Office Of The Superintendent Of Financial Institutions Osfi

The stability of Canada's financial system, often a quiet backdrop to everyday economic activity, is facing intensified scrutiny. Mounting global uncertainties, rising interest rates, and the looming threat of a recession are casting long shadows, putting increased pressure on the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI), the nation’s financial regulator.
OSFI's role as the guardian of financial stability is now more critical than ever. The regulator is tasked with navigating a complex landscape of potential risks, safeguarding the interests of depositors, policyholders, and creditors while ensuring the continued solvency of federally regulated financial institutions.
This article delves into OSFI's evolving mandate, its strategies for mitigating emerging risks, and the challenges it faces in a rapidly changing global financial environment.
OSFI's Mandate and Core Functions
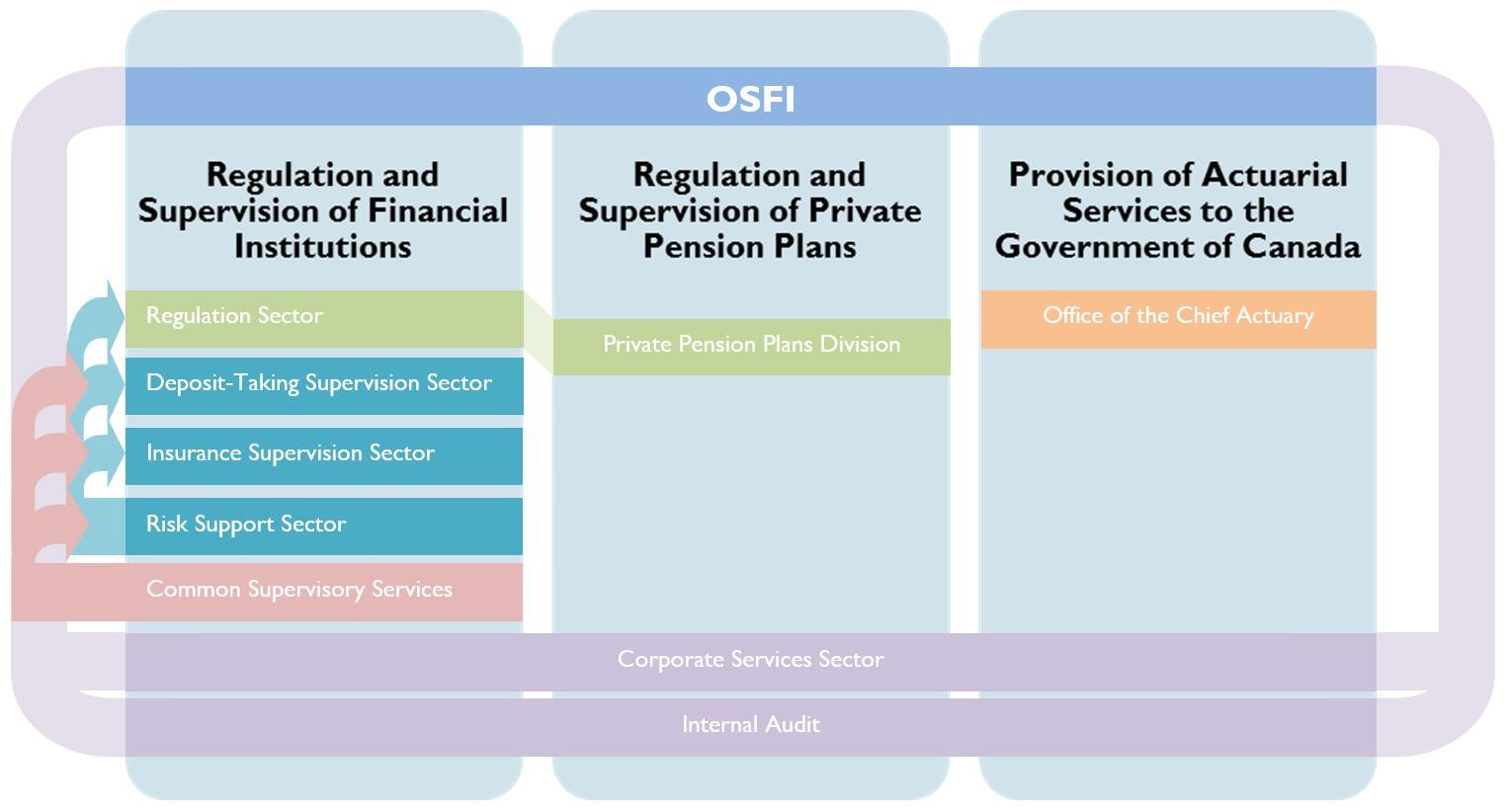
The Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI), established in 1987, operates as an independent agency of the Government of Canada. Its primary mandate is to protect depositors, policyholders, financial institution creditors and pension plan members, while contributing to public confidence in the Canadian financial system.
OSFI achieves this through a combination of supervision, regulation, and early intervention. Supervision involves monitoring the financial condition and risk management practices of federally regulated financial institutions (FRFIs) and private pension plans.
Regulation entails developing and implementing prudential standards and guidelines. Early intervention allows OSFI to take corrective action when an institution is experiencing financial difficulties, preventing further deterioration and minimizing losses.
Navigating a Landscape of Emerging Risks
The global financial landscape is constantly evolving, presenting new and complex challenges for regulators like OSFI. Recent years have seen a surge in risks stemming from macroeconomic factors, technological disruptions, and geopolitical instability.
Rising interest rates, while aimed at curbing inflation, pose a significant threat to borrowers and can lead to increased mortgage defaults. OSFI has responded by tightening mortgage underwriting standards and stress-testing FRFIs' resilience to potential economic downturns.
"OSFI is actively monitoring the impact of higher interest rates on borrowers and financial institutions," says Peter Routledge, Superintendent of Financial Institutions, in a recent statement. "We are prepared to take further action if necessary to safeguard the stability of the financial system."
The Digital Frontier: Cybersecurity and Fintech
The rapid adoption of digital technologies in the financial sector presents both opportunities and risks. While Fintech innovations can improve efficiency and accessibility, they also create new avenues for cyberattacks and data breaches.
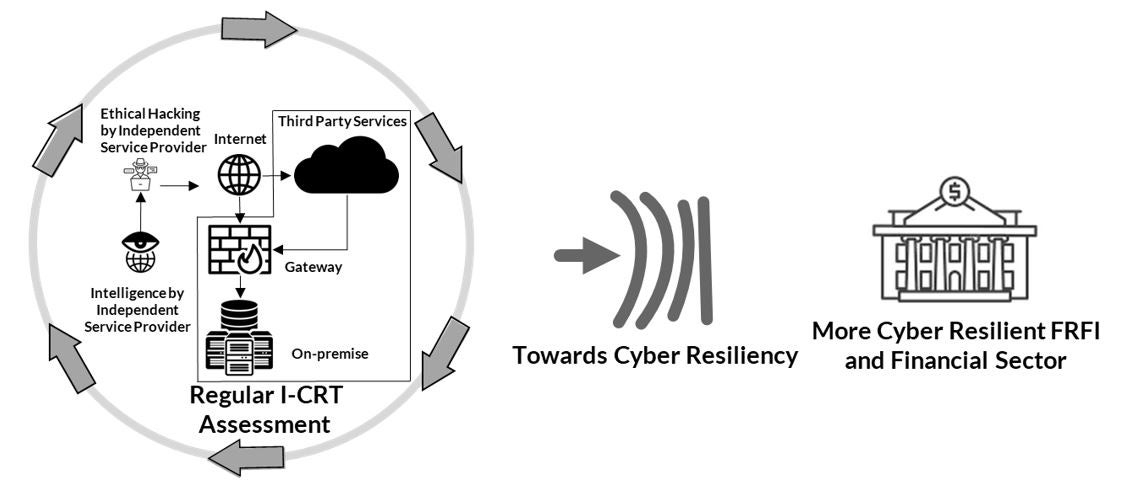
OSFI is working to enhance its cybersecurity oversight and ensure that FRFIs have robust defenses against cyber threats. It has issued guidance on cybersecurity risk management and is collaborating with international organizations to share best practices.
Furthermore, OSFI is actively engaging with the Fintech industry to understand the potential implications of new technologies and develop appropriate regulatory frameworks.
Climate Change: A Systemic Risk
Climate change is increasingly recognized as a systemic risk to the financial system. Extreme weather events can disrupt economic activity and damage assets, while the transition to a low-carbon economy can impact the value of investments.
OSFI is developing a climate risk management framework for FRFIs, requiring them to assess and manage their exposure to climate-related risks. This includes assessing the impact of climate change on their lending portfolios and investment strategies.
OSFI is also working with international regulators to develop consistent standards for climate risk disclosure.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its efforts, OSFI faces several challenges in fulfilling its mandate. Maintaining its independence from political influence is crucial to ensuring its credibility and effectiveness.
Keeping pace with the rapid pace of technological change requires continuous learning and adaptation. Attracting and retaining skilled staff with expertise in areas such as cybersecurity and climate risk is also essential.
Looking ahead, OSFI is likely to continue to focus on strengthening its supervisory framework, enhancing its risk management capabilities, and collaborating with international regulators. The Canadian financial system is fundamentally sound, but constant vigilance and proactive regulation are essential to maintaining its stability in an increasingly uncertain world.



+–.jpg)