Mentoring Is The Cornerstone Of Which Of The Following

In today's rapidly evolving world, the demand for skilled professionals far outstrips the current supply, creating a significant gap across various industries. This skills deficit, coupled with the challenges of navigating complex career paths, necessitates a renewed focus on effective strategies for talent development. One such strategy, consistently lauded for its efficacy, is mentorship.
Mentoring is the cornerstone of professional development, leadership cultivation, succession planning, and organizational culture. It is a potent tool for transferring knowledge, fostering growth, and shaping future leaders.
The Multifaceted Role of Mentorship
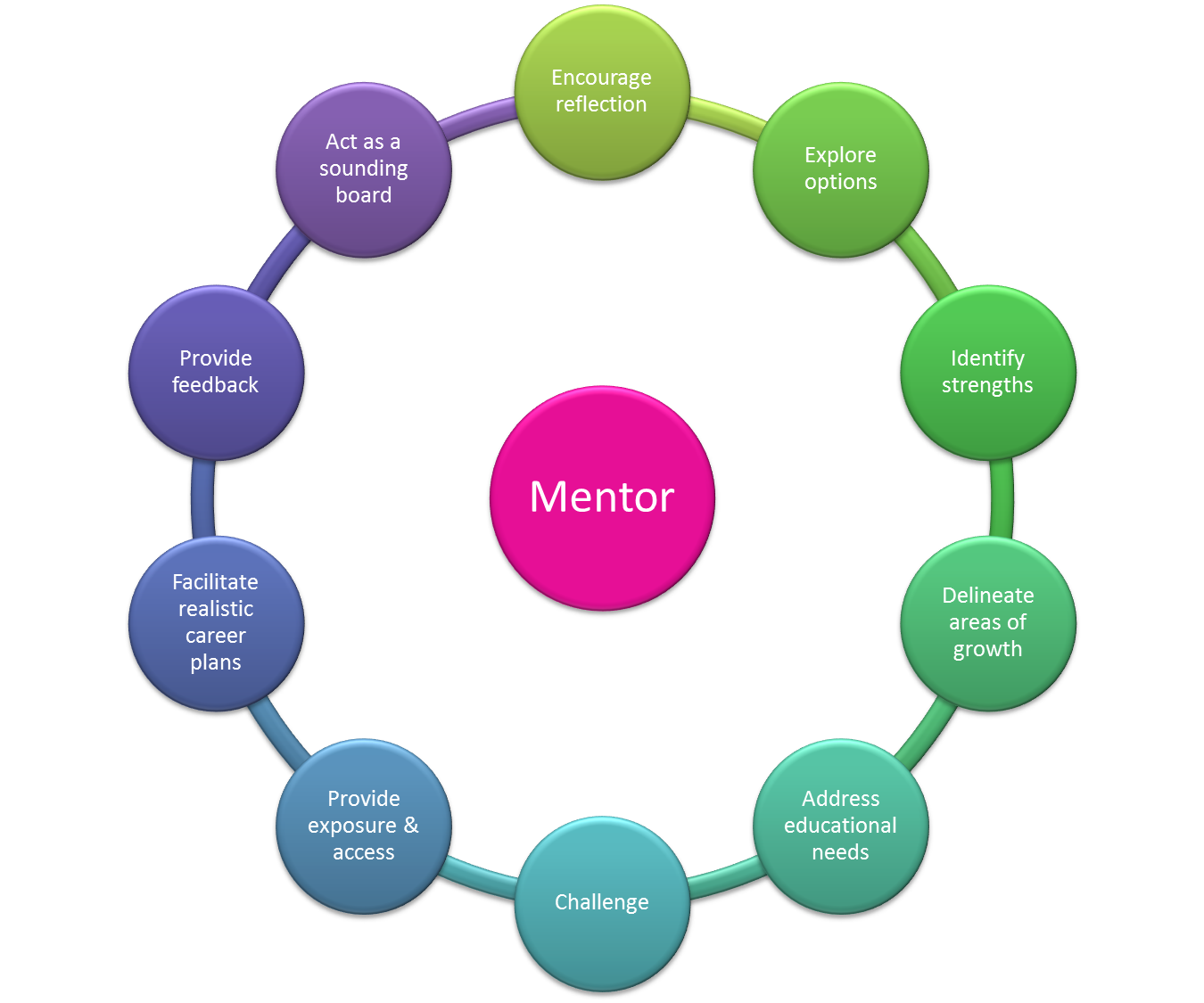
At its core, mentoring is a relationship-based process where an experienced individual (the mentor) provides guidance, support, and advice to a less experienced individual (the mentee). This relationship facilitates the mentee's professional and personal growth.
Professional Development: Shaping Skills and Careers
Mentoring significantly contributes to professional development by providing mentees with targeted skill enhancement opportunities. Mentors share their knowledge and experience.
This allows mentees to acquire new competencies and refine existing ones.
Moreover, mentors can help mentees identify career goals, explore different career paths, and create a roadmap for achieving their aspirations.
"Effective mentoring is not about telling people what to do, but about helping them to discover their own potential and find their own path,"says Dr. Eleanor Vance, a leading expert in leadership development.
Leadership Cultivation: Nurturing Future Leaders
Leadership cultivation is another area where mentoring plays a vital role. Mentees gain exposure to leadership styles and decision-making processes through observing their mentors.
Mentors help them develop essential leadership qualities like communication, empathy, and strategic thinking.
Through constructive feedback and guidance, mentors challenge mentees to step outside their comfort zones and take on leadership responsibilities, thus preparing them for future leadership roles.
Succession Planning: Ensuring Continuity and Stability
Succession planning, a critical aspect of organizational management, also benefits greatly from mentoring programs. By identifying and developing high-potential employees through mentorship, organizations can ensure a smooth transition of leadership and expertise when senior leaders retire or move on.
Mentoring ensures that the next generation of leaders is equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain organizational stability and drive future growth.
Harvard Business Review highlights that organizations with strong succession planning programs are better equipped to adapt to change and maintain a competitive edge.
Organizational Culture: Fostering Engagement and Inclusion
Mentoring can also significantly impact organizational culture. By creating a culture of support, collaboration, and continuous learning, mentoring programs foster greater employee engagement and satisfaction.
Mentoring can break down silos, promote diversity and inclusion, and create a sense of belonging within the organization.
Employees who feel supported and valued are more likely to be productive, innovative, and committed to the organization's success.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, implementing effective mentoring programs can be challenging. Organizations must carefully select mentors who possess the necessary skills, experience, and commitment to guide and support their mentees.
Clear goals and expectations should be established for the mentoring relationship, and regular check-ins should be conducted to ensure that the program is meeting its objectives.
Furthermore, organizations must address potential barriers to participation, such as time constraints, lack of resources, and cultural differences.
The Future of Mentoring
As technology continues to reshape the workplace, mentoring programs are also evolving. Virtual mentoring platforms, online resources, and mobile apps are becoming increasingly popular, providing greater flexibility and accessibility to mentoring opportunities.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also being used to match mentors and mentees based on their skills, interests, and goals, leading to more effective and personalized mentoring experiences.
The future of mentoring will likely involve a combination of traditional and technology-enabled approaches, creating a more dynamic and inclusive mentoring ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mentoring stands as a vital cornerstone of professional development, leadership cultivation, succession planning, and organizational culture. By investing in effective mentoring programs, organizations can empower their employees, cultivate future leaders, and create a more engaged, inclusive, and successful workforce.
The return on investment (ROI) in mentorship is substantial, leading to improved employee retention, increased productivity, and enhanced organizational performance.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, the importance of mentoring will only continue to grow.







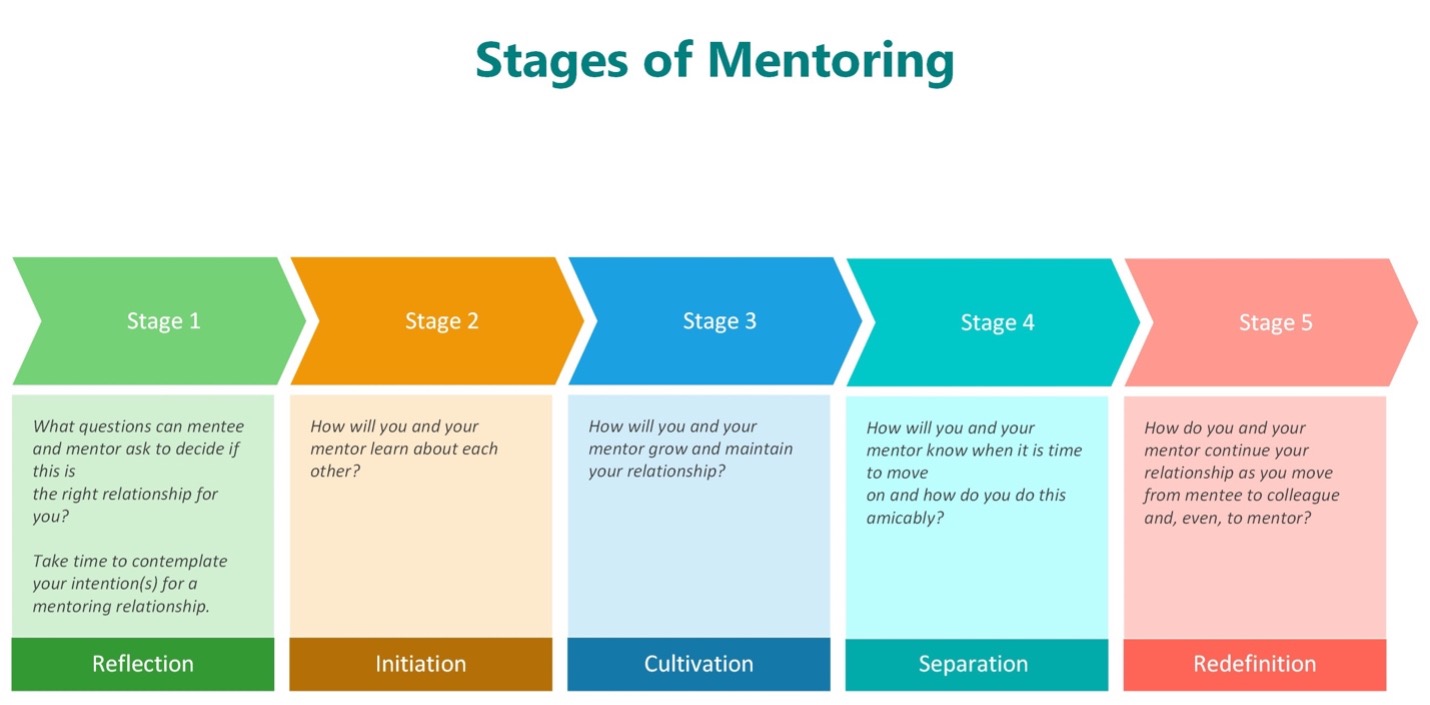

:+Benefits+of+Workplace+Mentoring.jpg)