How Much Leucine Is Required To Stimulate Muscle Protein Synthesis

The quest to optimize muscle growth has driven countless hours of research, and at the heart of this pursuit lies a crucial question: How much leucine is truly needed to ignite muscle protein synthesis (MPS)? This seemingly simple inquiry unlocks the potential for athletes, bodybuilders, and even aging individuals to maximize their muscle-building capacity.
The exact amount of leucine required to stimulate MPS remains a complex and debated topic within the scientific community. While studies have pinpointed ranges, individual factors like age, training status, protein source, and overall dietary intake significantly influence optimal leucine requirements. Understanding these nuances is critical for tailoring nutrition strategies that effectively promote muscle growth and repair.
The Central Role of Leucine
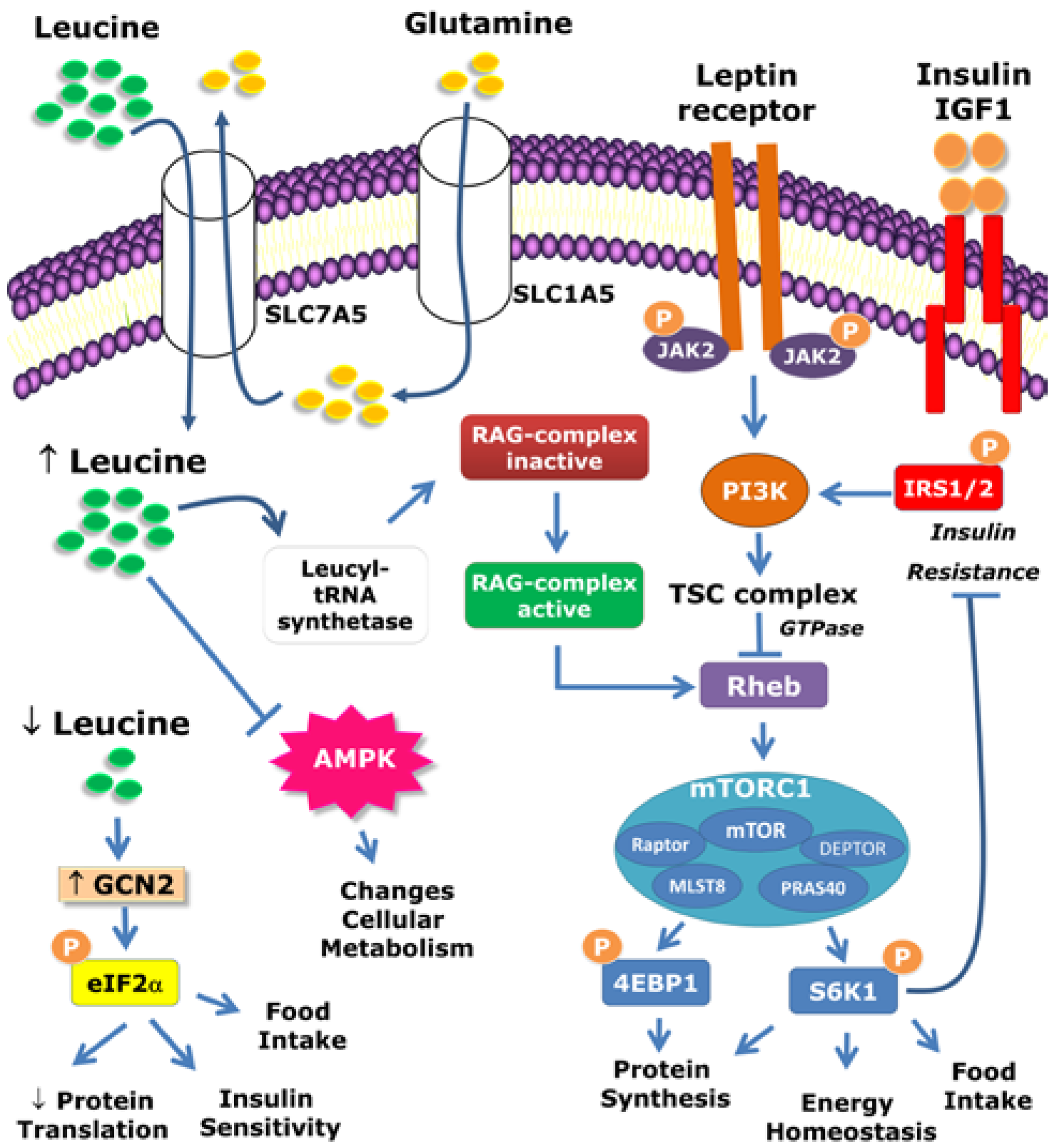
Leucine, an essential branched-chain amino acid (BCAA), acts as a key anabolic trigger within muscle cells. It directly stimulates the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, a critical signaling cascade responsible for initiating MPS. Think of it as the 'on' switch for muscle growth.
When leucine levels reach a certain threshold within the muscle, mTOR is activated, leading to increased protein synthesis. This process involves the assembly of amino acids into new muscle proteins, ultimately contributing to muscle hypertrophy and repair after exercise.
Deciphering the Dosage: Studies and Recommendations
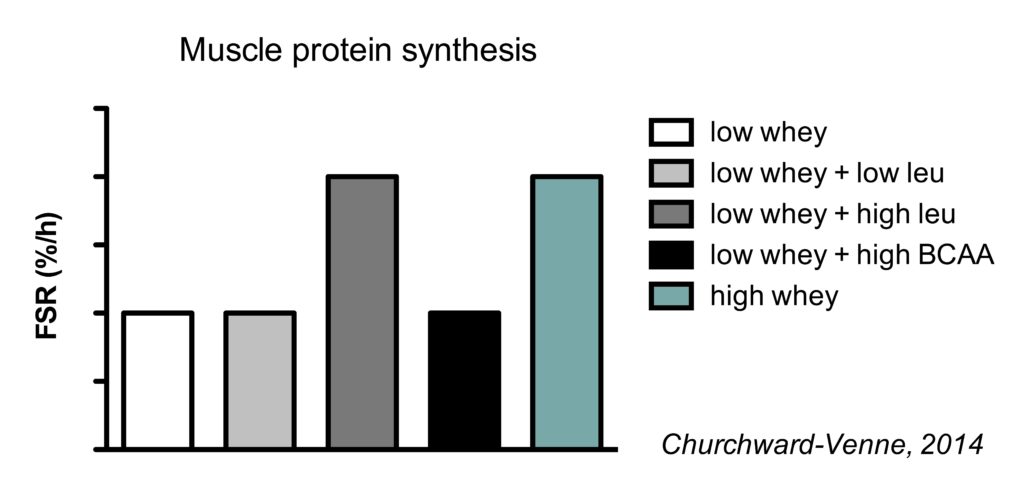
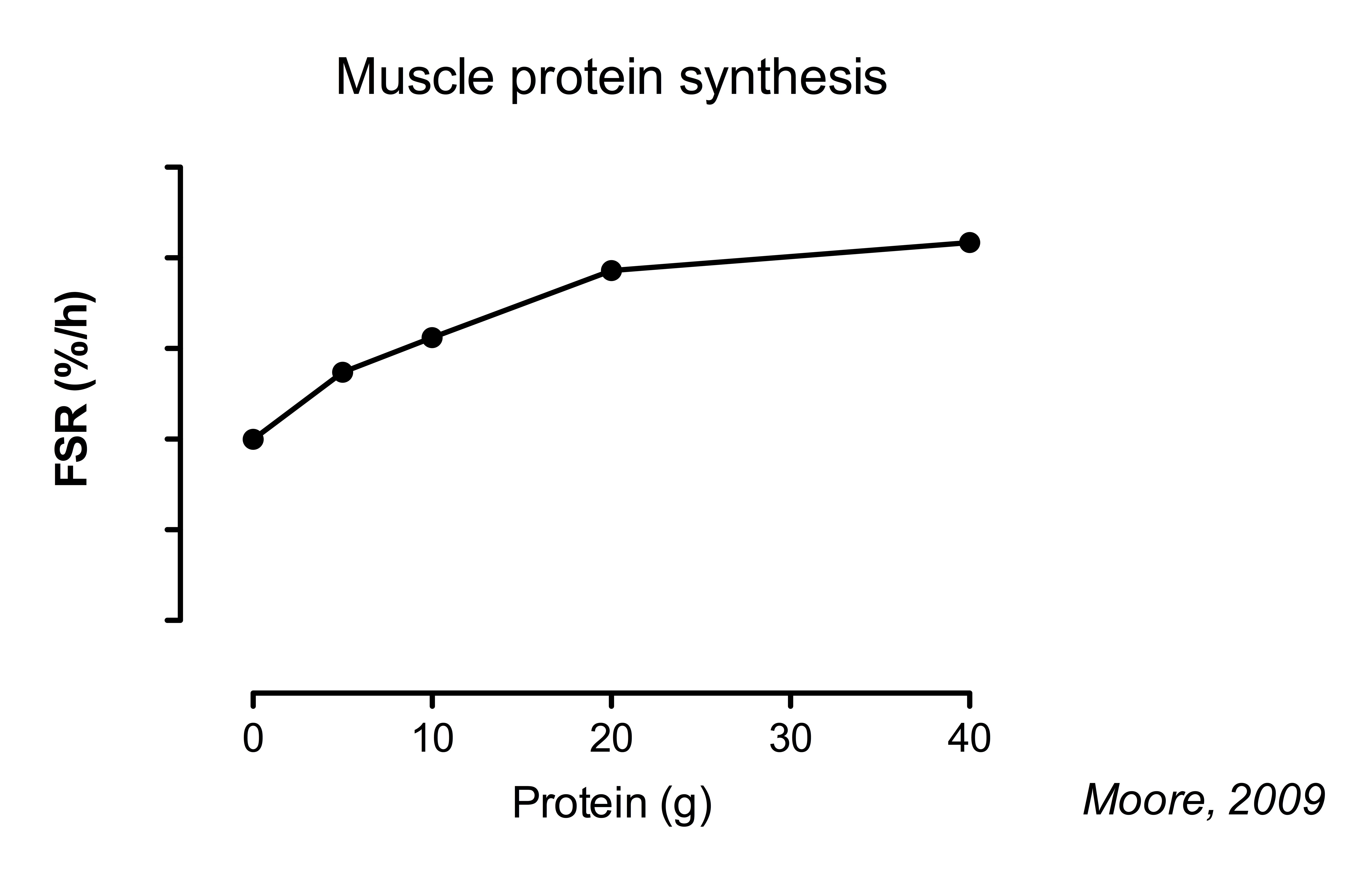
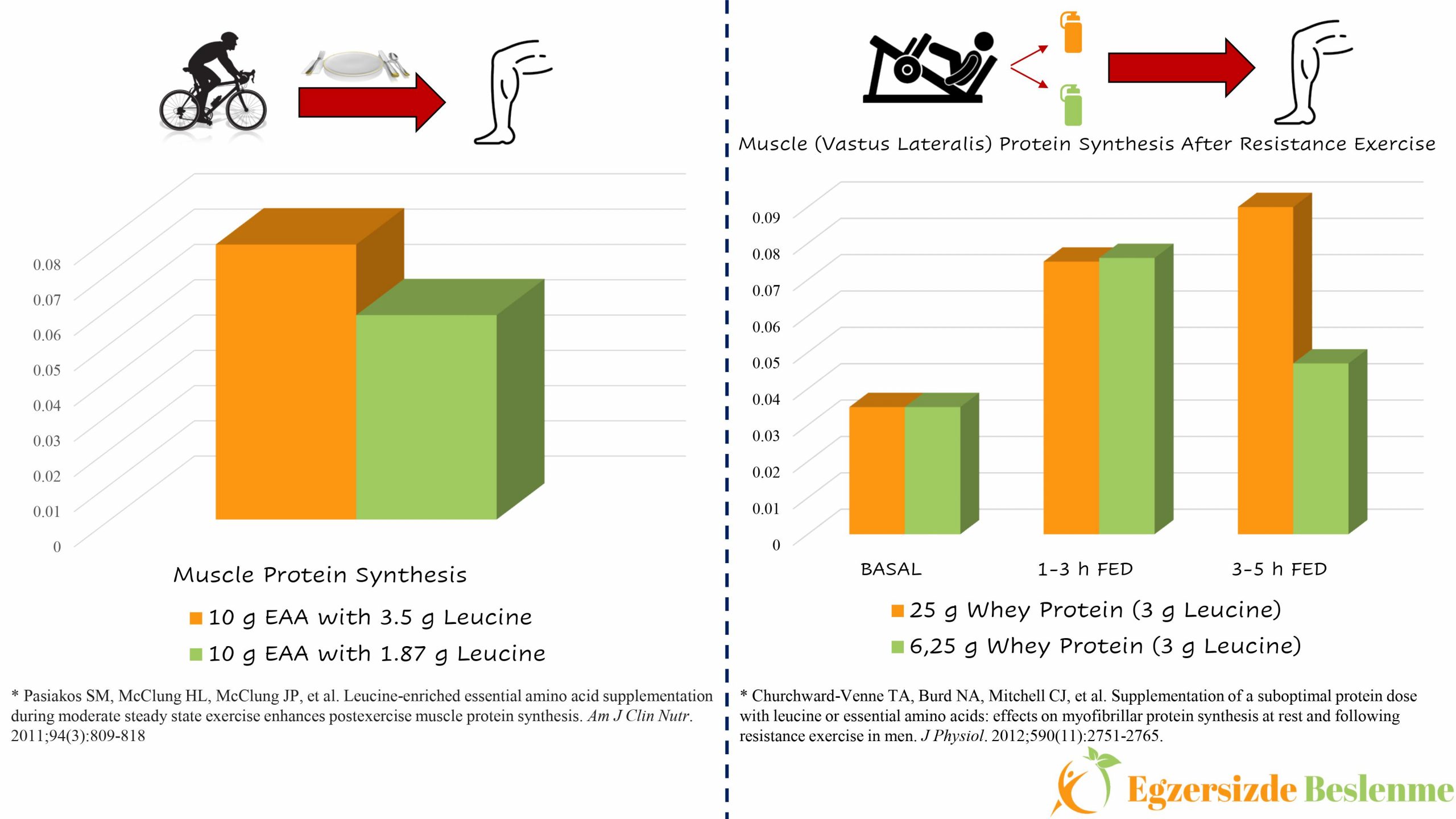
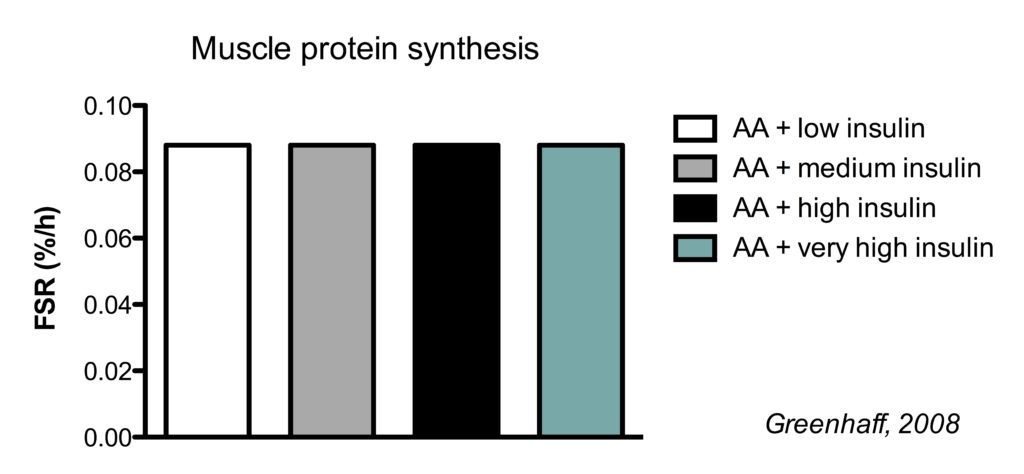
Research indicates that a leucine intake of 2-3 grams per meal is generally sufficient to maximize MPS in young, healthy adults. This translates to approximately 0.05 grams of leucine per kilogram of body weight.
A landmark study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that consuming 2.5 grams of leucine significantly increased MPS compared to a placebo or lower leucine doses. However, it's important to note that this is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Different protein sources contain varying amounts of leucine. Whey protein, known for its rapid absorption and high leucine content, is often favored for post-workout consumption due to its efficient stimulation of MPS. Other sources, such as casein and soy protein, may require larger quantities to achieve a similar effect.
The Influence of Age and Training Status
As we age, our bodies become less sensitive to the anabolic effects of leucine. A phenomenon known as anabolic resistance emerges, requiring older adults to consume higher doses of leucine to achieve comparable MPS rates to younger individuals.
Studies have shown that older adults may need up to 4-5 grams of leucine per meal to overcome anabolic resistance and effectively stimulate muscle growth. This highlights the importance of adjusting protein intake, specifically leucine, to combat age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia).
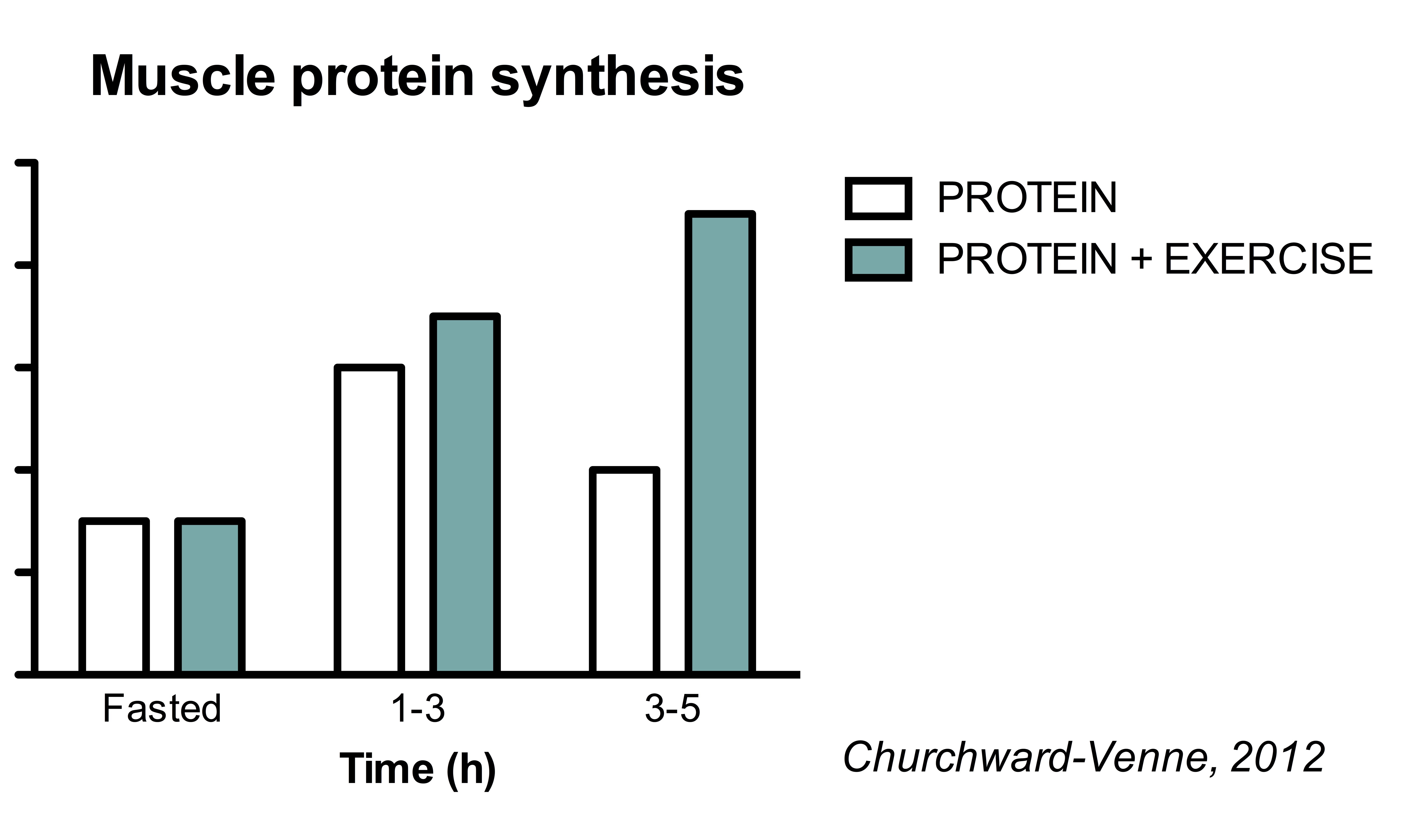
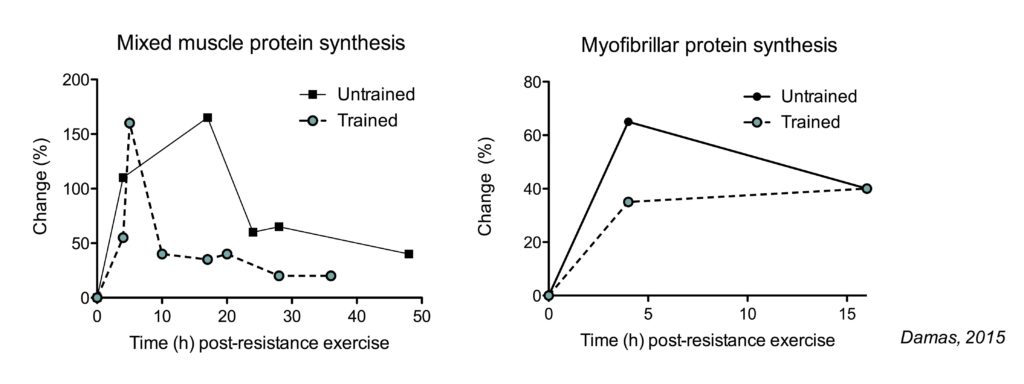
Trained athletes, particularly those engaged in resistance training, also exhibit increased leucine requirements. Their muscles become more efficient at utilizing leucine, leading to greater MPS rates and enhanced recovery. The exact amount depends on the training intensity and volume.
Beyond Leucine: The Importance of a Complete Protein Intake
While leucine plays a pivotal role, it's crucial to remember that MPS requires a complete array of essential amino acids. Focusing solely on leucine supplementation without adequate overall protein intake can limit muscle growth potential.
Consuming a complete protein source that provides all nine essential amino acids ensures that the body has the building blocks necessary for synthesizing new muscle proteins. Leucine acts as the trigger, but the other amino acids are the essential materials for construction.
Practical Applications: Optimizing Leucine Intake Through Diet
To effectively incorporate leucine into your diet, consider including leucine-rich foods such as beef, chicken, fish, eggs, dairy products, and legumes. Supplementing with whey protein after workouts can also provide a convenient and efficient way to boost leucine levels.
For individuals with higher leucine requirements, such as older adults or athletes, strategically timing leucine-rich meals around exercise can further enhance MPS. Distributing protein intake evenly throughout the day can also optimize muscle growth.
It is always best to consult with a registered dietician or sports nutritionist to determine the optimal leucine intake based on individual needs and goals.
The Future of Leucine Research
Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of leucine's role in MPS. Scientists are exploring the effects of different leucine formulations, such as leucine metabolites and leucine peptides, on muscle growth and recovery.
Future studies will likely focus on personalized nutrition strategies that tailor leucine intake to individual genetic profiles and metabolic responses. This could lead to more precise and effective approaches to optimizing muscle growth and combating age-related muscle loss.
Considering Individual Variability
It's essential to acknowledge that individual responses to leucine can vary significantly. Factors such as genetics, gut microbiome composition, and hormonal status can influence leucine absorption and utilization.
Monitoring muscle protein synthesis through techniques like stable isotope tracer methods can help assess individual leucine requirements. This advanced approach allows for a more personalized and data-driven approach to nutrition.
Conclusion: Leucine as a Key, Not the Entire Orchestra
In conclusion, while leucine is a critical trigger for muscle protein synthesis, it's just one piece of the puzzle. A holistic approach that considers overall protein intake, individual factors, and timing is essential for maximizing muscle growth. Ongoing research promises to further refine our understanding of leucine's role, paving the way for more personalized and effective strategies for optimizing muscle health across the lifespan.