Can Untreated Celiac Disease Cause Weight Gain

Imagine a seemingly healthy individual, diligently following what they believe is a balanced diet, yet inexplicably gaining weight. Frustration mounts as their clothes feel tighter, and the scale relentlessly climbs, defying their best efforts. Could there be an underlying medical condition playing a hidden role in this perplexing weight gain?
The relationship between untreated celiac disease and weight is often misunderstood. While weight loss is a common symptom, the reverse – weight gain – can also occur, particularly upon diagnosis and during the initial stages of treatment. This article explores the complexities of this phenomenon, shedding light on the reasons behind weight gain in individuals with untreated celiac disease and offering guidance on managing this unexpected outcome.
Understanding Celiac Disease
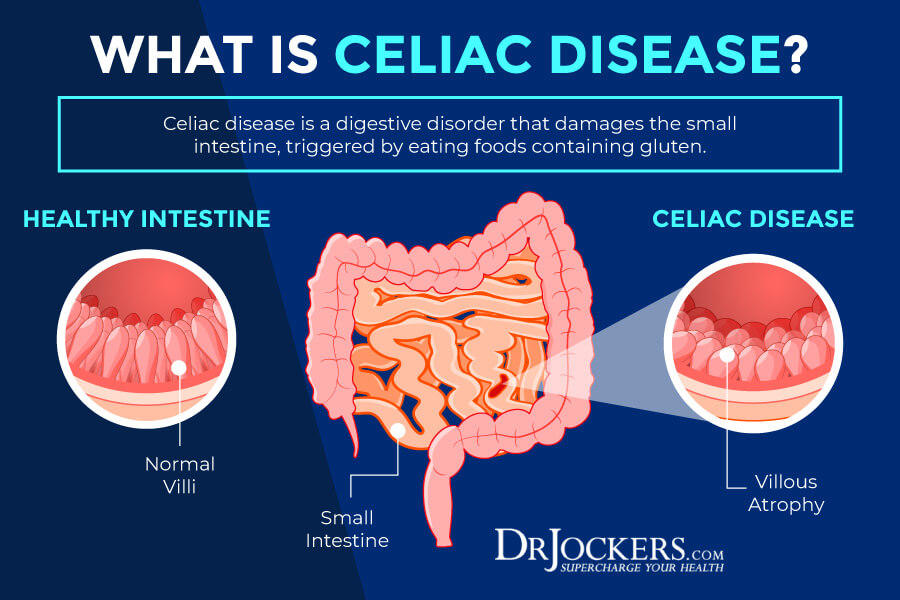
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. In individuals with celiac disease, gluten ingestion leads to damage in the small intestine. This damage impairs the absorption of nutrients, leading to a variety of symptoms.
Traditionally, celiac disease has been associated with symptoms like weight loss, diarrhea, fatigue, and abdominal pain. However, the presentation of celiac disease can be highly variable, with some individuals experiencing atypical or even seemingly contradictory symptoms.
The Atypical Presentation of Celiac Disease
According to the Celiac Disease Foundation, the spectrum of symptoms associated with celiac disease is broadening as diagnostic tools become more refined. Atypical symptoms such as anemia, skin rashes, neurological problems, and even weight gain are increasingly recognized.
The misconception that celiac disease exclusively leads to weight loss stems from the understanding that the condition impairs nutrient absorption. While this is indeed a significant consequence, it doesn't fully explain the complex interplay of factors at play.
Why Weight Gain with Untreated Celiac Disease?
The possibility of weight gain with untreated celiac disease might seem counterintuitive, but several mechanisms can contribute to this phenomenon. One key factor is the body's inflammatory response to gluten.
Chronic inflammation, a hallmark of untreated celiac disease, can disrupt hormonal balance and metabolic processes. This disruption can lead to increased insulin resistance and altered fat storage, contributing to weight gain.
Furthermore, some individuals with untreated celiac disease may experience an increased appetite or cravings for high-calorie foods as their bodies attempt to compensate for nutrient deficiencies. This compensatory mechanism can inadvertently lead to overeating and weight gain.
Another important aspect to consider is the gut microbiome. Untreated celiac disease can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to an imbalance that favors weight gain.
The Post-Diagnosis Weight Gain
Paradoxically, weight gain is also commonly observed after the diagnosis of celiac disease and the initiation of a gluten-free diet. This often surprises and concerns newly diagnosed individuals.
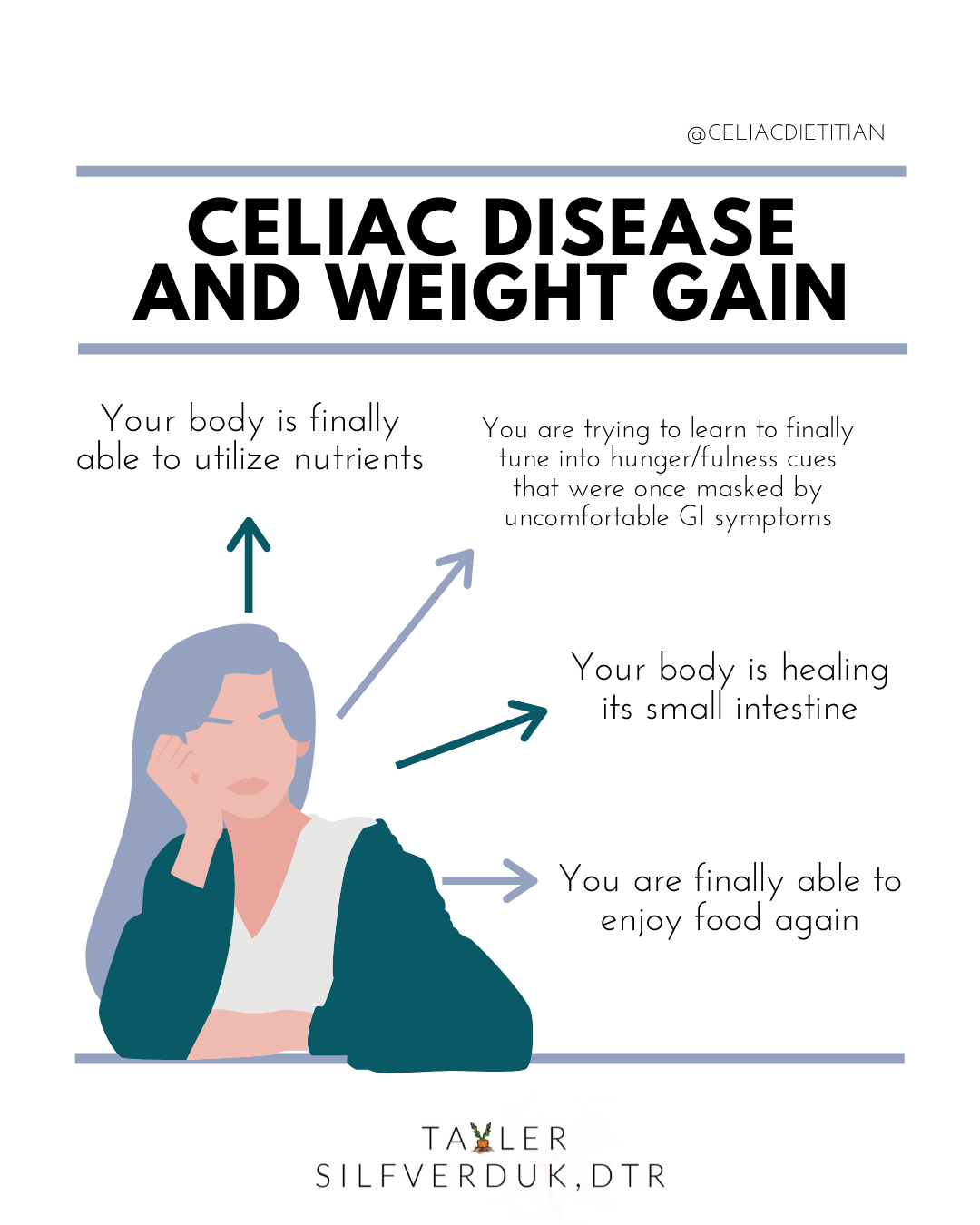
When individuals eliminate gluten from their diet, the inflammation in the small intestine begins to subside. This allows the body to heal and start absorbing nutrients more efficiently.
As nutrient absorption improves, individuals may experience increased energy levels and a restored appetite. This can lead to increased food intake and subsequent weight gain, especially if they are not mindful of portion sizes and dietary choices.
Additionally, many gluten-free processed foods are higher in calories, fat, and sugar than their gluten-containing counterparts. Reliance on these processed foods can contribute to unintended weight gain.
Managing Weight While Living Gluten-Free
It's important for individuals with celiac disease to work with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to develop a personalized nutrition plan. This plan should focus on nutrient-dense, whole foods and balanced macronutrient ratios.
Emphasis should be placed on incorporating naturally gluten-free foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains like quinoa and brown rice. Portion control is also essential for managing weight gain.
Careful label reading is crucial to avoid hidden sources of gluten and to make informed choices about processed gluten-free foods. Choosing products with lower sugar and fat content is advisable.
Regular physical activity is also an important component of weight management and overall health for individuals with celiac disease. Engaging in a variety of activities, including cardio and strength training, can help burn calories and build muscle mass.
"Weight management after a celiac diagnosis is about more than just avoiding gluten," says Dr. Alessio Fasano, a leading expert in celiac disease. "It requires a holistic approach that addresses nutrient deficiencies, optimizes gut health, and promotes a healthy lifestyle."
Support groups and online communities can also provide valuable resources and encouragement for individuals navigating the challenges of living with celiac disease and managing their weight.
Beyond the Scale: Focusing on Overall Health
While weight management is an important aspect of health, it's crucial to remember that overall well-being encompasses more than just a number on the scale. Focusing on nutrient intake, energy levels, and quality of life is equally important.
The primary goal of a gluten-free diet is to heal the small intestine and alleviate symptoms associated with celiac disease. This improved health can lead to increased energy levels, better digestion, and improved overall well-being.
It's important to celebrate these positive changes and focus on building a sustainable, healthy lifestyle that supports both physical and mental well-being.
Conclusion
The relationship between celiac disease and weight is complex and multifaceted. While weight loss is a common symptom of untreated celiac disease, weight gain can also occur, both before and after diagnosis. Understanding the underlying mechanisms behind this phenomenon is crucial for managing weight effectively and promoting overall health.
By working closely with healthcare professionals, adopting a balanced gluten-free diet, and prioritizing a healthy lifestyle, individuals with celiac disease can achieve and maintain a healthy weight while enjoying improved quality of life. It's a journey that requires patience, self-compassion, and a commitment to long-term well-being. The focus shouldn't solely be on the number on the scale, but on nourishing the body and embracing a vibrant, healthy life, free from the debilitating effects of gluten.