Environmental Influences Include Which Of The Following

Imagine a tiny seed, nestled in the earth, yearning to sprout. Sunlight streams down, rain nourishes the soil, and gentle breezes sway the nascent stem. But what if the soil is depleted, the air polluted, or the sun obscured? The seed's fate, its very potential, hangs in the balance, a testament to the power of its surroundings. It's a simple analogy that encapsulates a complex reality: our environment shapes us, influences us, and ultimately, helps define who we are.
At the heart of the nature-versus-nurture debate lies a fundamental question: what molds human development? This article delves into the profound impact of environmental influences, exploring the myriad factors beyond genetics that shape our lives, from the moment we are conceived to our final breath. We will examine the physical, social, and cultural elements that contribute to our individual and collective identities, painting a comprehensive picture of the environmental forces at play.
Understanding the Scope of Environmental Influence
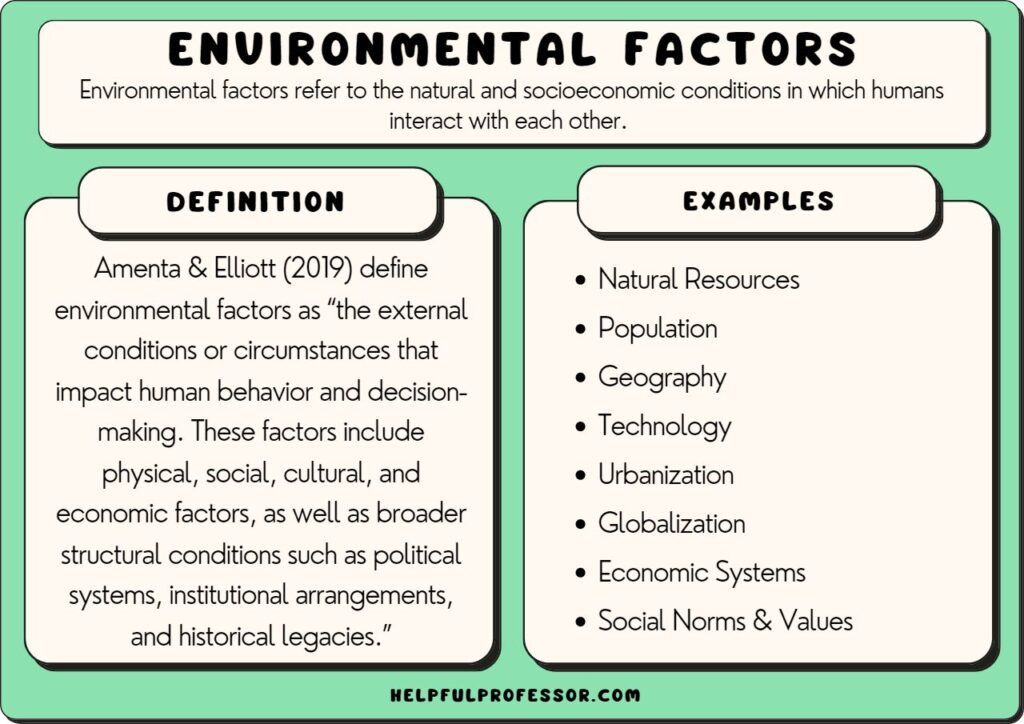
The term "environment," in this context, encompasses far more than just the natural world. It includes every external factor that affects an individual. This broad definition encompasses everything from prenatal conditions and early childhood experiences to socioeconomic status and cultural norms.
Essentially, environmental influences can be categorized into several key areas: physical environment, social environment, and cultural environment. Each of these categories exerts its own unique and powerful influence on human development.
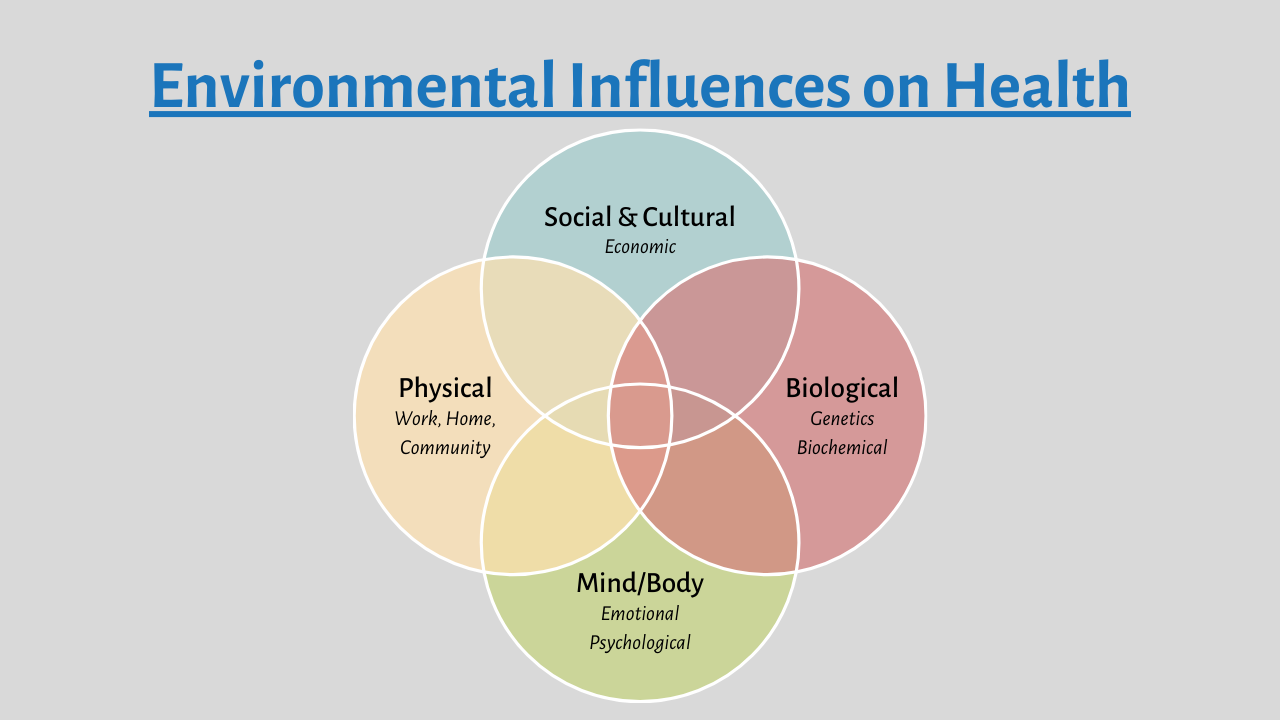
The Physical Environment: Our Immediate Surroundings
The physical environment refers to the tangible surroundings that directly impact our health and well-being. This includes factors like air and water quality, access to nutritious food, and the presence of pollutants or toxins.
Consider the impact of lead exposure on children. Studies by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have shown that even low levels of lead can cause developmental delays, learning disabilities, and behavioral problems. This highlights the profound and lasting effects of a seemingly invisible environmental toxin.
Access to green spaces and recreational areas also falls under this category. Research consistently demonstrates that spending time in nature reduces stress, improves mental health, and promotes physical activity. The absence of such resources, particularly in urban environments, can contribute to a range of health problems.
The Social Environment: Our Interpersonal Connections
Our social environment encompasses the people and institutions that surround us, including family, friends, schools, and communities. These interactions shape our beliefs, values, and behaviors.
The influence of family is arguably the most significant during early childhood. A nurturing and supportive family environment fosters emotional security, self-esteem, and social competence. Conversely, a dysfunctional or abusive family environment can have devastating consequences, leading to trauma, mental health issues, and difficulties in forming healthy relationships later in life.
Schools play a vital role in shaping intellectual and social development. A positive school environment, characterized by supportive teachers, challenging curriculum, and opportunities for extracurricular activities, can help students thrive academically and socially. Bullying, discrimination, and inadequate resources can hinder students' progress and negatively impact their well-being.
The Cultural Environment: Shared Beliefs and Values
The cultural environment represents the shared beliefs, values, customs, and traditions that characterize a particular group or society. These cultural norms influence everything from our eating habits and religious beliefs to our political views and social interactions.
For example, cultural attitudes towards education can significantly impact academic achievement. In some cultures, education is highly valued and students are encouraged to excel. In others, education may be less emphasized, leading to lower levels of academic attainment.
Similarly, cultural norms surrounding gender roles can shape individuals' opportunities and aspirations. In societies with rigid gender roles, women may face limited opportunities in education, employment, and leadership positions. These limitations can have a profound impact on their lives and potential.
Socioeconomic Status: A Powerful Environmental Force
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a composite measure that encompasses income, education, and occupation. It is a powerful environmental factor that influences access to resources and opportunities.
Children from low-SES backgrounds often face numerous disadvantages, including inadequate housing, poor nutrition, and limited access to healthcare and education. These challenges can negatively impact their physical and cognitive development, perpetuating a cycle of poverty.
Studies have shown a strong correlation between SES and academic achievement. Children from high-SES backgrounds tend to perform better in school, attend better colleges, and earn higher incomes than their low-SES counterparts. This disparity highlights the importance of addressing socioeconomic inequalities to ensure that all children have the opportunity to reach their full potential.
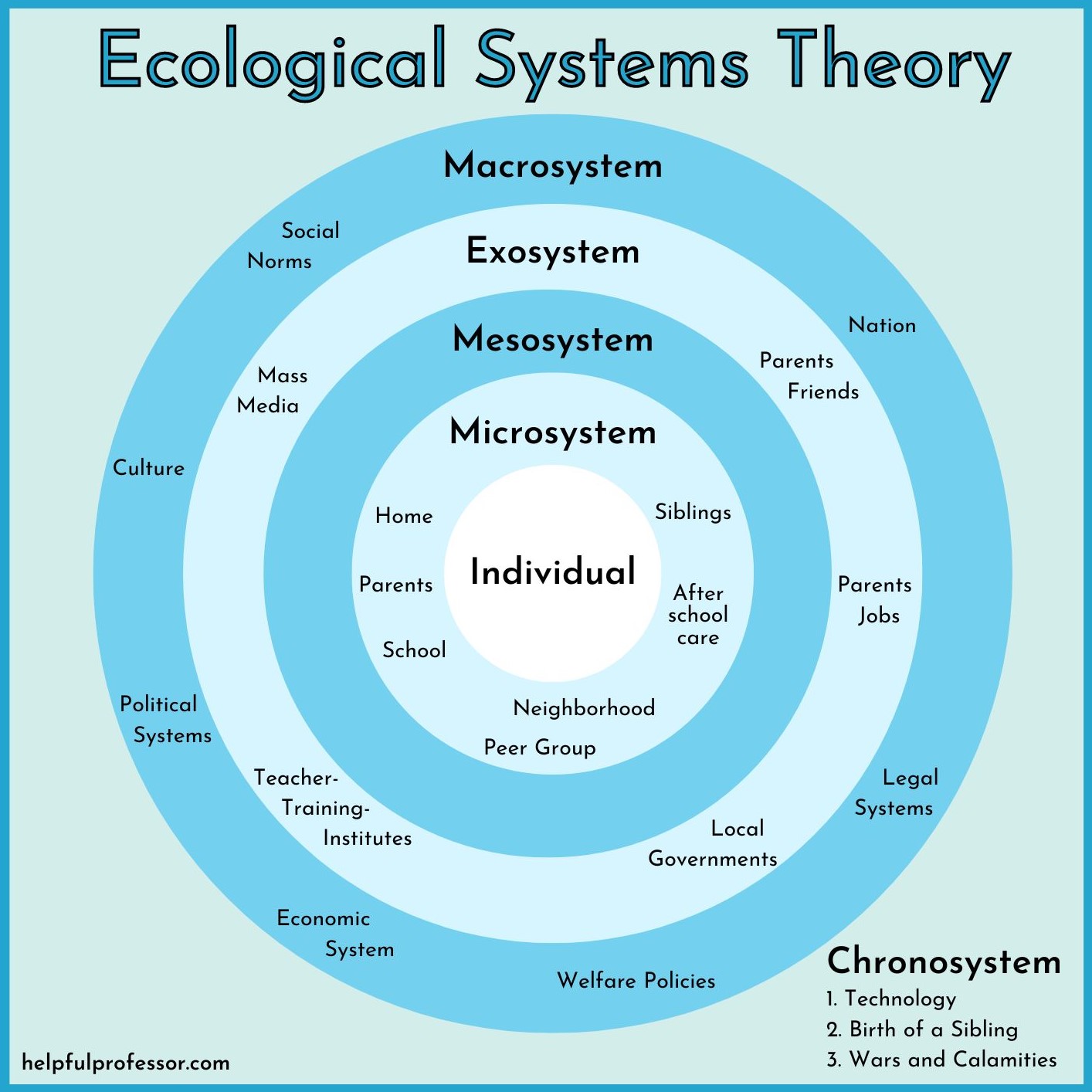
The Interplay of Nature and Nurture
While this article focuses on environmental influences, it's important to acknowledge the complex interplay between nature (genetics) and nurture (environment). These two forces are not mutually exclusive; they interact and influence each other in intricate ways.
Genes provide the blueprint for our development, but the environment determines how those genes are expressed. For example, a person may have a genetic predisposition to obesity, but whether or not they actually become obese depends on their diet and lifestyle.
The field of epigenetics explores how environmental factors can alter gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence. These epigenetic changes can be passed down to future generations, highlighting the long-term impact of environmental exposures.
Looking Ahead: Creating Healthier Environments
Understanding the profound impact of environmental influences is crucial for creating healthier and more equitable societies. By addressing environmental risks and promoting supportive environments, we can improve the health, well-being, and potential of individuals and communities.
This requires a multi-faceted approach, including policies that protect the environment, reduce poverty, and promote access to education, healthcare, and other essential resources. It also requires a shift in cultural attitudes towards valuing diversity, promoting inclusion, and fostering social justice.
Ultimately, creating a better world for future generations depends on our willingness to recognize and address the environmental factors that shape our lives. It's about cultivating the right conditions, just like the gardener tending to the soil, to allow every seed to flourish and reach its full potential. It's about acknowledging that we are all interconnected, and that the health and well-being of each individual is inextricably linked to the health and well-being of the environment around us. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for addressing many of these challenges on a global scale.