Depends On Oxygen Delivery And Aerobic Mechanisms.

The human body's reliance on oxygen and aerobic mechanisms is a fundamental aspect of physiology, influencing everything from athletic performance to basic survival. A deeper understanding of these processes is constantly evolving, impacting medical treatments and training regimens alike.
This article examines the intricate interplay between oxygen delivery, aerobic metabolism, and their significance in various contexts, supported by scientific studies and expert insights. It explores how deficiencies in these systems can lead to health complications and how optimizing them can enhance well-being.
The Critical Role of Oxygen
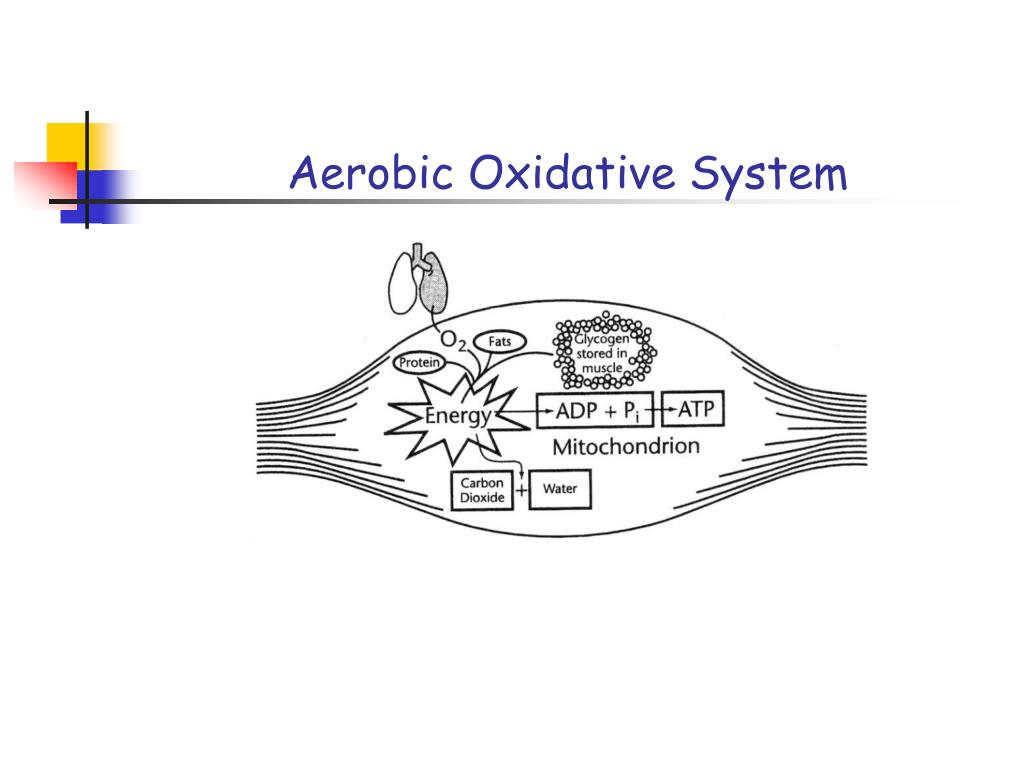
Oxygen is the lifeblood of aerobic organisms. It is crucial for cellular respiration, the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy.
This energy, in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), fuels all bodily functions. Without sufficient oxygen, these functions falter.
Oxygen Delivery Systems
The respiratory system, comprised of the lungs and airways, is responsible for taking in oxygen from the environment. This oxygen then binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
The cardiovascular system transports these oxygen-rich red blood cells throughout the body. This efficient delivery mechanism ensures that tissues and organs receive the oxygen they need to function.
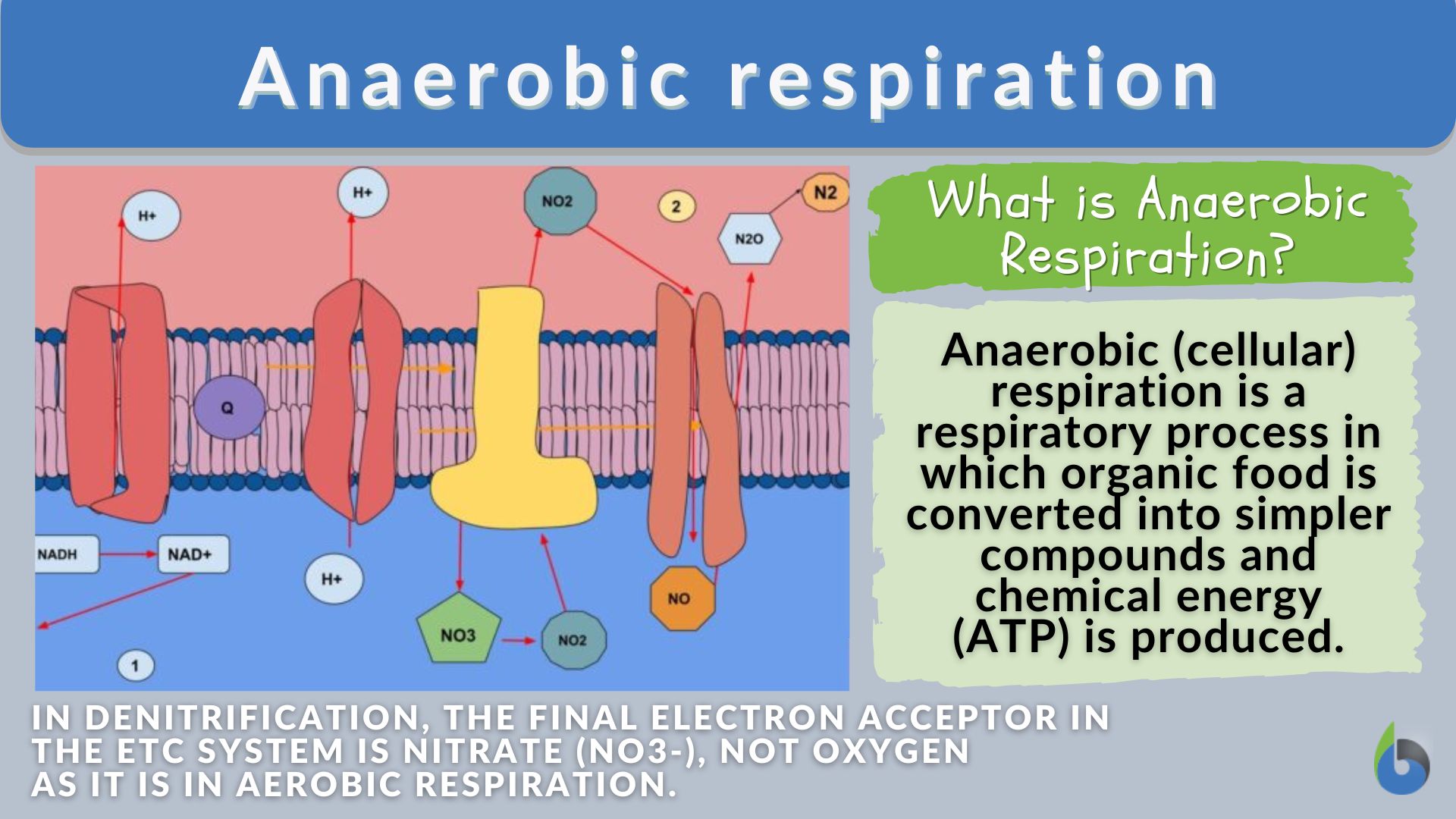
Any impairment in either system can lead to hypoxia, a condition characterized by insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues.
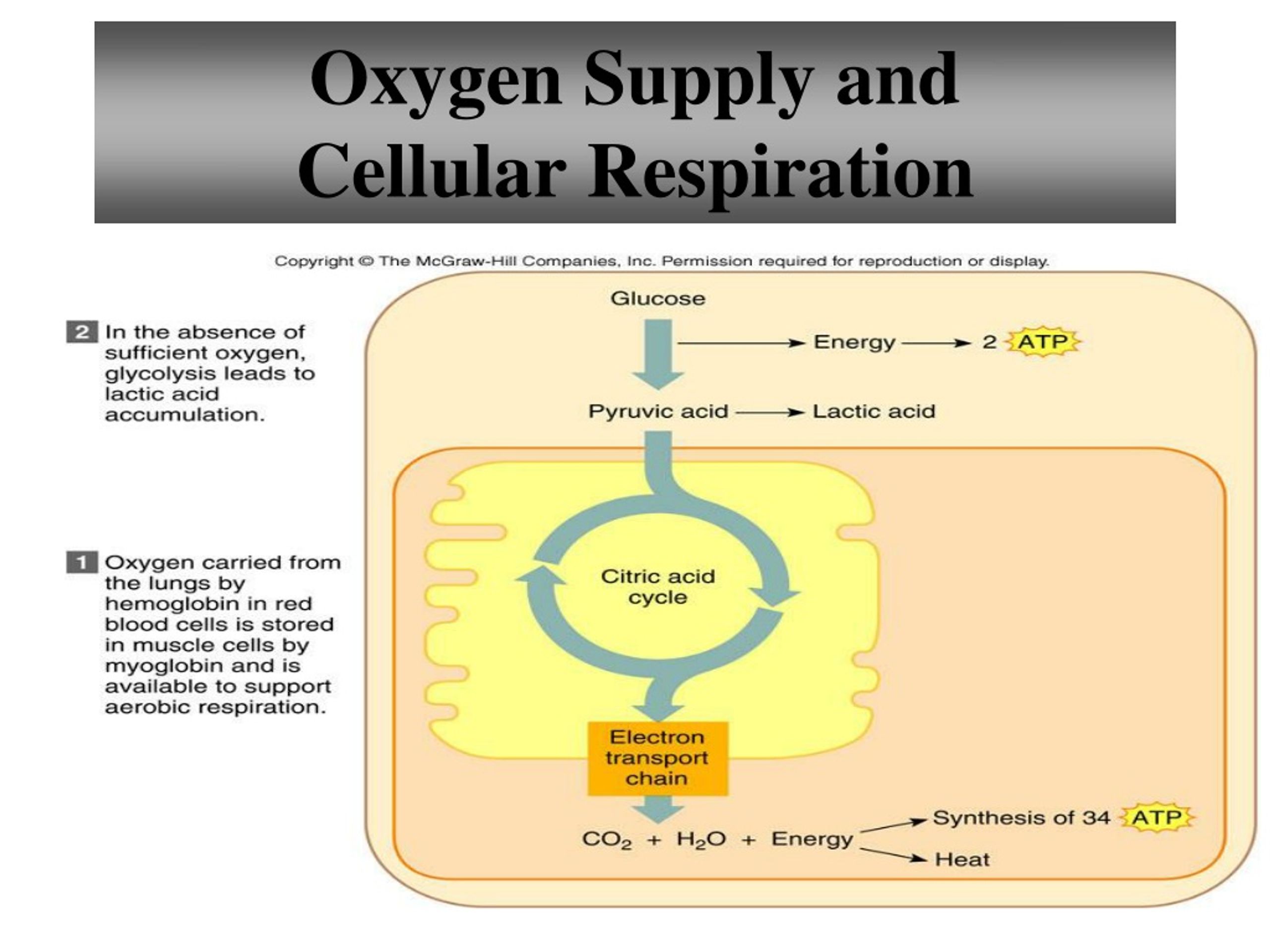
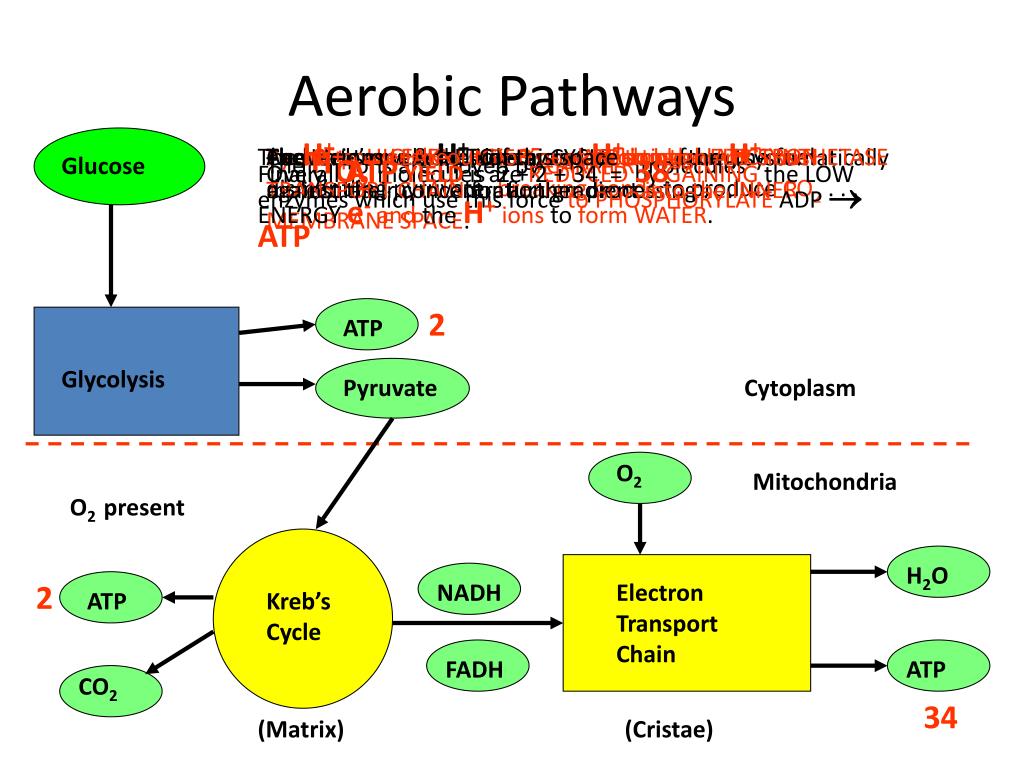
Aerobic Metabolism: The Engine of Life
Aerobic metabolism occurs within the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cells. This process uses oxygen to break down glucose, fats, and proteins.
It produces significantly more ATP than anaerobic metabolism, which occurs in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic metabolism, while faster, produces byproducts like lactic acid that can lead to fatigue and muscle soreness.
The efficiency of aerobic metabolism is vital for sustained physical activity and overall health.
Factors Affecting Aerobic Capacity
Aerobic capacity, also known as VO2 max, refers to the maximum amount of oxygen a person can utilize during intense exercise. It is a key indicator of cardiovascular fitness.
Factors that affect aerobic capacity include genetics, age, sex, and training status. Regular exercise, particularly endurance training, can significantly improve VO2 max.
Conversely, sedentary lifestyles can lead to a decline in aerobic capacity, increasing the risk of chronic diseases.
Implications for Health and Disease
Disruptions in oxygen delivery and aerobic metabolism can have profound health consequences. These disruptions can manifest as a wide range of conditions.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart failure, and anemia are examples of conditions that impair oxygen delivery. These impairments compromise the body’s ability to function correctly.
Metabolic disorders like diabetes and mitochondrial diseases directly affect the efficiency of aerobic metabolism, leading to energy deficits and various health problems.
Therapeutic Interventions
Medical interventions aimed at improving oxygen delivery and aerobic metabolism are crucial for managing these conditions. Oxygen therapy is often used to supplement oxygen levels in patients with respiratory problems.
Cardiac rehabilitation programs can improve cardiovascular function and aerobic capacity in patients with heart disease. Furthermore, dietary modifications and exercise regimens can enhance metabolic efficiency in individuals with diabetes.
Researchers are also exploring novel therapies targeting mitochondrial dysfunction to improve energy production in patients with mitochondrial diseases. These interventions demonstrate the multifaceted approach to addressing problems in oxygen delivery and aerobic metabolism.
The Impact on Athletic Performance
The link between oxygen delivery, aerobic metabolism, and athletic performance is well-established. Athletes across various disciplines rely on efficient oxygen utilization for optimal performance.
Endurance athletes, such as marathon runners and cyclists, require high aerobic capacities to sustain prolonged periods of activity. Strength and power athletes, while relying more on anaerobic metabolism, still benefit from efficient oxygen recovery between bursts of activity.
Training techniques aimed at improving VO2 max and lactate threshold are integral to athletic training programs. These techniques help athletes push their limits and achieve peak performance.
“Understanding the intricate details of oxygen delivery and aerobic metabolism is crucial not only for athletes but also for anyone seeking to improve their overall health and well-being,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading exercise physiologist.
Dr. Carter emphasized the importance of regular physical activity and a balanced diet in optimizing these processes. She also highlighted the significance of consulting with healthcare professionals to address any underlying health conditions that may affect oxygen utilization.
Conclusion
The human body's reliance on oxygen delivery and aerobic mechanisms is undeniable. It underlies nearly all aspects of human physiology and health.
Understanding these processes and their implications is essential for maintaining optimal health and performance. Continued research promises even deeper insights into optimizing oxygen utilization and mitigating the impact of related diseases.
By focusing on healthy lifestyle choices and seeking appropriate medical care when needed, individuals can ensure their bodies are equipped to thrive on the power of oxygen and aerobic metabolism.




+aerobic+respiration.jpg)








.jpg)
