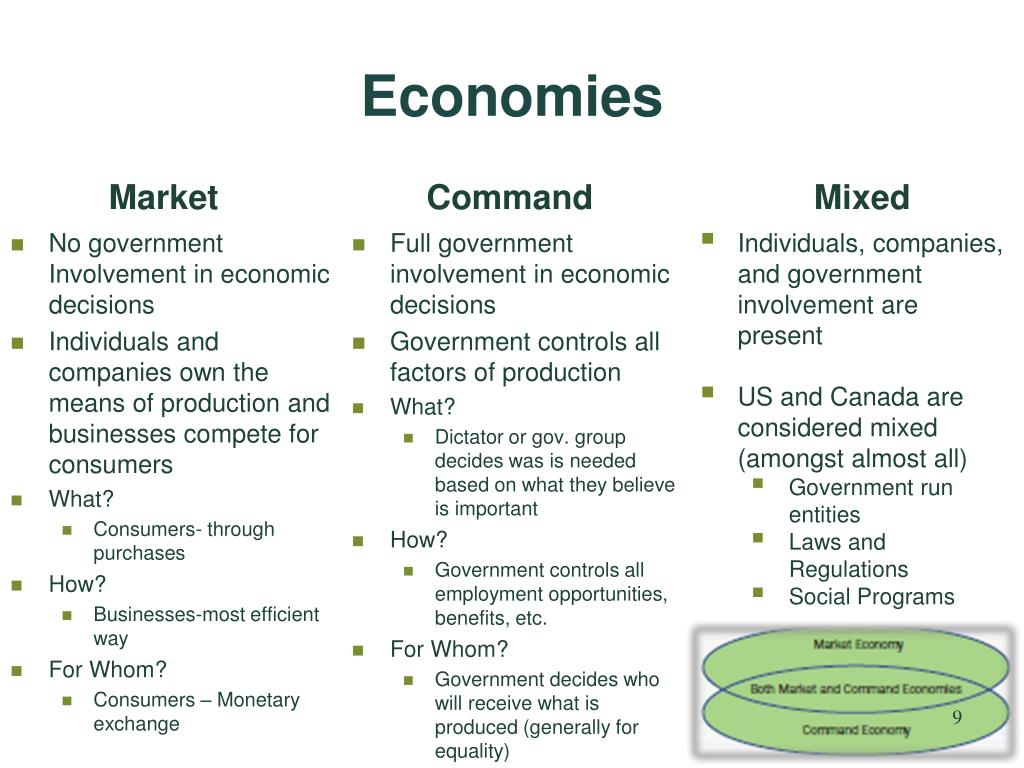
Chapter 3 Political And Economic Analysis

The specter of economic instability and political upheaval looms large across the globe, fueled by interconnected crises ranging from escalating geopolitical tensions to persistent inflationary pressures. Understanding the intricate interplay between political decisions and economic outcomes is now more critical than ever for policymakers, businesses, and citizens alike.
This article delves into the key elements of Chapter 3 Political and Economic Analysis, exploring how these forces shape national and international landscapes. It will examine how political systems, government policies, and global events impact economic performance, investment strategies, and overall societal well-being. We'll explore the implications of these dynamics for future stability and growth.
The Foundations of Political Economy
Political economy, at its core, analyzes how political and economic systems interact and influence each other. It acknowledges that economic outcomes are not solely determined by market forces, but are also shaped by political institutions, power structures, and government policies.
Adam Smith, often considered the father of modern economics, recognized this interplay centuries ago. His work emphasized the importance of both free markets and a strong, impartial government to ensure stability and prosperity.
Political Systems and Economic Development
The type of political system in place can significantly impact a nation's economic trajectory. Democracies, with their emphasis on checks and balances and citizen participation, often foster more inclusive and sustainable economic growth, but are not immune to short-term political pressures.
Authoritarian regimes, while potentially capable of implementing rapid economic reforms, often lack the transparency and accountability necessary for long-term stability, leading to potential corruption and unequal distribution of wealth, according to a report by Transparency International.
According to The Economist Intelligence Unit, countries with robust democratic institutions tend to have higher levels of human development and economic freedom.
Government Policies and Economic Performance
Government policies, ranging from fiscal spending to monetary policy, play a crucial role in shaping economic performance. Fiscal policies, which involve government spending and taxation, can stimulate demand, reduce inequality, or address specific market failures.
However, poorly designed fiscal policies can lead to unsustainable debt levels and inflation, hindering long-term growth. Monetary policy, typically managed by central banks, focuses on controlling inflation and maintaining financial stability through interest rate adjustments and other tools.
Effective monetary policy requires careful consideration of economic conditions and a commitment to maintaining price stability, as highlighted by recent statements from the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank.
The Role of Regulation
Regulation is another critical aspect of government policy that impacts economic activity. Well-designed regulations can protect consumers, promote competition, and safeguard the environment.
However, excessive or poorly designed regulations can stifle innovation, increase costs for businesses, and hinder economic growth. Striking the right balance between regulation and economic freedom is a constant challenge for policymakers, according to an OECD report on regulatory reform.
Deregulation of specific industries can also lead to increased risk and instability, as evidenced by the 2008 financial crisis, which was partially attributed to inadequate oversight of the financial sector.
Global Economic and Political Interdependence
In an increasingly interconnected world, global economic and political forces have a profound impact on national economies. International trade, investment flows, and geopolitical events can all significantly affect a country's economic performance.
Trade agreements, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements, aim to reduce trade barriers and promote economic integration. However, trade disputes and protectionist measures can disrupt global supply chains and hinder economic growth.
Geopolitical tensions, such as the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, can create significant economic disruptions, leading to increased energy prices, supply chain bottlenecks, and heightened uncertainty, as noted by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The Impact of Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical risks, including political instability, terrorism, and cyberattacks, can also have significant economic consequences. These risks can disrupt business operations, reduce investment, and increase uncertainty in financial markets.
Companies must carefully assess and manage geopolitical risks when making investment decisions, as highlighted by risk management firms such as Control Risks and Verisk Maplecroft.
Effective risk management strategies include diversifying investments, strengthening cybersecurity defenses, and developing contingency plans to mitigate potential disruptions.
Future Trends and Challenges
Looking ahead, several key trends and challenges will shape the future of political economy. Climate change, technological disruption, and rising inequality are just a few of the major forces that will demand innovative policy responses.
Climate change poses a significant threat to economic stability, with potential impacts ranging from extreme weather events to resource scarcity. Governments and businesses must invest in sustainable development and climate resilience to mitigate these risks.
Technological disruption, driven by automation and artificial intelligence, is transforming industries and labor markets. Governments must invest in education and training to prepare workers for the jobs of the future and address the potential for increased inequality.
Addressing Inequality
Rising inequality is a major challenge facing many countries, with potential consequences for social cohesion and political stability. Governments must implement policies that promote inclusive growth, such as progressive taxation, investments in education and healthcare, and social safety nets.
Addressing inequality requires a multi-faceted approach that tackles the root causes of poverty and promotes equal opportunities for all citizens, as argued by economists such as Thomas Piketty and Anthony Atkinson.
Ultimately, navigating the complexities of political economy requires a holistic understanding of the interplay between political and economic forces. By carefully considering these dynamics, policymakers, businesses, and citizens can work together to create a more stable, prosperous, and equitable future.