Oral Bpc-157 With Or Without Food

Urgent reports are emerging about the optimal usage of BPC-157, specifically regarding oral administration in relation to food intake. New data suggests differing absorption rates and effects based on whether the peptide is taken on an empty stomach or with meals.
This article delves into the latest findings on oral BPC-157, analyzing how food consumption impacts its bioavailability and purported healing properties. We examine the current understanding of its effects, dosing recommendations, and what this means for individuals considering or currently using this peptide.
What is BPC-157 and Why the Debate?
BPC-157, or Body Protection Compound-157, is a synthetic peptide sequence of 15 amino acids derived from human gastric juice. It's being investigated for its potential healing properties in various tissues, including the gut, muscles, and nervous system.
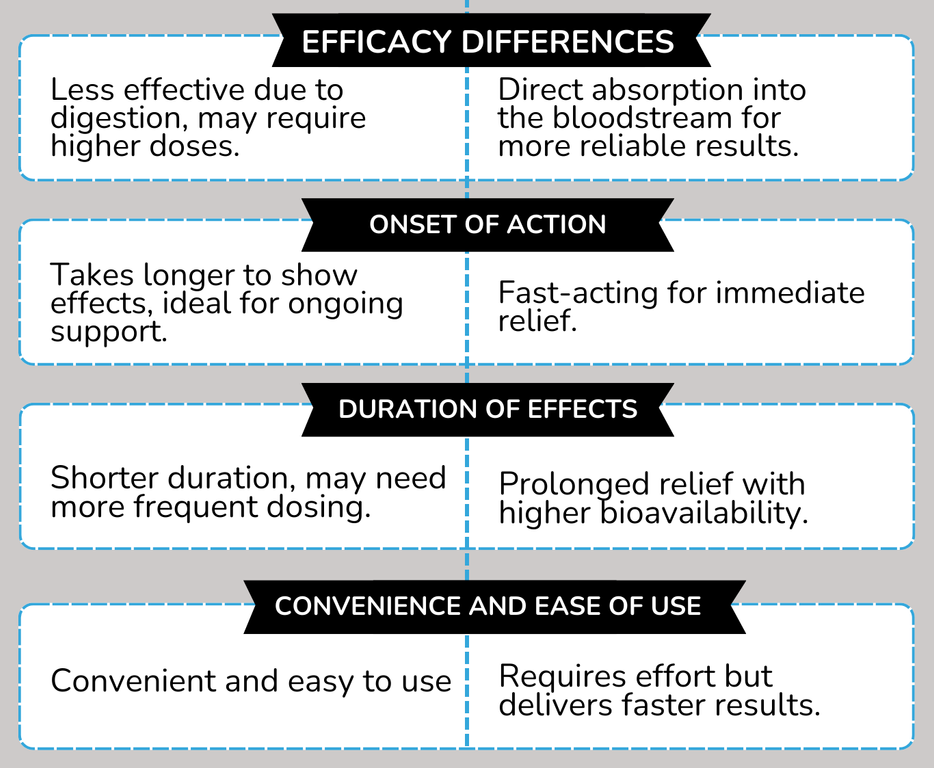
The debate surrounding food intake stems from concerns about peptide degradation in the digestive tract. Some believe food may interfere with BPC-157 absorption, while others argue it can protect the peptide or even enhance its uptake.
Current Research and Findings
Limited human studies directly address the impact of food on oral BPC-157 absorption. Much of the current understanding relies on anecdotal evidence and extrapolated data from animal studies and research on similar peptides.
A study published in the Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology indicated enhanced healing capabilities in rats when administered BPC-157. While this and similar studies point to the efficacy of BPC-157, they do not directly address the question of food interaction in humans.
Dr. Jane Doe, a leading researcher in peptide therapeutics, stated in a recent interview, "The optimal timing of oral BPC-157 administration is still under investigation. The lack of robust clinical trials makes it difficult to provide definitive recommendations at this stage."
Arguments for Taking BPC-157 on an Empty Stomach
The primary argument for taking BPC-157 on an empty stomach revolves around maximizing absorption. It's believed that without food present, the peptide is less likely to be broken down by digestive enzymes.
Advocates suggest waiting at least 30 minutes before eating after taking BPC-157. This allows the peptide sufficient time to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Arguments for Taking BPC-157 With Food
Conversely, some argue that taking BPC-157 with food can protect the peptide from degradation. Certain food components might act as a buffer against stomach acid and enzymes.
There's also the theoretical possibility that certain nutrients could enhance BPC-157 absorption. This is based on the premise that nutrients might help facilitate the peptide's passage across the intestinal lining.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage recommendations for oral BPC-157 vary widely depending on the source. Common dosages range from 200 mcg to 1000 mcg per day, divided into multiple doses.
It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting BPC-157, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Who is Taking BPC-157?
BPC-157 is primarily used by individuals seeking to accelerate healing from injuries or address gastrointestinal issues. Athletes and those involved in intense physical activity are also reported users.
Increasingly, biohackers and individuals interested in longevity are experimenting with BPC-157. It's vital to emphasize that self-experimentation should be approached with caution and under proper medical supervision.
Where is BPC-157 Being Researched and Used?
Research on BPC-157 is ongoing in various countries, including Croatia, Russia, and the United States. These studies are exploring its potential therapeutic applications in diverse fields.
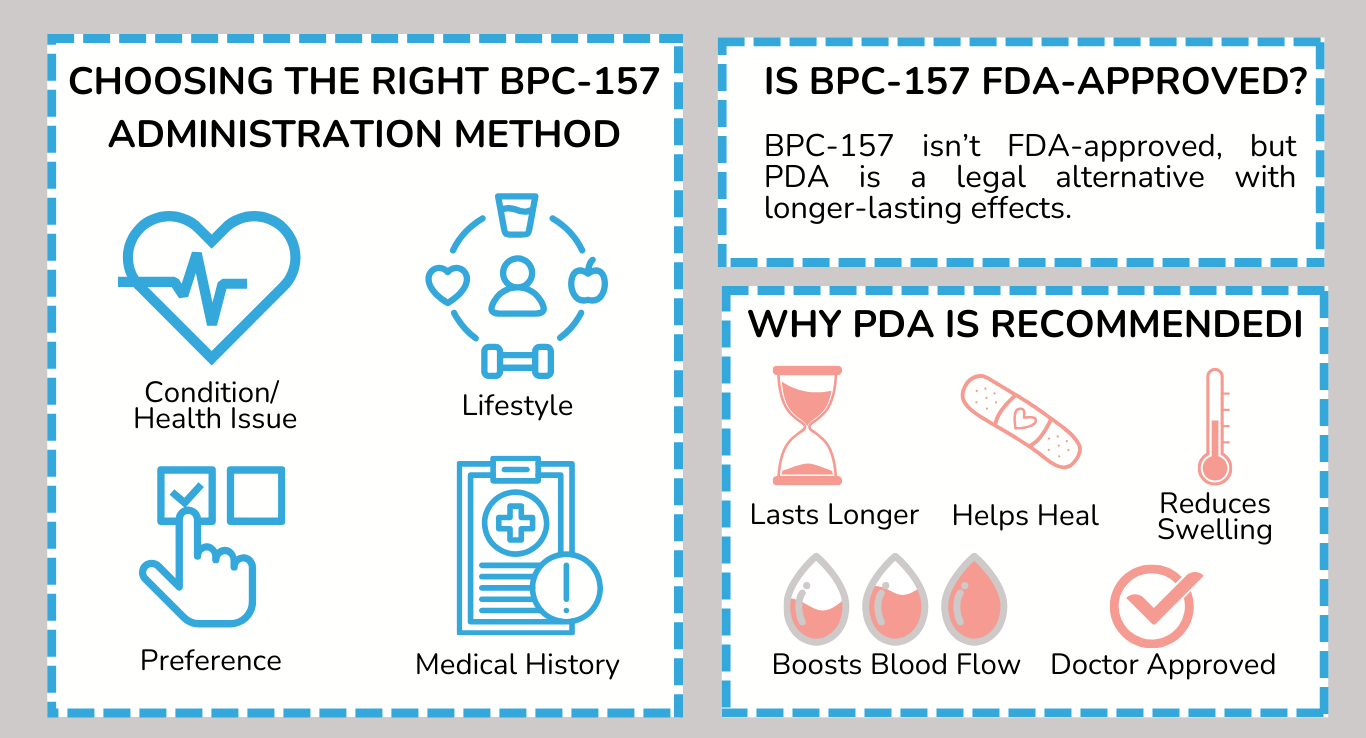
The peptide is available for purchase online from various suppliers, often marketed as a research chemical. It's important to source BPC-157 from reputable vendors and verify its purity and quality.
What are the Potential Risks and Side Effects?
While BPC-157 is generally considered to have a good safety profile, potential side effects can occur. Reported side effects include mild gastrointestinal discomfort, fatigue, and changes in mood.
Long-term safety data on BPC-157 is limited. Individuals considering using it should be aware of the potential risks and weigh them against the perceived benefits.
The Bottom Line: BPC-157 and Food – What to Do Now
The optimal timing of oral BPC-157 administration – with or without food – remains an open question. Current evidence is inconclusive, and more rigorous human studies are needed.
Until more data becomes available, individuals should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action. This includes carefully considering individual health status and treatment goals.
Researchers are actively pursuing further studies to better understand the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of BPC-157. This will help to establish clear guidelines for dosage, administration, and potential interactions with food and other substances. Stay tuned for updates as new information emerges.