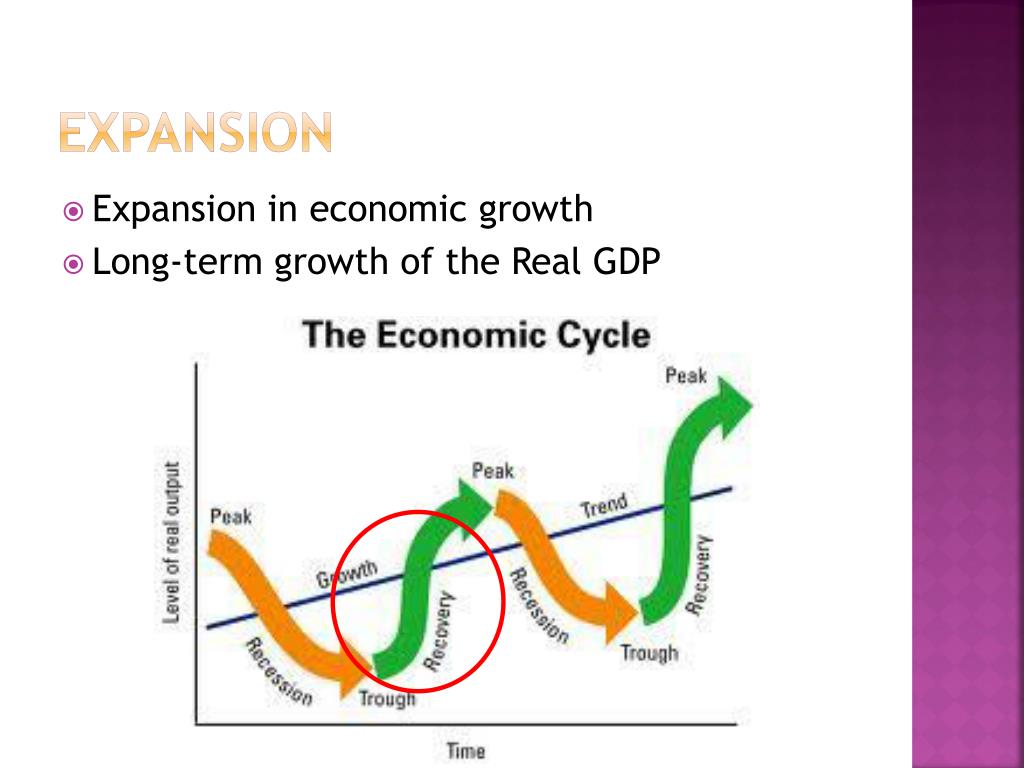
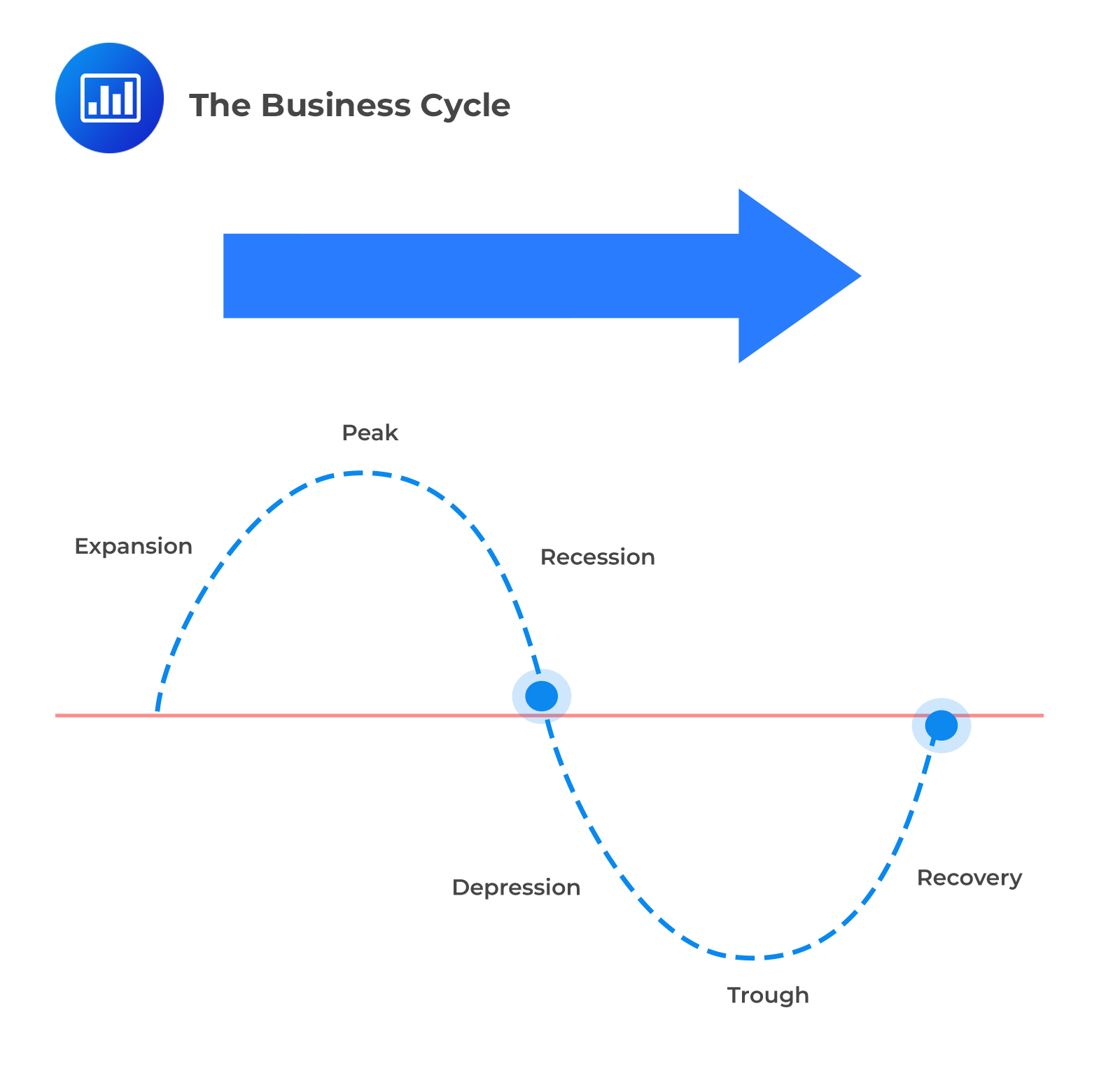
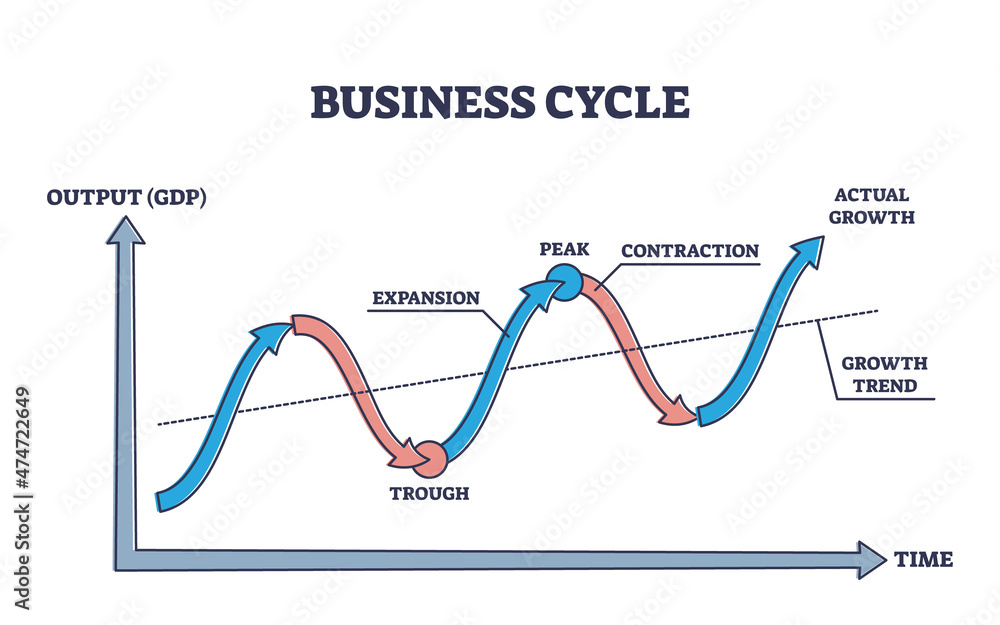
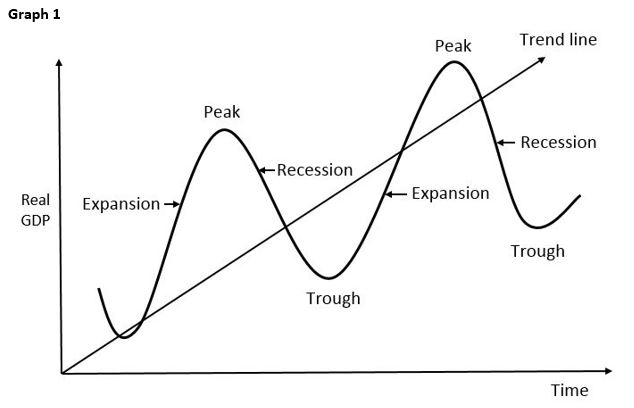
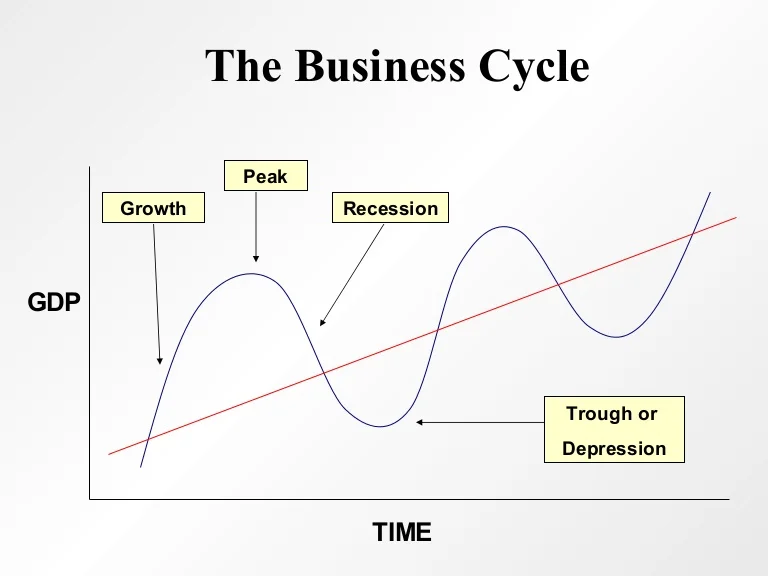
During The Expansion Phase Of The Business Cycle
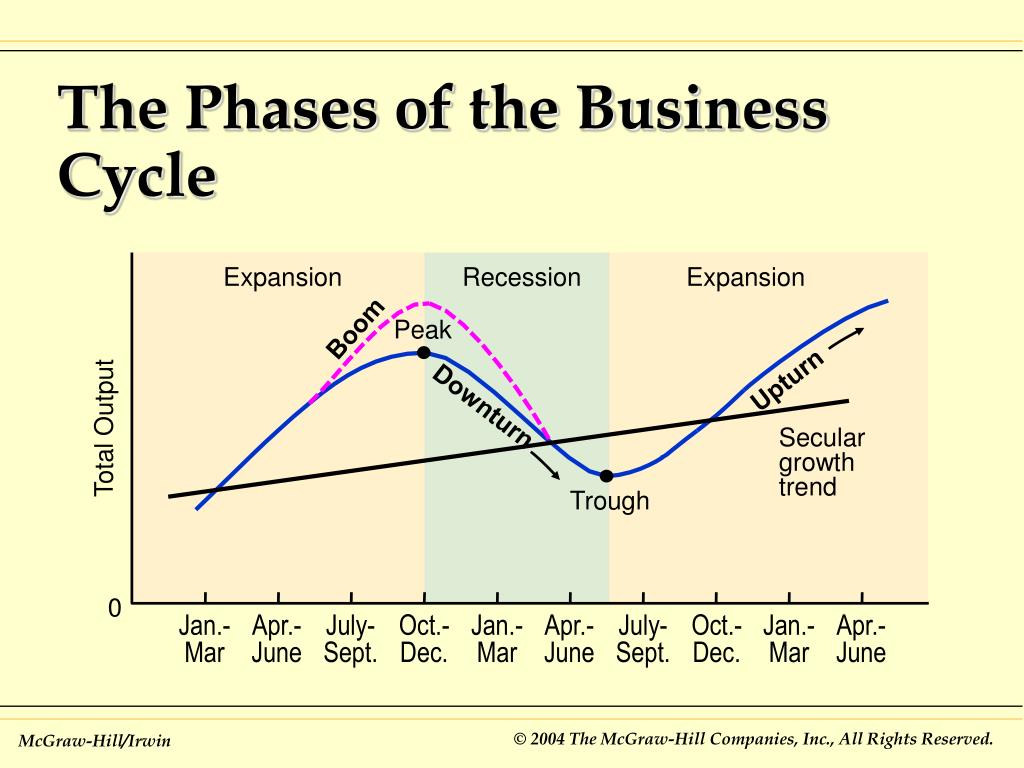
Economic indicators surge, signaling a robust expansion phase across multiple sectors. Businesses are reporting increased profits and hiring, fueled by rising consumer demand and investment.
This rapid growth, while positive, raises concerns about potential inflationary pressures and the need for strategic fiscal management to ensure sustainable long-term stability. The current expansion shows no signs of slowing, presenting both opportunities and challenges for policymakers and businesses alike.
Key Sectors Experiencing Growth
The technology sector is leading the charge, with software and hardware companies reporting record sales. Increased demand for cloud computing and artificial intelligence solutions fuels this growth, impacting companies like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
The manufacturing sector is also experiencing a resurgence. New orders are up, particularly for durable goods, reflecting increased business investment in capital equipment and expansion projects.
The housing market continues to be robust, driven by low interest rates and strong demand, particularly in suburban and rural areas. However, rising material costs and labor shortages are creating headwinds for builders.
Labor Market Dynamics
The unemployment rate has fallen to 3.7%, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Job creation is strong across most industries, although some sectors, like hospitality, are still recovering from earlier downturns.
Wage growth is accelerating as companies compete for scarce talent. This wage inflation, while benefiting workers, could contribute to broader inflationary pressures.
Skills gaps remain a significant challenge. Many employers report difficulty finding qualified workers, particularly in technical fields and skilled trades.
Inflationary Pressures Mounting
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 4.9% year-over-year in April, exceeding economists' expectations. This elevated inflation is driven by a combination of supply chain bottlenecks, increased consumer demand, and rising energy prices.
The Federal Reserve is under increasing pressure to raise interest rates to combat inflation. The Fed has already signaled its intention to begin tapering its asset purchases, a first step towards tightening monetary policy.
Businesses are facing tough decisions about whether to absorb rising costs or pass them on to consumers. Passing costs onto consumers could dampen demand, while absorbing costs could squeeze profit margins.
Regional Variations
The economic expansion is not uniform across all regions of the country. The Sun Belt states are experiencing particularly strong growth, fueled by migration and business investment.
Some regions, particularly those dependent on industries like tourism or energy, are lagging behind. Targeted economic development initiatives may be needed to help these regions catch up.
Urban centers are seeing a gradual recovery as people return to offices and cultural attractions. However, remote work trends continue to reshape the commercial real estate market.
Policy Responses and Future Outlook
The Biden administration is focused on infrastructure investment and addressing supply chain bottlenecks. These initiatives are intended to support long-term economic growth and alleviate inflationary pressures.
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projects continued economic growth in the near term, but at a slower pace than recent quarters. Concerns remain about the potential for a recession if the Federal Reserve tightens monetary policy too aggressively.
Businesses and policymakers must carefully navigate the current economic environment to ensure sustainable growth and avoid a boom-and-bust cycle. Ongoing monitoring of economic indicators and proactive adjustments to fiscal and monetary policy are crucial.
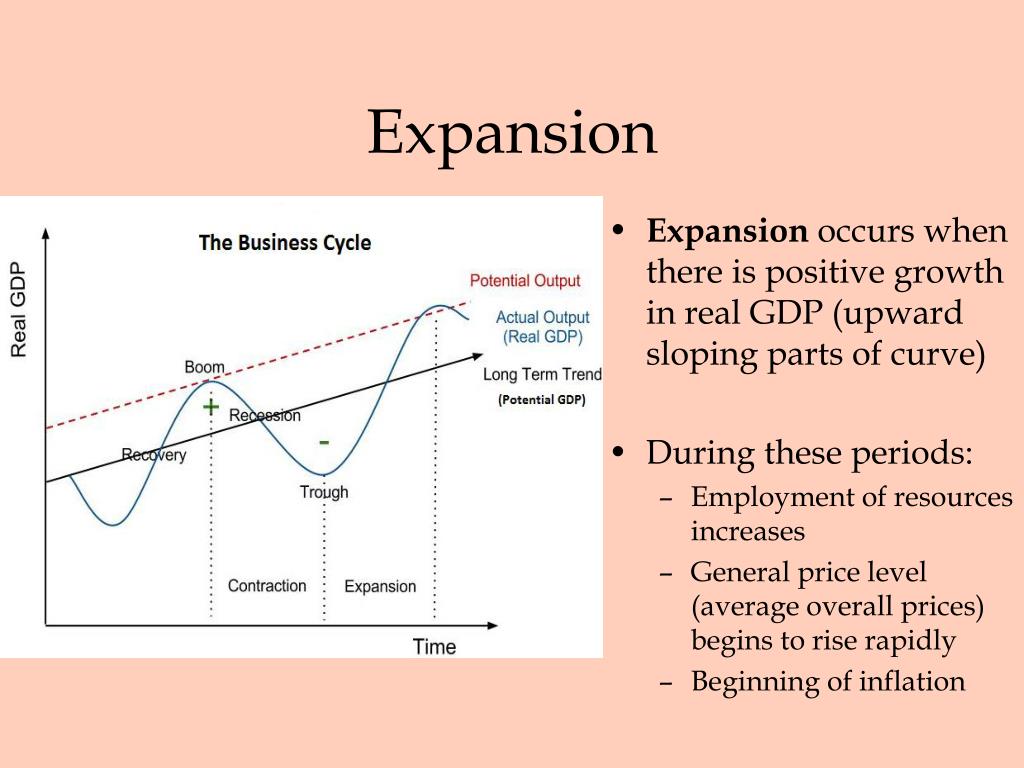
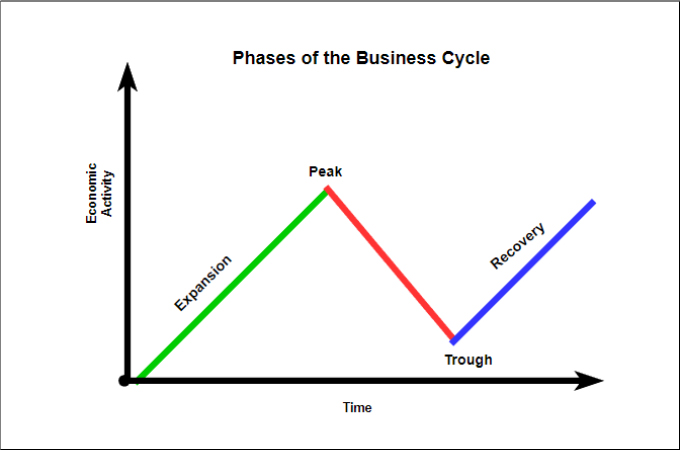


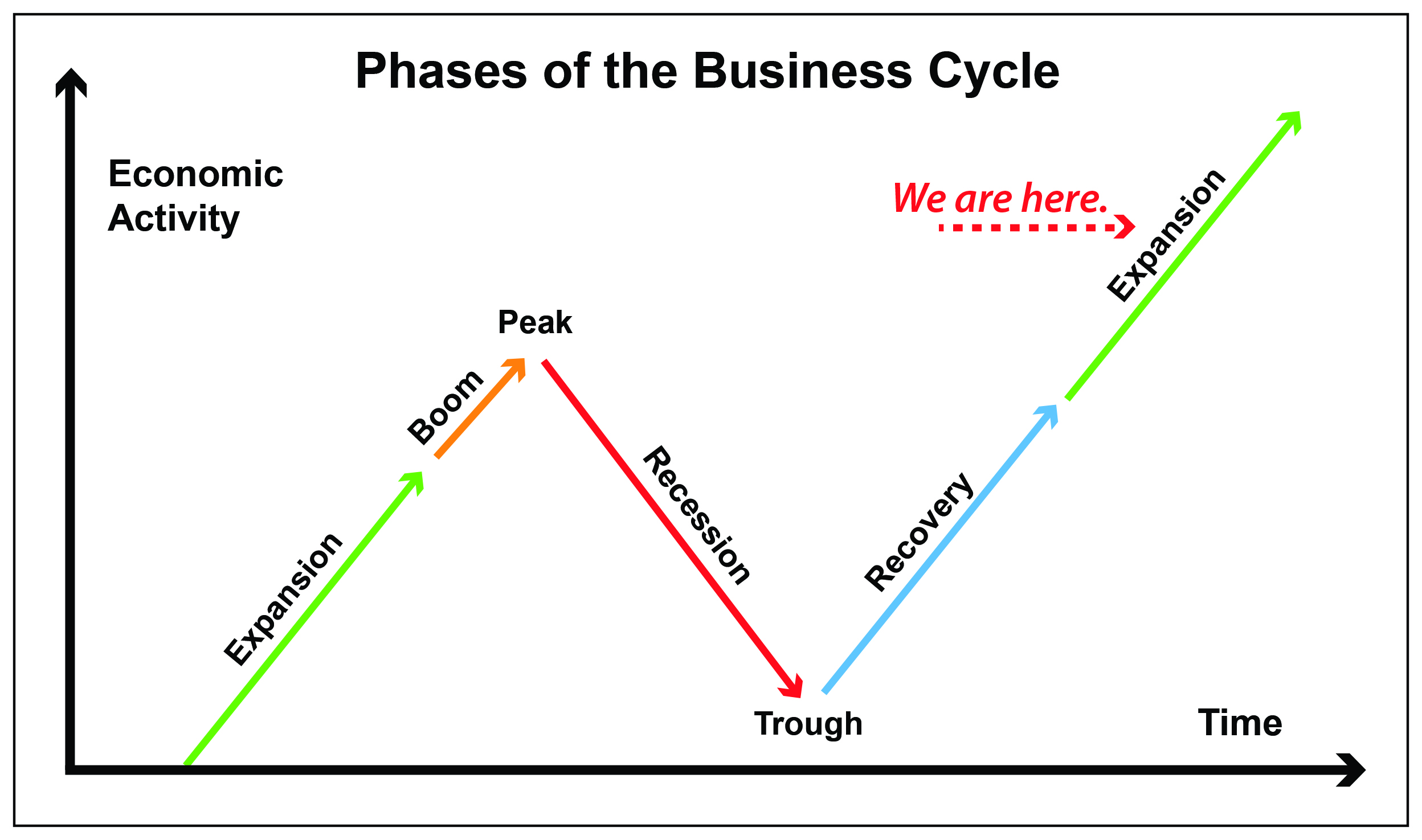
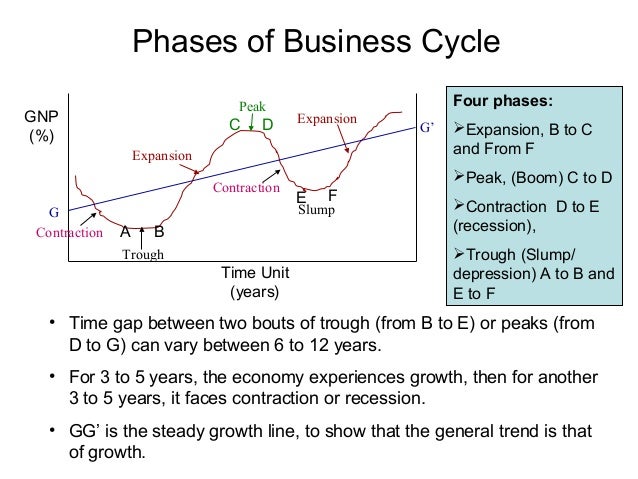
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phasesofthebusinesscycle-c7cb7a3ce6894e86a3e44d5b0fe4d5e2.jpg)
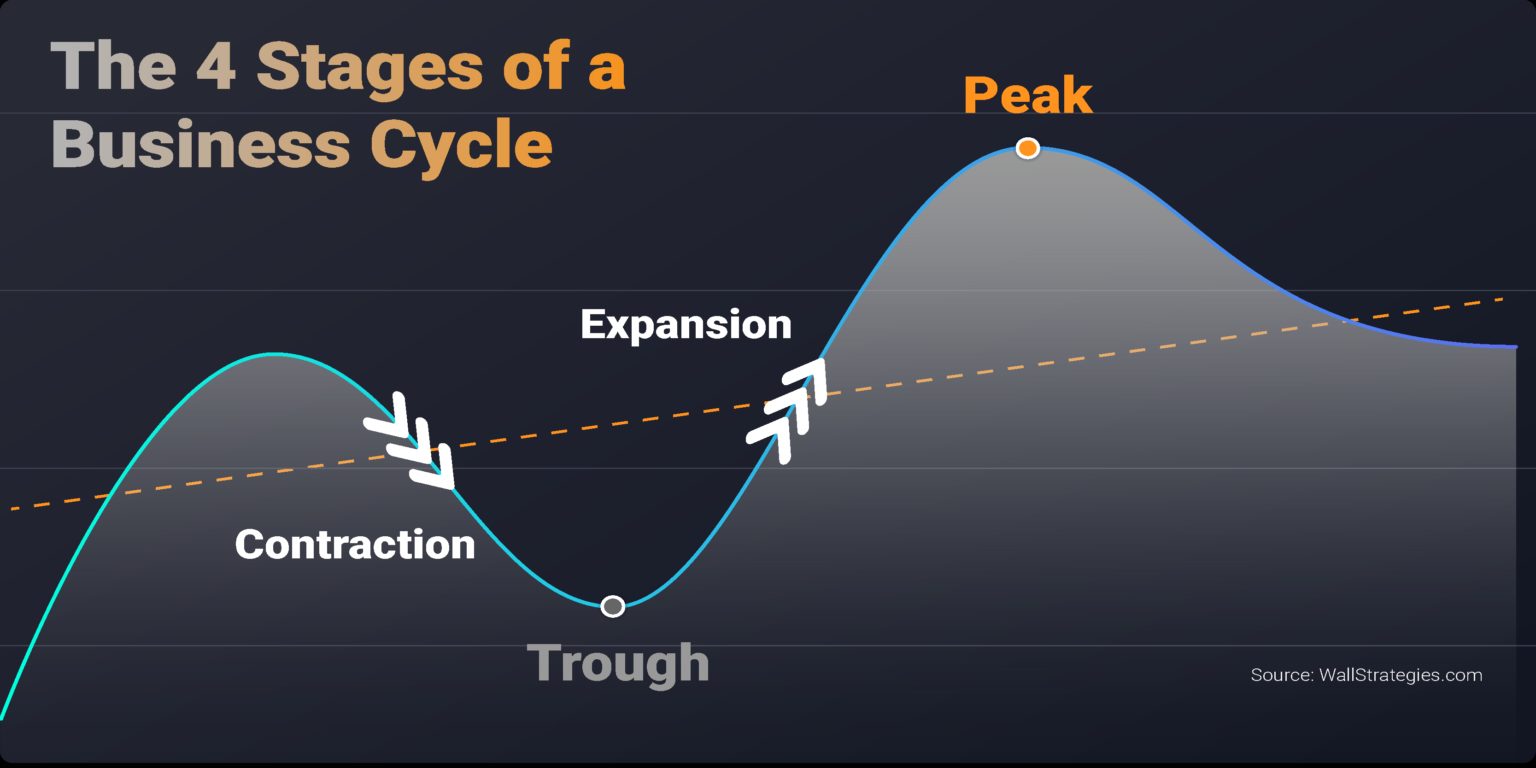
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)
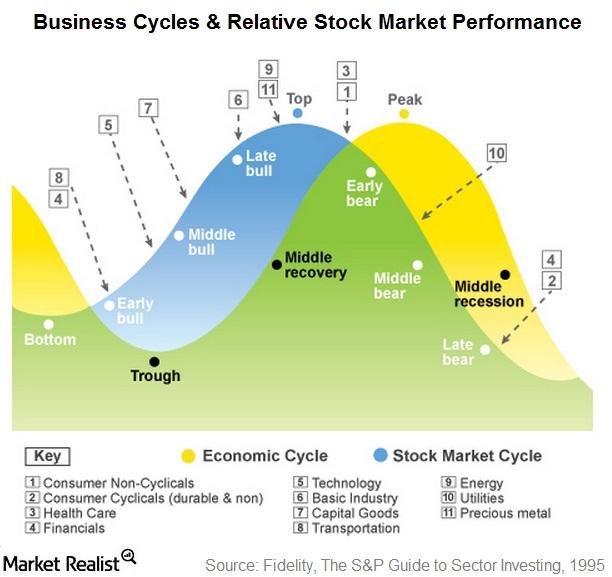
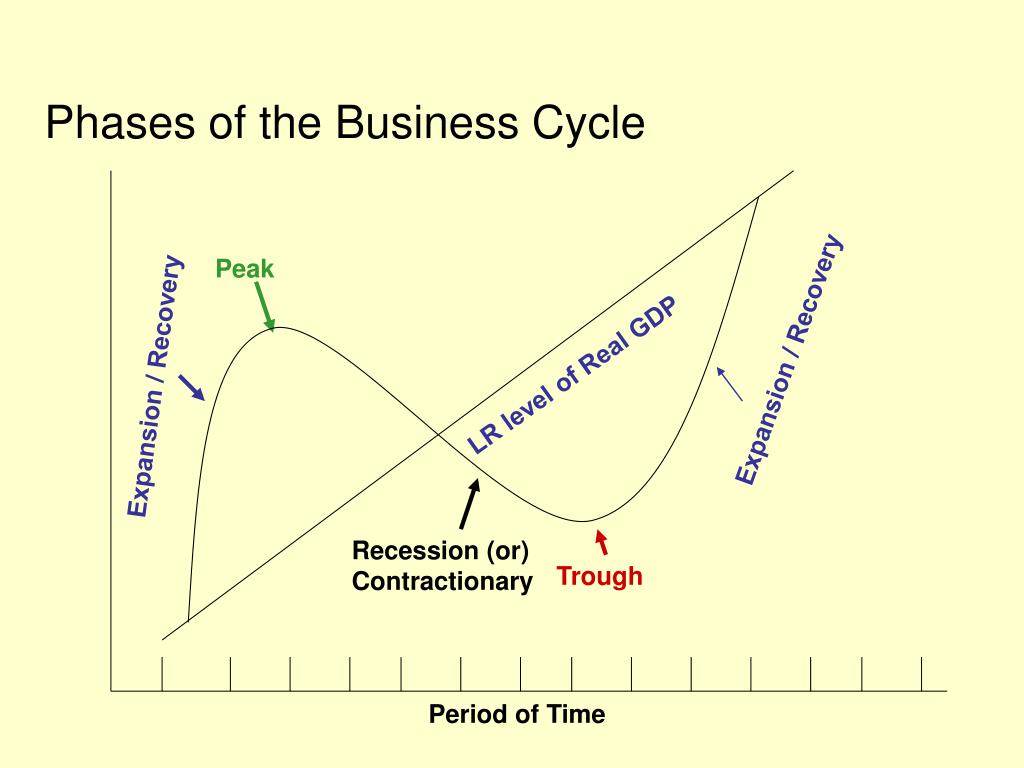
.png)