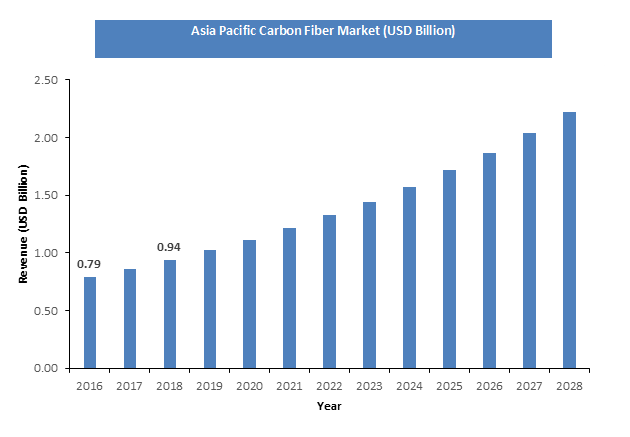
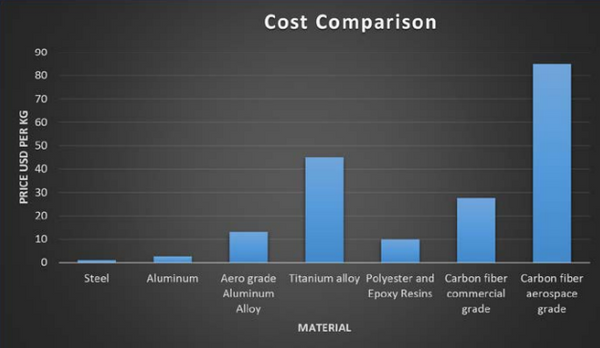
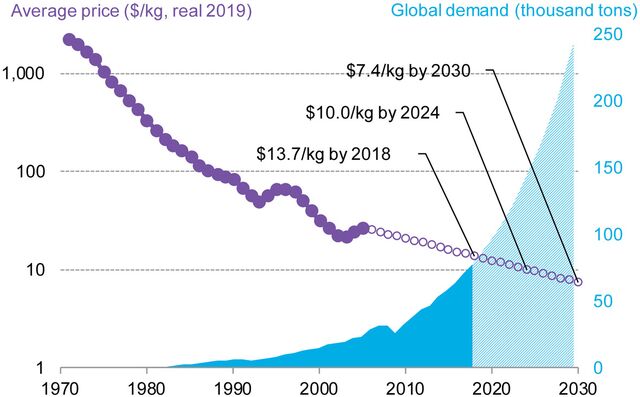
Cost Of Carbon Fiber Per Kg
Imagine a Formula 1 race, the sleek cars hugging the curves at breathtaking speeds. Or picture a state-of-the-art Boeing 787 Dreamliner soaring effortlessly through the sky. What do these seemingly disparate feats of engineering have in common? The answer lies in a material that's as strong as it is light: carbon fiber. The cost of this wonder material, often measured per kilogram, is a crucial factor influencing its adoption across various industries.
At its core, the price per kilogram of carbon fiber dictates its accessibility and integration into a wide spectrum of applications, from aerospace and automotive to sports equipment and renewable energy. Understanding the factors that influence this cost – from raw material sourcing and manufacturing processes to technological advancements and market demand – is essential for businesses and consumers alike.
A Look Back: The Genesis of Carbon Fiber
The story of carbon fiber begins in the late 19th century with Joseph Swan's experiments using carbon filaments for light bulbs. However, it wasn't until the late 1950s that high-performance carbon fiber, as we know it today, emerged.
Early carbon fiber was expensive and difficult to produce. The real breakthrough came in the 1960s, when processes were developed to manufacture carbon fiber from polyacrylonitrile (PAN), a polymer that's still the most common precursor today.
These initial advancements significantly improved the strength and stiffness of carbon fiber, paving the way for its use in demanding applications.
The Price Landscape: A Complex Equation
The cost of carbon fiber per kilogram isn't a static number. It fluctuates based on a confluence of factors, making it a complex economic equation.
The type of carbon fiber plays a significant role. Standard modulus carbon fiber, often used in automotive applications, typically costs less than high-modulus or ultra-high-modulus fibers, which are preferred for aerospace and other high-performance applications.
The quality and grade of the fiber also contribute to price variations, with higher grades commanding a premium due to their superior strength and consistency.
Raw Materials and Manufacturing: The Foundation of the Cost
The primary raw material for most carbon fiber production is PAN. The cost of PAN, derived from acrylonitrile, can fluctuate based on the price of oil and natural gas, as well as supply and demand dynamics.
The manufacturing process itself is energy-intensive. It involves heating the PAN fibers in a controlled atmosphere to remove non-carbon elements and align the carbon atoms, a process called carbonization.
The energy costs, labor, and capital investments in advanced equipment all contribute to the final cost per kilogram.
Supply and Demand: The Market's Influence
Like any commodity, the cost of carbon fiber is also influenced by supply and demand. Increased demand from industries like aerospace and automotive can drive prices up, especially if supply chains face disruptions.
Conversely, an oversupply of carbon fiber could lead to price reductions as manufacturers compete for market share. Economic cycles and geopolitical events can also play a role in shaping the supply-demand balance.
Technological Advancements: A Hope for Cost Reduction
Innovation is a key driver of cost reduction in the carbon fiber industry. Researchers and manufacturers are continually exploring new precursors, manufacturing processes, and recycling methods to make carbon fiber more affordable.
Alternative precursors, such as lignin derived from wood or textile waste, are being investigated to reduce reliance on PAN. Improved manufacturing techniques, such as plasma oxidation and microwave heating, promise to lower energy consumption and production time.
Advances in automation and process control can also improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Current Cost Estimates: A Range of Possibilities
Providing a precise, universally applicable cost per kilogram for carbon fiber is challenging due to the factors mentioned above. However, we can provide a general estimate based on available data.
Standard modulus carbon fiber typically ranges from $15 to $30 per kilogram. High-modulus carbon fiber can cost significantly more, ranging from $70 to $150 per kilogram or even higher for specialized grades.
These are broad estimates, and actual prices can vary based on specific requirements, order volumes, and supplier agreements.
Applications Across Industries: Why Carbon Fiber Matters
The unique properties of carbon fiber – its high strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and resistance to corrosion – make it invaluable across a wide range of industries.
In the aerospace industry, carbon fiber composites are used in aircraft structures, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency. Automotive manufacturers use carbon fiber to build lighter, faster, and more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Sports equipment, such as bicycles, golf clubs, and tennis rackets, benefit from the strength and stiffness of carbon fiber. Renewable energy applications, such as wind turbine blades, rely on carbon fiber to create longer, lighter, and more efficient blades.
The Future of Carbon Fiber: Sustainability and Affordability
The future of carbon fiber is inextricably linked to sustainability and affordability. As environmental concerns grow, the industry is focusing on developing more sustainable production methods and promoting the use of recycled carbon fiber.
Recycled carbon fiber, recovered from end-of-life products or manufacturing waste, offers a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative to virgin carbon fiber.
Continued research and development in alternative precursors, efficient manufacturing processes, and recycling technologies will be crucial in driving down costs and expanding the use of carbon fiber in a more sustainable manner.
A Concluding Thought
The cost of carbon fiber per kilogram is more than just a number; it's a key indicator of the material's accessibility and potential to revolutionize industries. While the cost remains a barrier to wider adoption in some sectors, ongoing innovations and a growing focus on sustainability offer a promising outlook.
As we move towards a future where lightweight, strong, and sustainable materials are increasingly essential, the story of carbon fiber – its past, present, and future – is one worth following closely. The future is being molded, quite literally, by this remarkable material.
Ultimately, carbon fiber represents not just a material, but a pathway towards innovation and efficiency. It holds the potential to reshape our world in profound ways, from the vehicles we drive to the energy we harness.