Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Vs Nicotinamide Riboside

The quest for longevity and improved health has fueled intense research into compounds that can boost cellular function. Two prominent contenders in this arena are Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) and its precursors, particularly Nicotinamide Riboside (NR). But which one reigns supreme, and what are the key differences consumers should be aware of?
This article will delve into the ongoing scientific debate surrounding NAD+ and NR, exploring their mechanisms, potential benefits, and the current state of evidence.
Understanding NAD+ and Its Importance
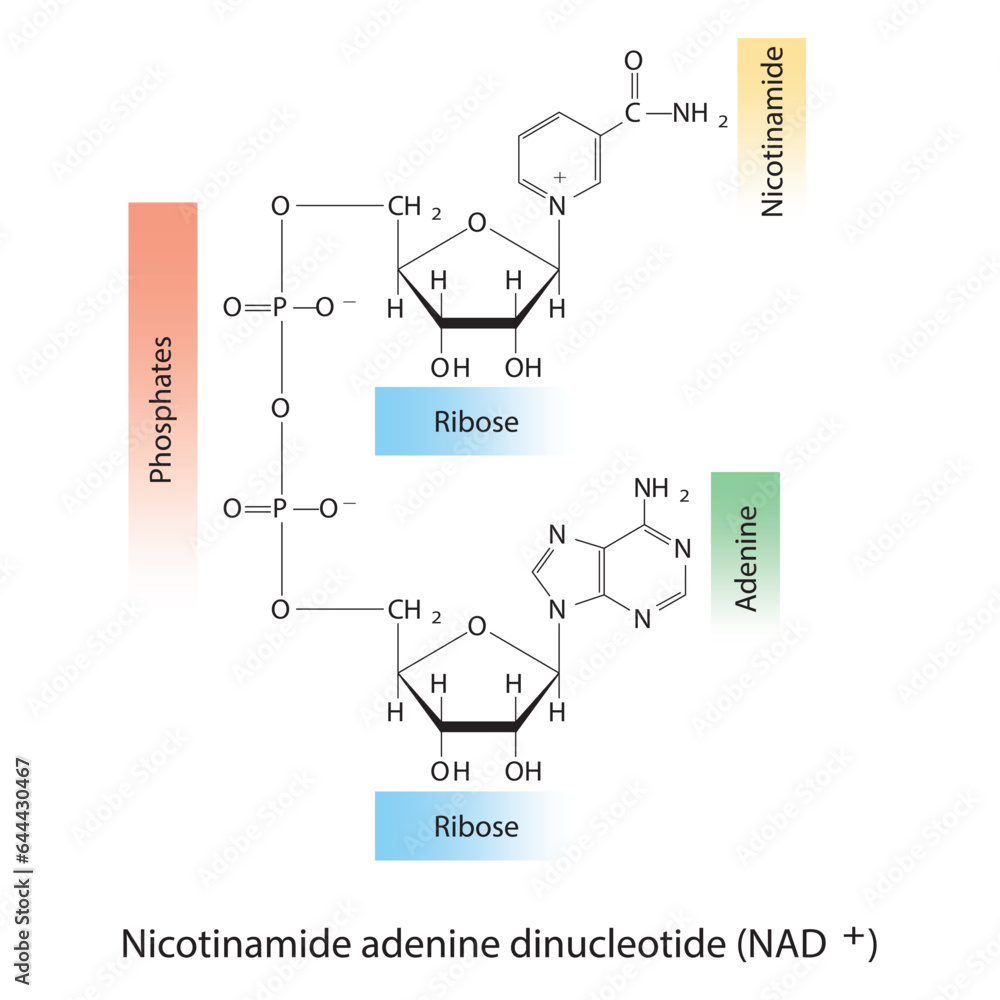
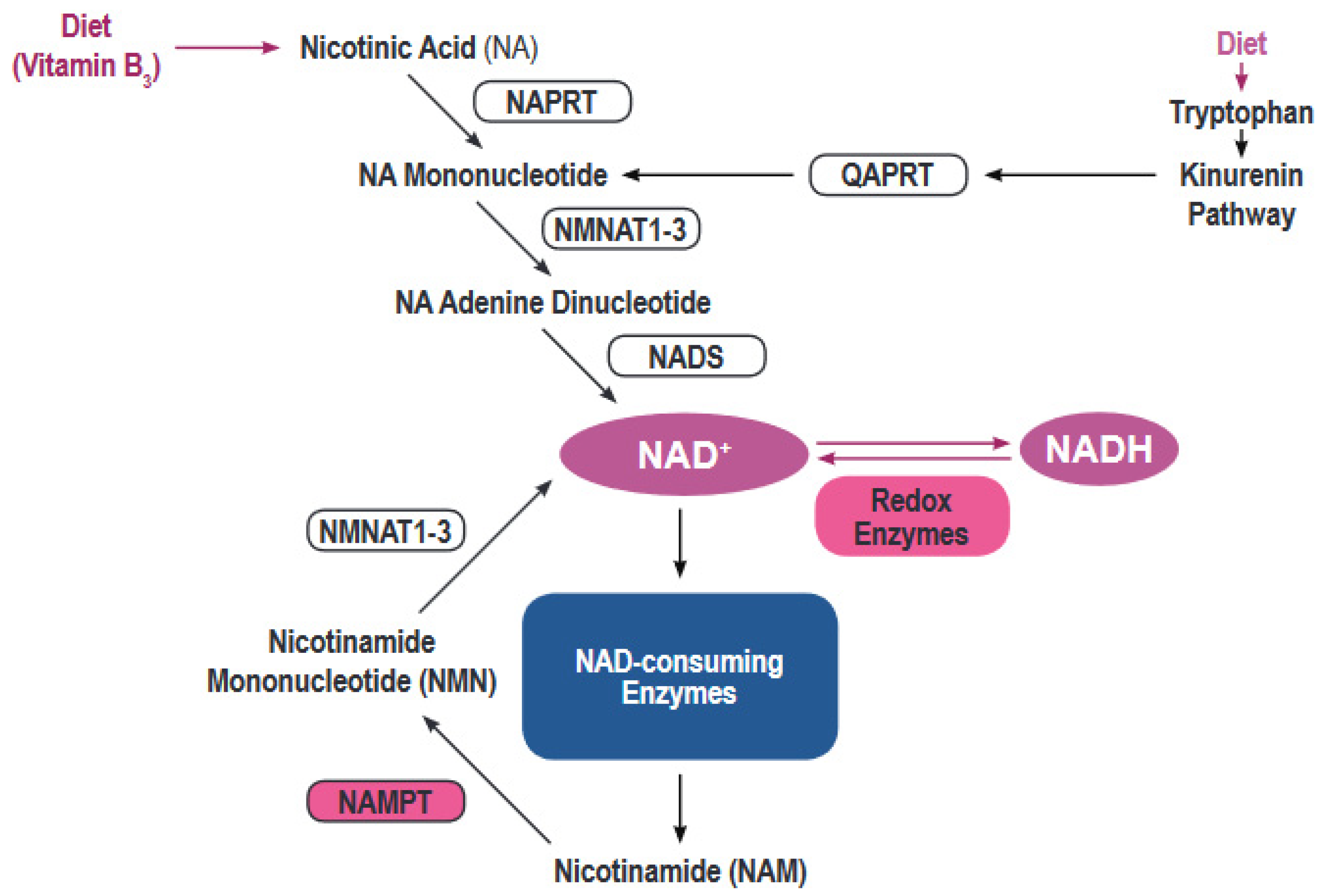
NAD+ is a crucial coenzyme found in every living cell. It plays a vital role in hundreds of metabolic processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and cell signaling. Reduced levels of NAD+ are associated with aging and various age-related diseases, such as neurodegeneration, heart disease, and diabetes, according to studies published in journals like Nature and Science.
Researchers believe boosting NAD+ levels could potentially mitigate these effects and promote healthy aging.
The Role of Nicotinamide Riboside
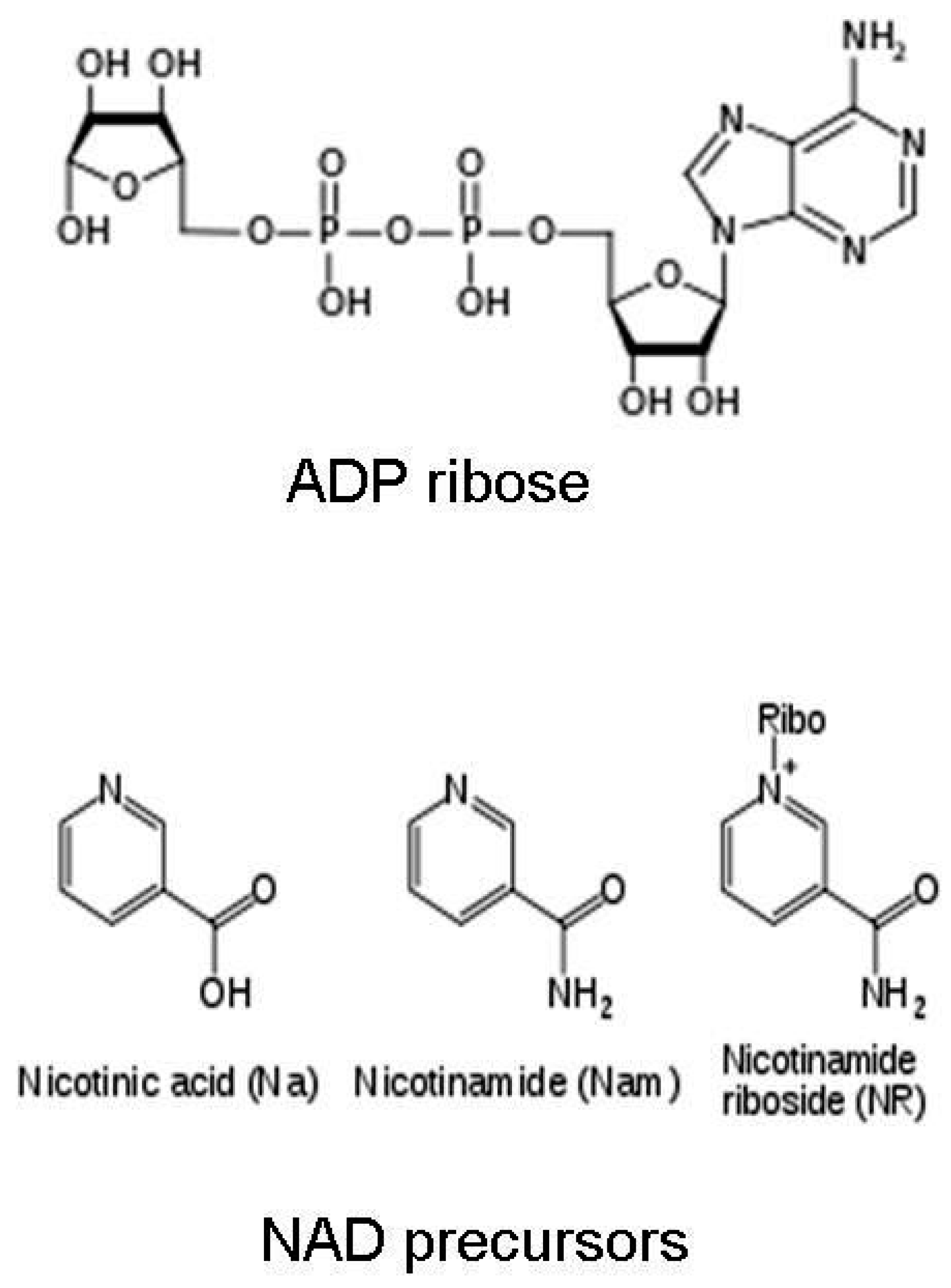
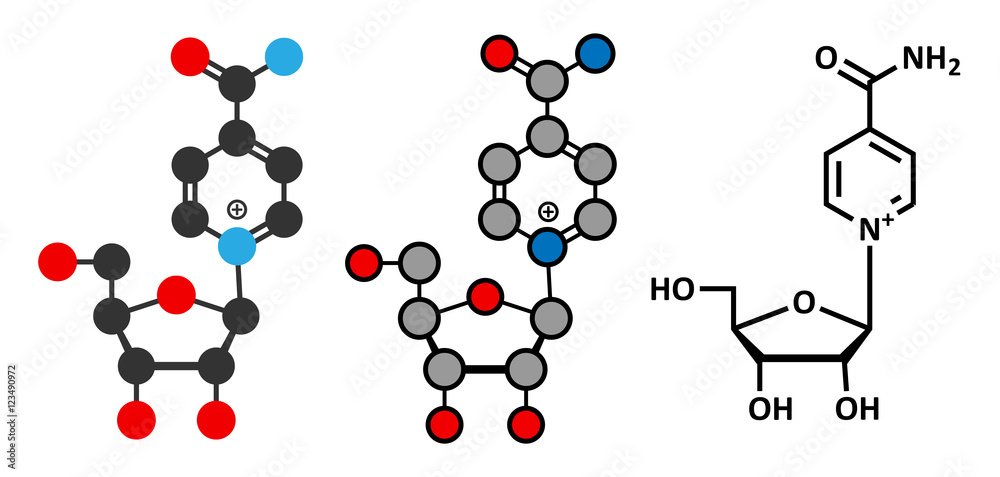
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) is a form of vitamin B3 and a precursor to NAD+. It is one of several molecules that the body can use to create NAD+. Other precursors include nicotinamide (NAM) and nicotinic acid (NA).
NR has gained popularity as a dietary supplement because it can efficiently raise NAD+ levels in the body. Supplements containing NR are widely available, marketed for their potential anti-aging and health-enhancing properties.
The Debate: Direct NAD+ Supplementation vs. NR
A central question in the field is whether direct NAD+ supplementation is superior to taking precursors like NR.
Direct NAD+ supplementation faces challenges. NAD+ is a large molecule and may not be easily absorbed when taken orally. Furthermore, some research suggests that oral NAD+ is broken down in the digestive system before it can be absorbed into the bloodstream, as highlighted in a review published in the Journal of Nutritional Science.
NR, on the other hand, is believed to be more easily absorbed and converted into NAD+ within cells. This has made it a more appealing option for many consumers.
Scientific Evidence and Clinical Trials
Numerous studies have investigated the effects of NR supplementation on NAD+ levels and various health outcomes.
Clinical trials have shown that NR supplementation can effectively increase NAD+ levels in humans. Studies published in journals such as PLOS One and Cell Metabolism have demonstrated this increase, but the long-term health benefits of sustained NAD+ elevation are still under investigation.
Some research suggests that NR may improve metabolic health, enhance muscle function, and protect against neurodegenerative diseases. However, many of these studies are preliminary, and more extensive, long-term clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings and establish optimal dosages.
Potential Benefits and Risks
The potential benefits of boosting NAD+ levels, whether through NR or other means, are considerable.
These include improved energy production, enhanced DNA repair, and protection against age-related diseases. Proponents suggest that maintaining high NAD+ levels could lead to a longer and healthier lifespan.
However, potential risks and side effects of NR supplementation need to be considered. While NR is generally considered safe, some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as nausea, fatigue, or headaches. There are also concerns about the long-term effects of sustained NAD+ elevation, as well as possible interactions with other medications.
Regulation and Consumer Considerations
The supplement industry is not as strictly regulated as the pharmaceutical industry. This means that the quality and purity of NR supplements can vary significantly.
Consumers should choose reputable brands that conduct third-party testing to ensure the purity and potency of their products. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting NR supplementation is also advisable, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications.
The Future of NAD+ Research
Research on NAD+ and its precursors, including NR, is a rapidly evolving field. Scientists are continuing to explore the mechanisms by which NAD+ influences health and aging, as well as the optimal strategies for boosting NAD+ levels.
Future research will likely focus on long-term clinical trials to assess the efficacy and safety of NR supplementation for various health outcomes. Researchers are also exploring other potential NAD+-boosting strategies, such as dietary interventions and exercise.
Conclusion
NAD+ is a vital coenzyme with a crucial role in cellular health and aging. While direct NAD+ supplementation faces challenges, Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) has emerged as a promising NAD+ precursor. Research indicates that NR can effectively raise NAD+ levels in humans, but the long-term health benefits and potential risks of sustained NAD+ elevation require further investigation.
As the science evolves, consumers should stay informed, choose reputable products, and consult with healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about NAD+ supplementation.