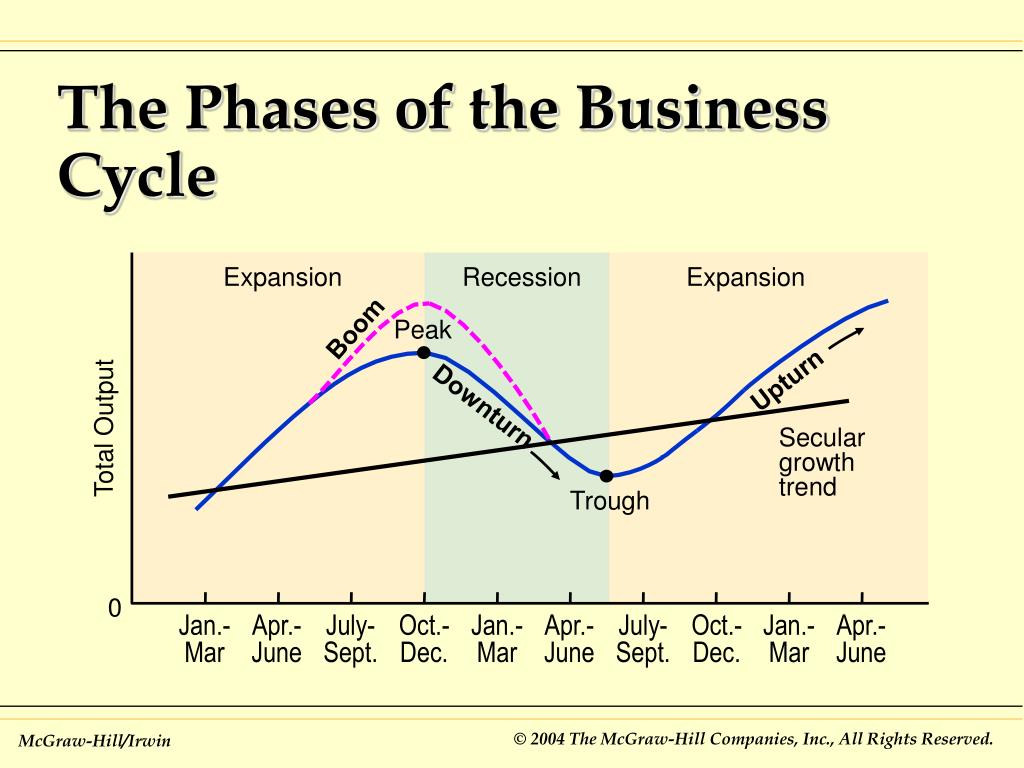
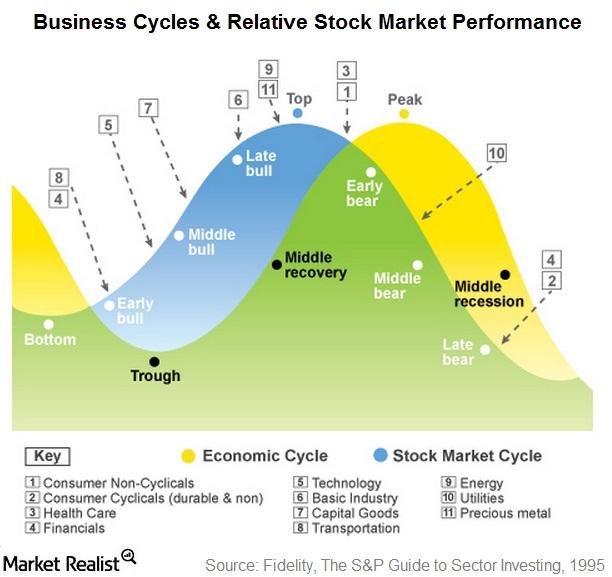
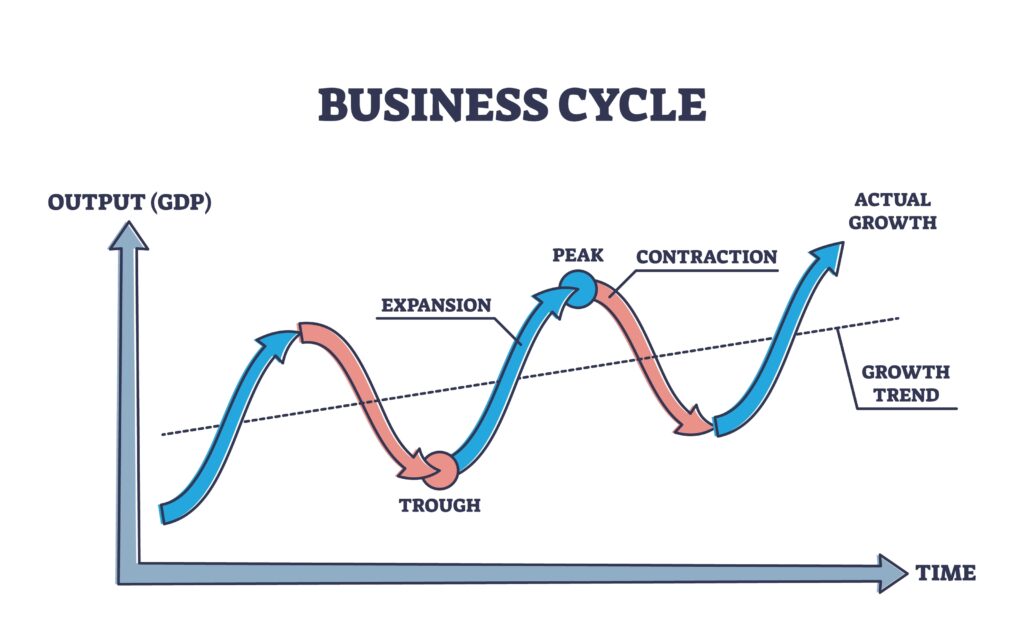
The business cycle consists of four primary phases: Expansion, Peak, Contraction, and Trough. Each phase has distinct characteristics and implications.
Expansion: Growth and Optimism
During an expansion, the economy experiences growth. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increases, unemployment falls, and consumer confidence rises.
Businesses increase production and investments, driven by heightened demand and optimistic forecasts. This period is generally characterized by increased lending and borrowing.
Peak: The Turning Point
The peak represents the highest point of economic activity in the cycle. It signifies the end of the expansion phase.
Indicators like inflation and capacity utilization often reach their maximum levels. This is a period of heightened economic vulnerability, and signals the need for caution.
Contraction: The Downturn
A contraction, also known as a recession, is a period of economic decline. GDP decreases, unemployment rises, and consumer spending falls.
Businesses cut back on investments and lay off workers, leading to further economic slowdown. This phase can be particularly challenging for individuals and businesses alike.
Trough: The Bottom and Rebound
The trough marks the lowest point of the contraction. It's the turning point where the economy begins to recover.
Economic activity starts to stabilize, and unemployment may begin to plateau. It signals the beginning of a new expansion phase and opportunities for strategic investment.
Current Economic Landscape
Recent data suggests a complex picture. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), the US GDP growth was 2.5% in 2023, showing resilience, but inflation remains a concern, hovering above the Federal Reserve’s target.
"The latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) data indicates persistent inflationary pressures," stated Dr. Anya Sharma, Chief Economist at Global Analytics, in a recent briefing. This could trigger further interest rate hikes.
Unemployment remains relatively low, but leading economic indicators suggest a potential slowdown in the coming months. The Federal Reserve is closely monitoring these developments.
Navigating the Cycle
Understanding the current phase of the business cycle is crucial for informed decision-making. Businesses should consider strategies for managing risk during a potential contraction.
Individuals should prioritize financial stability and consider diversifying investments. Staying informed about economic trends is more important than ever.
What's Next?
The Federal Reserve is expected to announce its next interest rate decision in the coming weeks. This decision could have significant implications for the direction of the economy.
Economists and analysts are closely watching key economic indicators for further signs of a potential shift. Staying informed and prepared is the best course of action in these uncertain times.
![Business Cycle Phases In Economics The BUSINESS [Economic] CYCLE: What is it Really? | The Leading](https://veritaseconomy.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/phases-of-the-business-cycle4.jpg)
/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)


.png)
/phasesofthebusinesscycle-c7cb7a3ce6894e86a3e44d5b0fe4d5e2.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)