Digestive Disorders Can Seriously Impact Nutrient Transfer And
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-wrong-with-my-stomach-4138111-5c454a7cc9e77c0001b21d85-5c2ddd1c5370453b8ec4ff45faefd184.png)
A silent epidemic is crippling nutrient absorption across the nation. Digestive disorders, often overlooked, are now confirmed to be significantly impairing nutrient transfer, leading to widespread health complications.
This article breaks down the urgent implications of compromised nutrient absorption due to digestive illnesses, emphasizing the scale of the problem and outlining the immediate need for increased awareness and proactive intervention.
The Scale of the Crisis
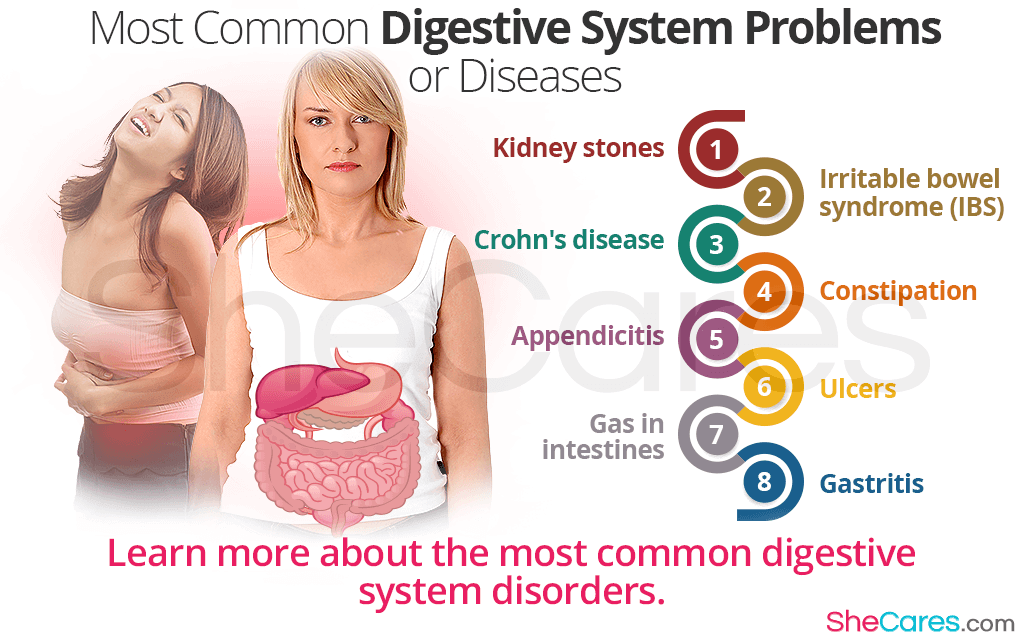
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) estimates that 60 to 70 million Americans are affected by digestive diseases. This staggering number underscores the magnitude of the problem.
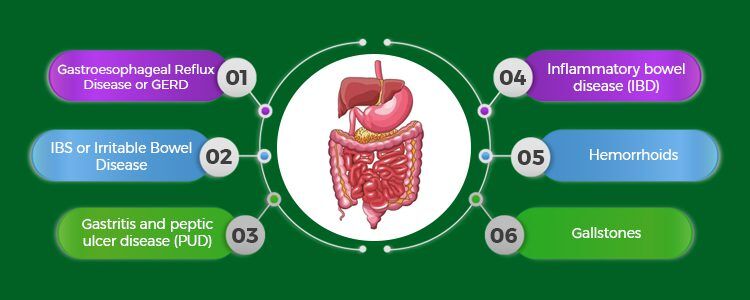
These conditions range from common ailments like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and acid reflux to more severe diseases like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
The common thread? Impaired nutrient absorption, with potentially devastating consequences for individual health and public health overall.
Nutrient Absorption Under Attack
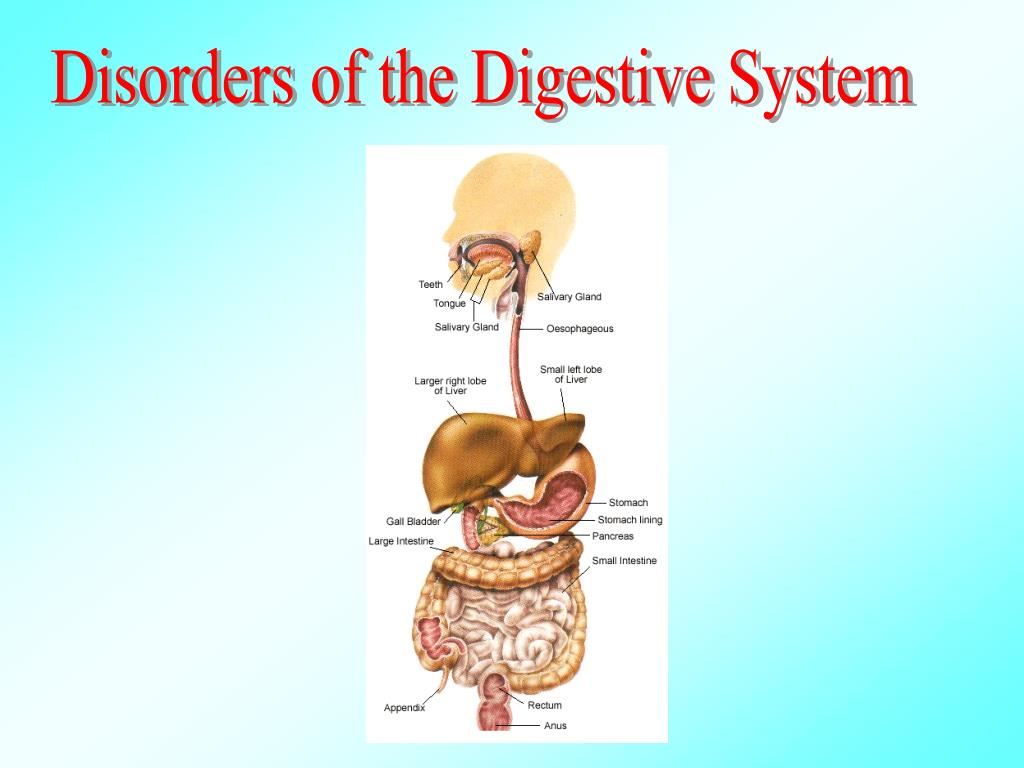
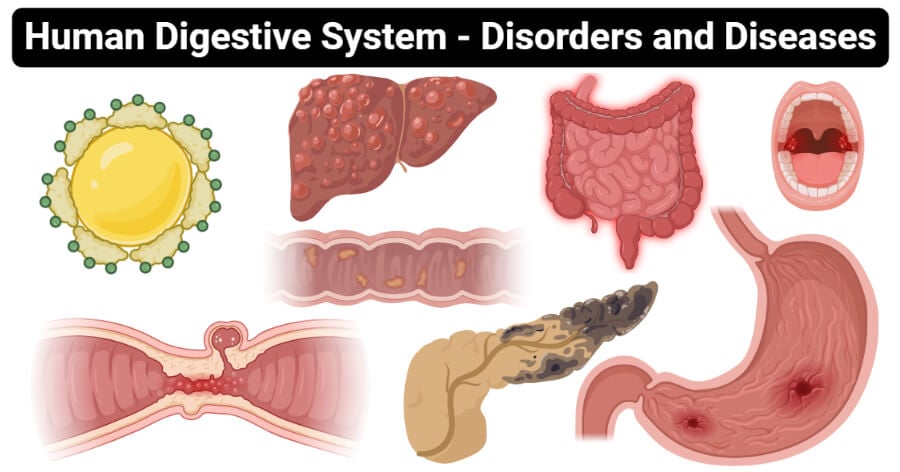
A healthy digestive system efficiently breaks down food and absorbs vital nutrients. Digestive disorders disrupt this delicate process at multiple points.
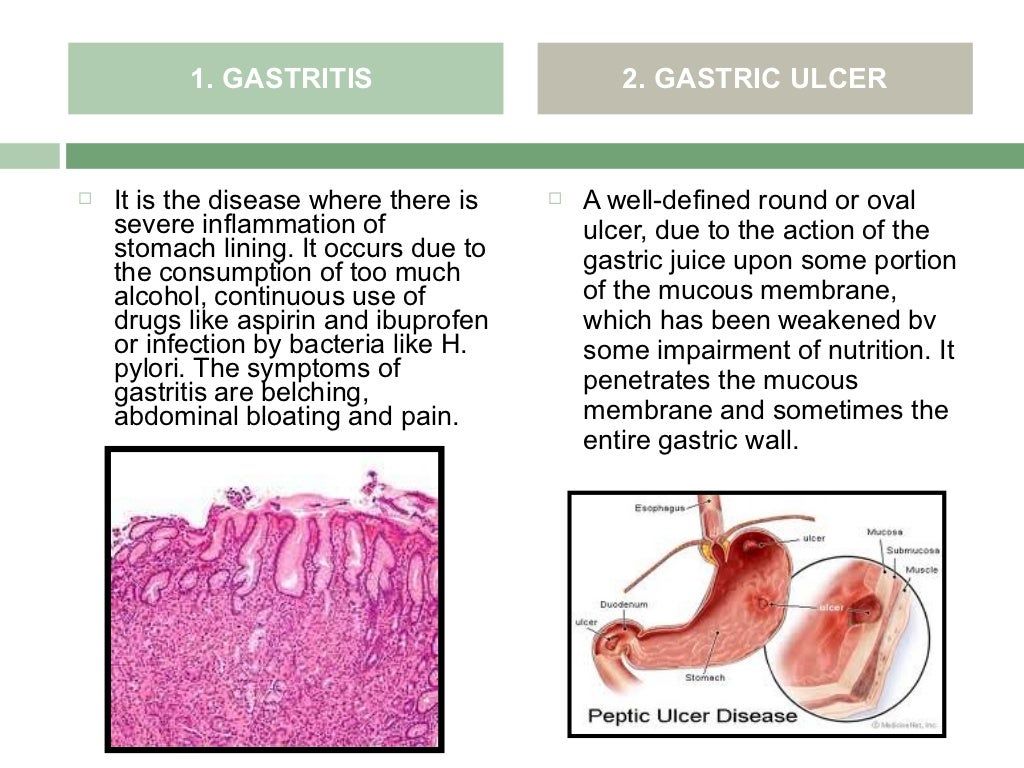
Inflammation, a hallmark of many digestive diseases, damages the intestinal lining. This damage reduces the surface area available for nutrient absorption, drastically impacting the body's ability to utilize food.
For example, in Crohn's disease, inflammation can occur anywhere in the digestive tract, leading to malabsorption of specific nutrients depending on the affected area.
Specific Impacts of Malabsorption
Vitamin deficiencies are a major concern. Vitamin D, essential for bone health and immune function, is frequently malabsorbed in individuals with digestive disorders.
Iron deficiency anemia is another common consequence. This results from the inability to absorb sufficient iron, leading to fatigue, weakness, and cognitive impairment.
Moreover, malabsorption of essential fatty acids can disrupt hormone production and neurological function. This may also impact cardiovascular health.
Who Is Most at Risk?
While digestive disorders can affect anyone, certain populations are at higher risk. Individuals with a family history of digestive diseases face an elevated risk.
Those who follow restrictive diets or have undergone gastrointestinal surgery are also susceptible. Furthermore, individuals with compromised immune systems are more vulnerable.
Age also plays a role, as digestive function naturally declines with age, increasing the risk of nutrient deficiencies in older adults.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
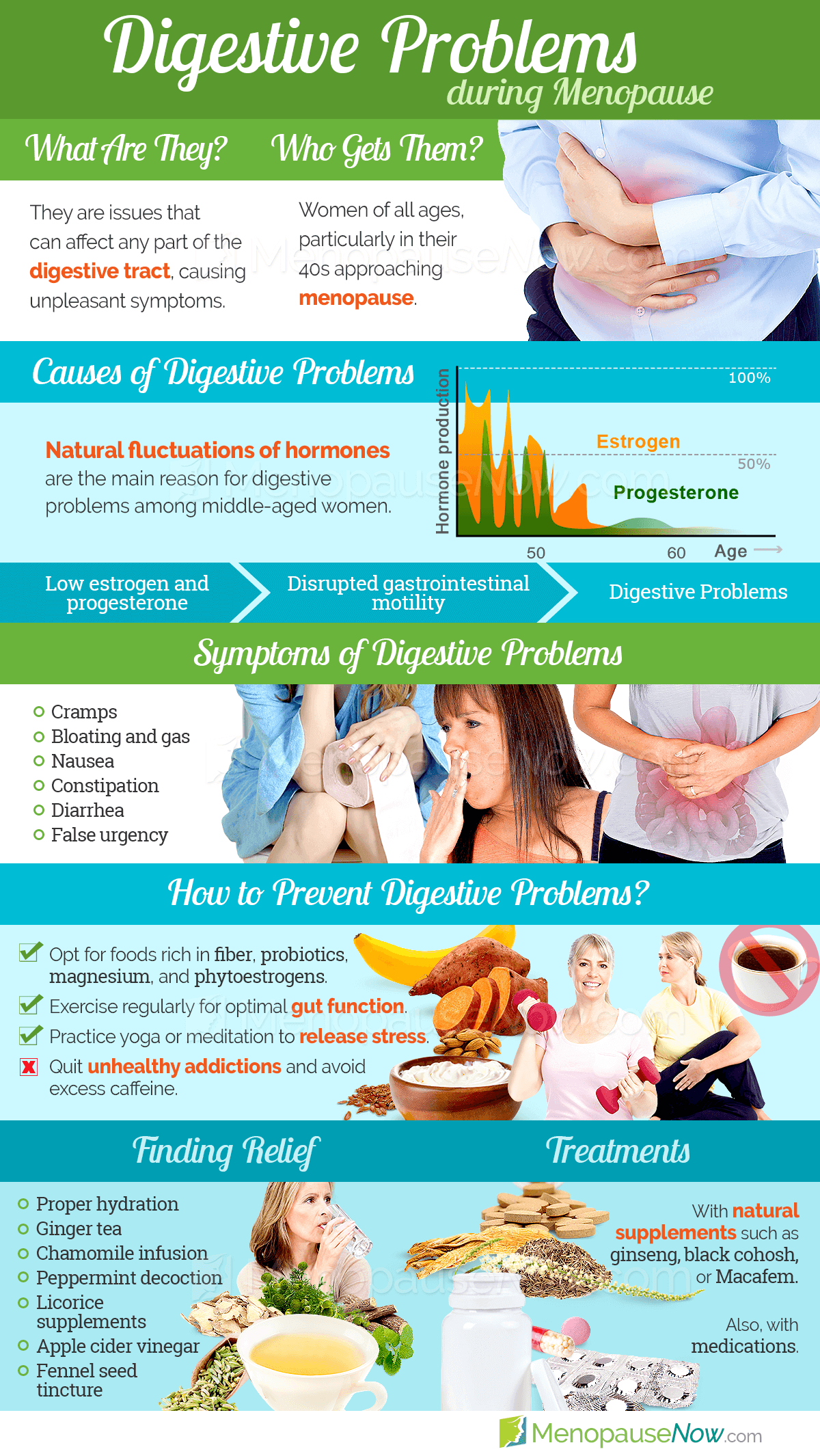
Early detection is crucial for mitigating the impact of malabsorption. Common symptoms include chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating.
Unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and skin rashes can also indicate a problem with nutrient absorption.
Anyone experiencing these symptoms should consult a healthcare professional for prompt diagnosis and management.
The Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing the underlying cause of malabsorption requires a thorough medical evaluation. This often includes blood tests to assess nutrient levels.
Stool tests can help identify infections or malabsorption of fat. Endoscopic procedures, such as colonoscopy or upper endoscopy, allow doctors to visualize the digestive tract and obtain biopsies.
These biopsies can reveal inflammation or other abnormalities that may be impairing nutrient absorption.
Treatment Strategies and Ongoing Developments
Treatment strategies vary depending on the underlying cause of the digestive disorder. Dietary modifications are often the first line of defense.
Supplementation with vitamins and minerals is frequently necessary to address deficiencies. Medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs or immunomodulators, may be prescribed to control inflammation.
Research is ongoing to develop more targeted therapies for digestive disorders and to improve nutrient absorption. The Crohn's & Colitis Foundation is a leading organization funding this crucial research.
Take Action Now
The impact of digestive disorders on nutrient transfer is a critical public health concern. Increased awareness and proactive intervention are essential to mitigate the consequences.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a digestive disorder, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Support research efforts aimed at improving the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of digestive diseases. Educate yourself and your community about the importance of gut health and nutrient absorption.


![Digestive Disorders Can Seriously Impact Nutrient Transfer And The digestive system [ Disease & Disorders] | PPT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thedigestivesystem-190425064702/85/The-digestive-system-Disease-Disorders-6-638.jpg)