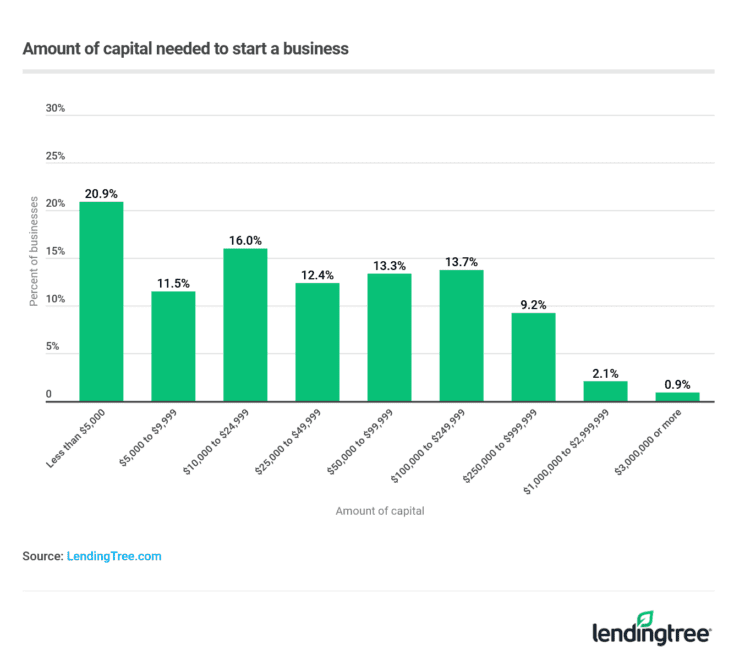
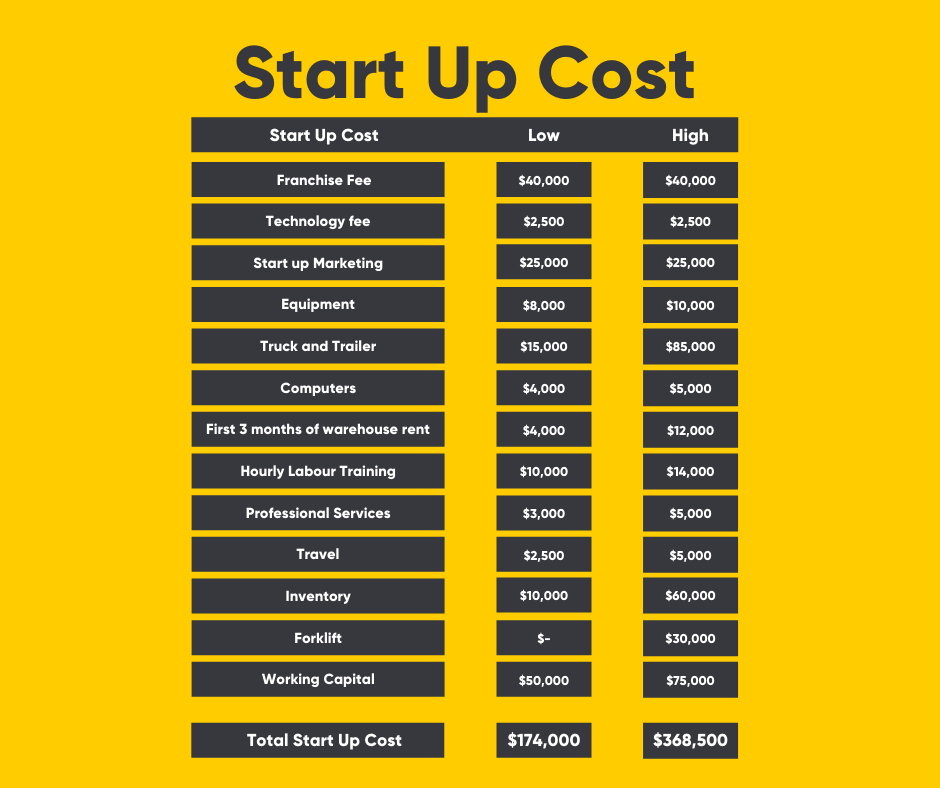
How Much Does It Cost To Buy An Existing Business

The dream of business ownership often conjures images of groundbreaking startups, but acquiring an existing, established business presents a viable and often more secure path to entrepreneurship. However, the financial realities of purchasing an existing company can be daunting, shrouded in complex valuation methods and varying market conditions. Understanding the true cost requires navigating a landscape of financial data, industry benchmarks, and negotiation strategies.
Nut Graf: This article will delve into the multifaceted question of how much it truly costs to buy an existing business. We will explore common valuation methods, analyze key factors that influence pricing, and offer insights from industry experts to provide a comprehensive guide for prospective buyers navigating this significant financial undertaking. Understanding these intricacies is paramount for making informed decisions and securing a successful acquisition.
Valuation Methods: Unveiling the True Worth
Several methodologies exist for determining the value of an existing business. Each approach considers different aspects and offers a unique perspective on the company’s financial standing. Choosing the right method, or a combination thereof, is crucial for arriving at a fair purchase price.
Asset Valuation: Assessing Tangible Resources
The asset valuation method focuses on the tangible assets of the business, such as property, equipment, and inventory. This approach calculates the net asset value (NAV) by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. It provides a baseline valuation, particularly useful for asset-heavy businesses.
However, asset valuation often overlooks intangible assets like brand reputation and customer relationships. Therefore, it's usually combined with other valuation methods.
Earnings Valuation: Projecting Future Profitability
Earnings valuation centers on the business's potential to generate future profits. This commonly involves methods like the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis, which projects future cash flows and discounts them back to their present value. The accuracy of this method depends heavily on the reliability of the projected financial forecasts.
Another approach is the Seller's Discretionary Earnings (SDE) method, often used for small businesses. It calculates the earnings available to a single owner-operator, adding back expenses like owner’s salary and benefits.
Market Valuation: Comparing Similar Transactions
Market valuation leverages data from recent sales of comparable businesses in the same industry and geographic area. This method relies on multiples of revenue, earnings, or other key financial metrics. Obtaining accurate data on comparable transactions can be challenging, making it essential to work with experienced brokers or valuation experts.
BizBuySell, a leading online marketplace for businesses for sale, publishes quarterly reports on business sale transactions, offering valuable insights into market trends and valuation multiples.
Factors Influencing the Purchase Price
Beyond the chosen valuation method, several factors can significantly impact the final purchase price. These include the company's financial performance, industry dynamics, and the overall economic climate.
- Financial Performance: Consistent revenue growth, profitability, and strong cash flow increase the value of a business. Conversely, declining financials can lower the purchase price.
- Industry Dynamics: Businesses in high-growth industries command higher valuations compared to those in mature or declining sectors. The level of competition also plays a significant role.
- Economic Climate: Economic recessions can depress business valuations, while periods of economic expansion tend to inflate prices. Interest rates and access to financing also influence the overall market.
- Intangible Assets: A strong brand, loyal customer base, and proprietary technology can significantly increase a business's value. These intangible assets are often difficult to quantify but are highly prized by buyers.
- Deal Structure: The terms of the deal, including the amount of cash upfront, seller financing, and earn-out provisions, can impact the overall cost. A seller willing to finance a portion of the purchase price may command a higher overall valuation.
Expert Insights and Negotiation Strategies
Navigating the complexities of business valuation and acquisition requires expert guidance. Business brokers, valuation specialists, and legal advisors can provide invaluable assistance throughout the process. "Buyers should always conduct thorough due diligence before making an offer," advises John Smith, a seasoned business broker at ABC Brokers.
Furthermore, negotiation is a critical aspect of the acquisition process. Buyers should be prepared to walk away if the asking price is unreasonable or the terms are unfavorable. Creative deal structuring, such as earn-out provisions tied to future performance, can help bridge the gap between the buyer's and seller's expectations.
"Don't be afraid to negotiate," says Jane Doe, a business acquisition consultant. "A well-structured deal can benefit both parties and ensure a successful transition."
Looking Ahead: Trends and Considerations
The business acquisition market is constantly evolving. Factors such as technological advancements, demographic shifts, and changing consumer preferences can impact valuations and deal structures. As more baby boomers retire, the supply of businesses for sale is expected to increase, potentially creating opportunities for buyers. Staying informed about industry trends and seeking expert advice are essential for navigating this dynamic landscape successfully.
Ultimately, the cost of buying an existing business is a complex calculation influenced by a multitude of factors. By understanding the valuation methods, key drivers of price, and the importance of expert guidance, prospective buyers can make informed decisions and increase their chances of a successful acquisition.