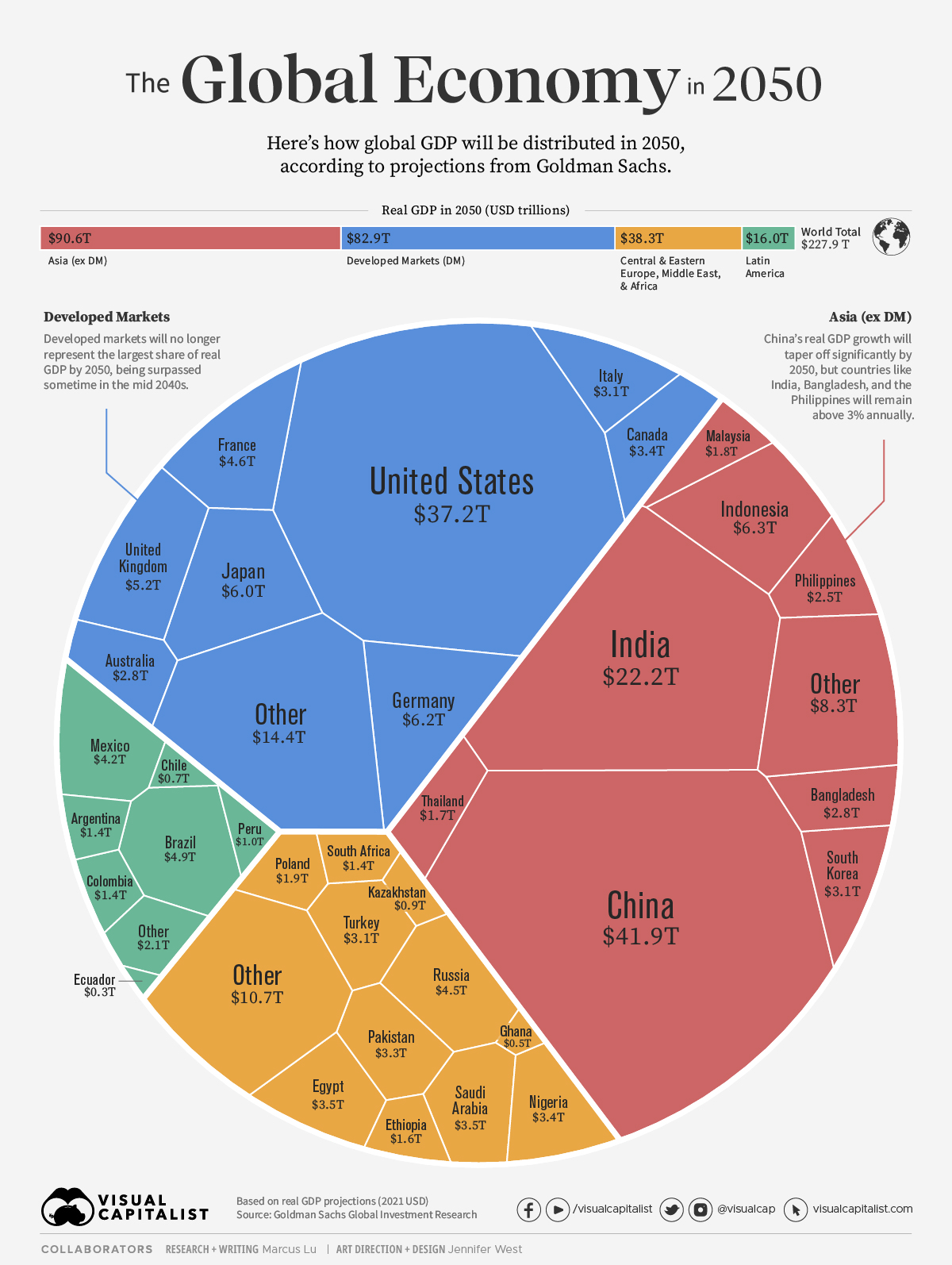
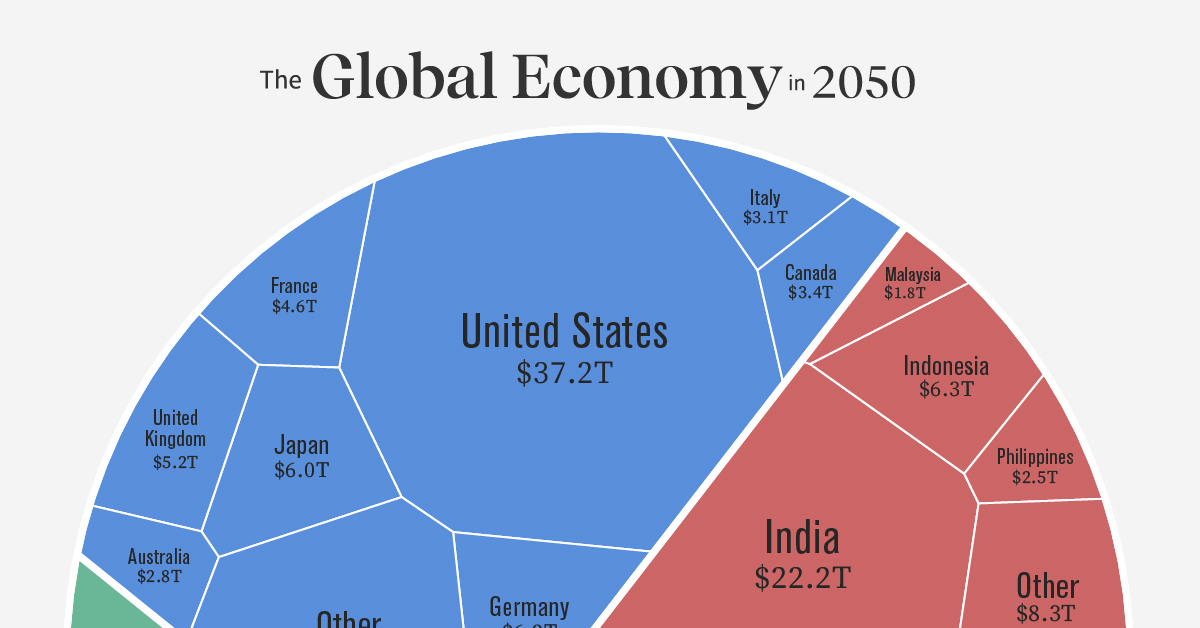
How Do Global Factors Influence The Economy In Your Country

The Australian economy, while often perceived as insulated, is deeply intertwined with global currents. From commodity prices to international interest rates, forces beyond our borders significantly shape the nation's economic landscape.
Understanding these global influences is crucial for Australian businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike, as they directly impact inflation, employment, and overall economic stability. This article delves into the key global factors affecting Australia’s economic performance.
Commodity Price Fluctuations: The Resource Curse and Blessing
Australia's economy is heavily reliant on its natural resources. As a major exporter of iron ore, coal, and gas, the nation's economic fortunes are closely linked to global commodity prices.
Increased demand from countries like China and India often leads to higher commodity prices, boosting Australia's export revenue and driving economic growth. Conversely, a slowdown in global demand or increased supply from other producers can depress prices, impacting the mining sector and the broader economy.
For example, a recent surge in demand for lithium, driven by the electric vehicle revolution, has significantly benefited Australian miners and the national economy. However, the volatility inherent in commodity markets poses a risk, highlighting the need for diversification.
Global Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) closely monitors global interest rates and monetary policy decisions of other major central banks, such as the US Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank.
When global interest rates rise, the RBA may feel pressure to increase Australia's interest rates to maintain the attractiveness of Australian assets to foreign investors. This can lead to higher borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing down economic growth.
Conversely, if global interest rates are low, the RBA may be more inclined to keep Australian interest rates low to stimulate domestic demand. The effectiveness of these strategies is often debated, considering Australia's unique economic characteristics.
International Trade Agreements and Geopolitical Risks
Australia's economic prosperity is dependent on international trade. Trade agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and the Australia-China Free Trade Agreement (ChAFTA), open up new markets for Australian goods and services, boosting exports and creating jobs.
However, geopolitical tensions and trade wars can disrupt global supply chains and negatively impact Australia's trade relationships. For instance, trade disputes between the United States and China have, at times, indirectly affected Australian exporters.
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has also led to increased energy prices and supply chain disruptions, impacting the Australian economy. Australia's geographical position and strong relationships with key trading partners help to mitigate some of these risks.
Exchange Rate Fluctuations
The value of the Australian dollar (AUD) is influenced by a range of global factors, including commodity prices, interest rate differentials, and investor sentiment.
A weaker AUD makes Australian exports more competitive in global markets, benefiting exporters and supporting economic growth. However, it also makes imports more expensive, potentially leading to higher inflation.
Conversely, a stronger AUD makes imports cheaper but can hurt exporters. The exchange rate acts as a shock absorber, cushioning the Australian economy from some of the impacts of global economic fluctuations.
Global Economic Growth and Recession Risks
The overall health of the global economy has a significant impact on Australia. A period of strong global economic growth typically translates into increased demand for Australian exports, boosting economic activity.
However, a global recession can have severe consequences for Australia, leading to a decline in exports, reduced investment, and job losses. Forecasting these global economic trends and preparing for potential downturns is crucial for Australian policymakers.
Recent concerns about a potential global recession, driven by rising inflation and interest rates, have prompted the RBA to adopt a more cautious approach to monetary policy.
In conclusion, the Australian economy is inextricably linked to the global economy. Commodity prices, interest rates, trade agreements, exchange rates, and overall global economic growth all play a crucial role in shaping Australia’s economic performance. Understanding these global influences is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern economy and ensuring sustainable economic growth.


-1690799066.png)