Problem Solving Definition In Business
Businesses are facing unprecedented challenges, forcing a critical re-evaluation of problem-solving strategies to survive and thrive.
This article dissects the core definition of problem-solving in a business context, highlighting its importance for navigating disruption, optimizing operations, and fostering innovation. Understanding this definition is now paramount for leaders at all levels.
Defining Problem Solving in the Business Arena
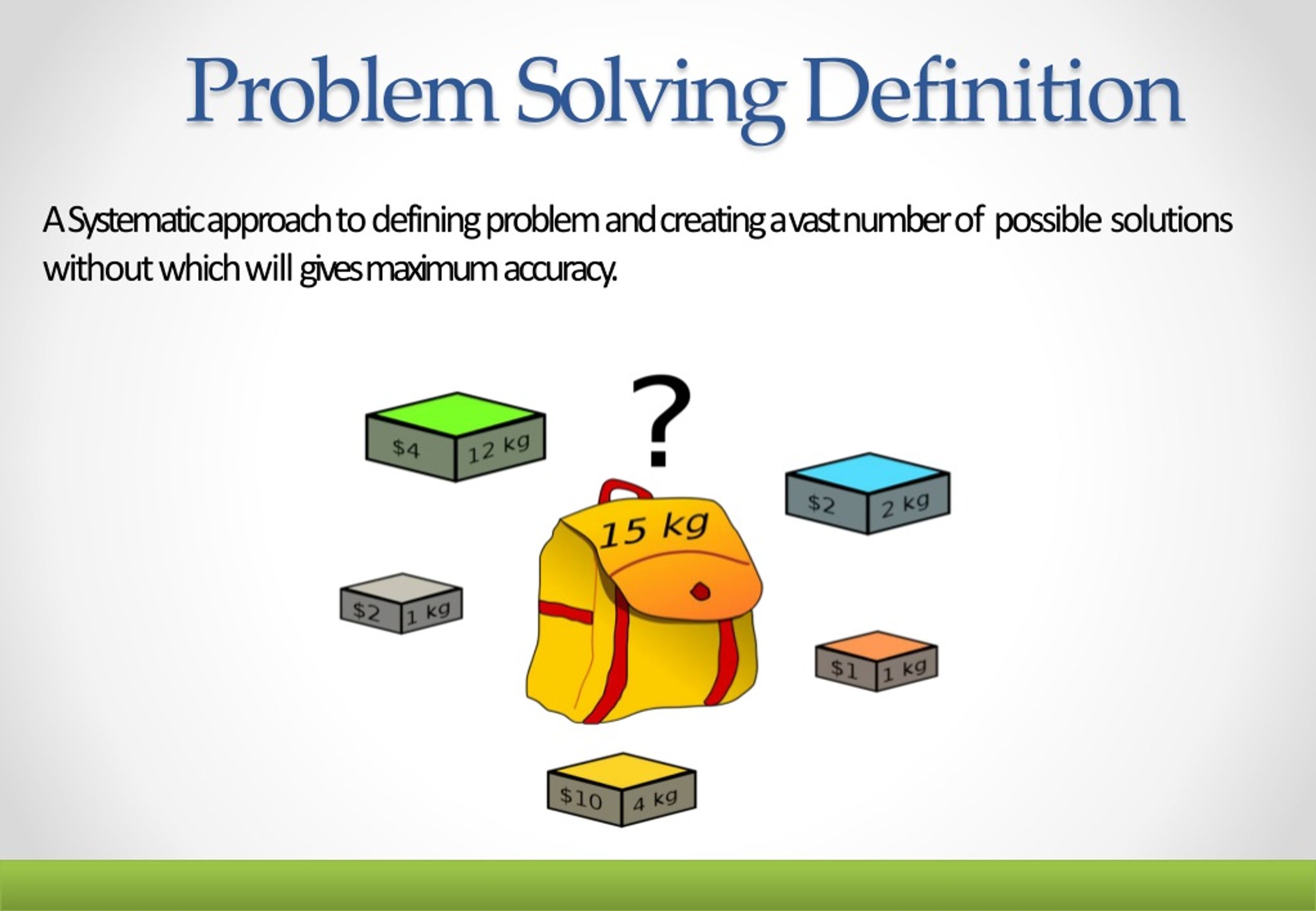
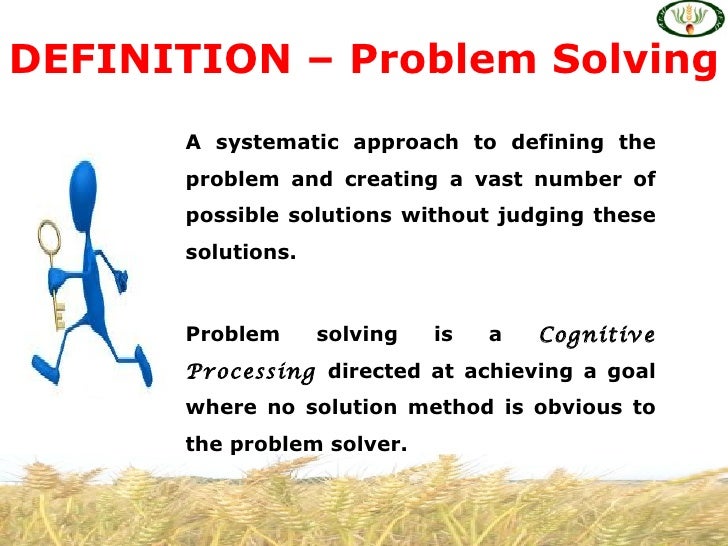
Problem-solving in business is not simply about fixing what’s broken. It's a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving obstacles that hinder a company's progress toward its goals.
This process necessitates a deep understanding of the business environment, internal operations, and the impact of decisions on stakeholders. Effective problem-solving moves beyond reactive measures to proactive strategies that anticipate and mitigate future challenges.
Key Components of Business Problem Solving
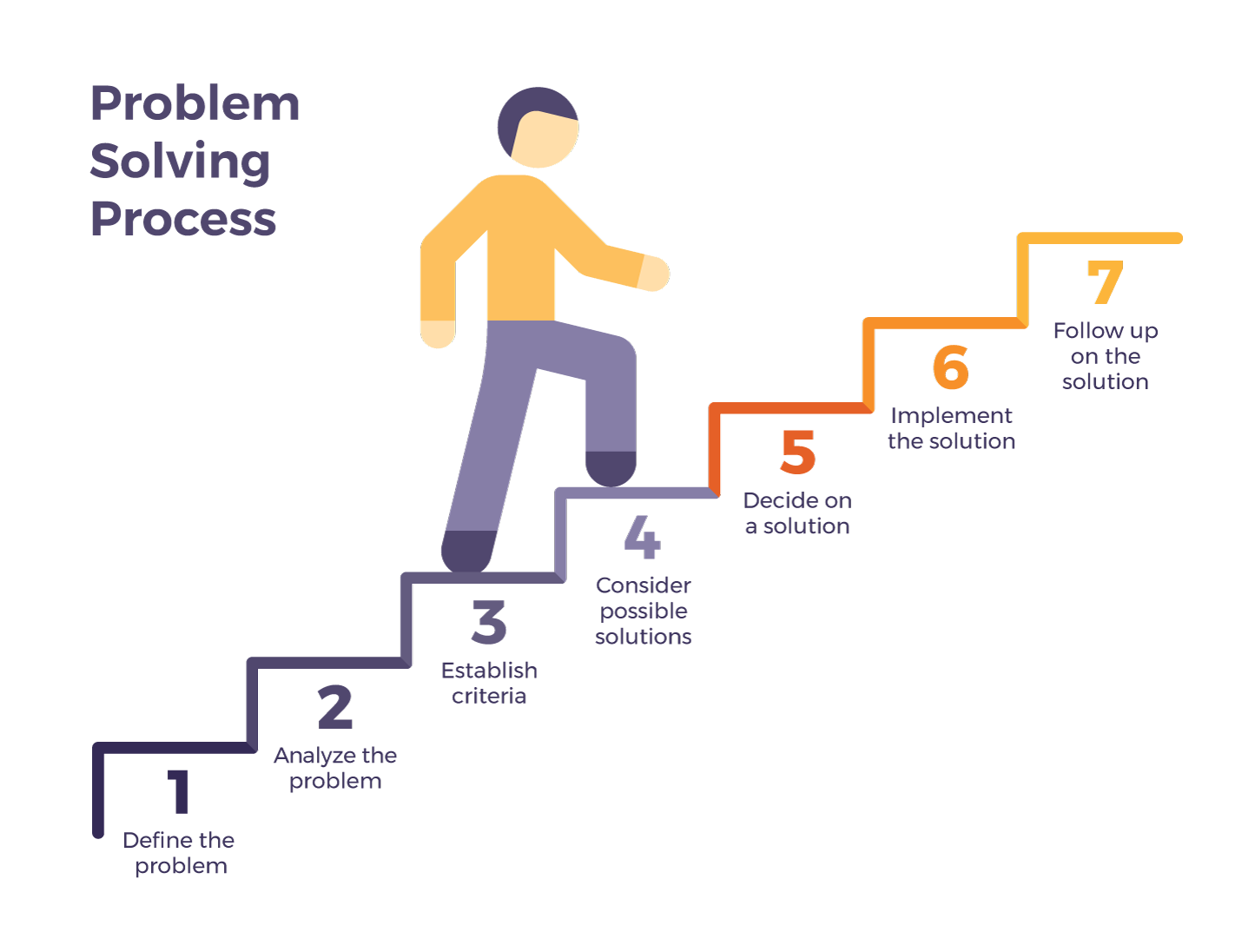
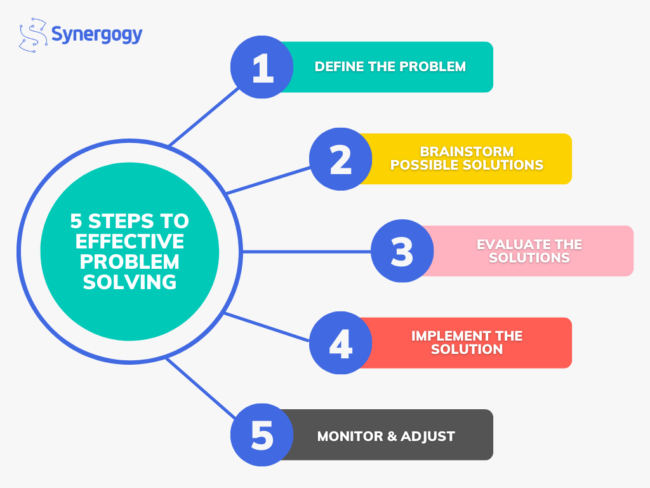
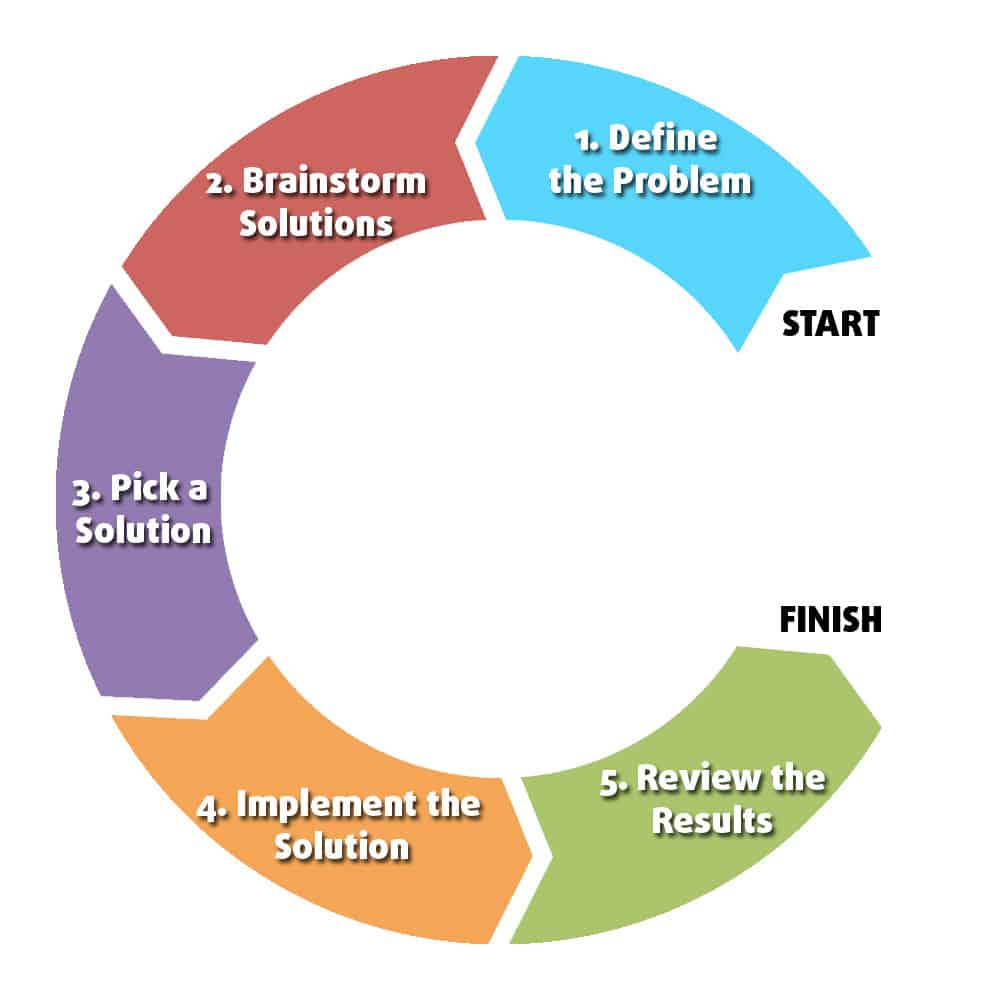
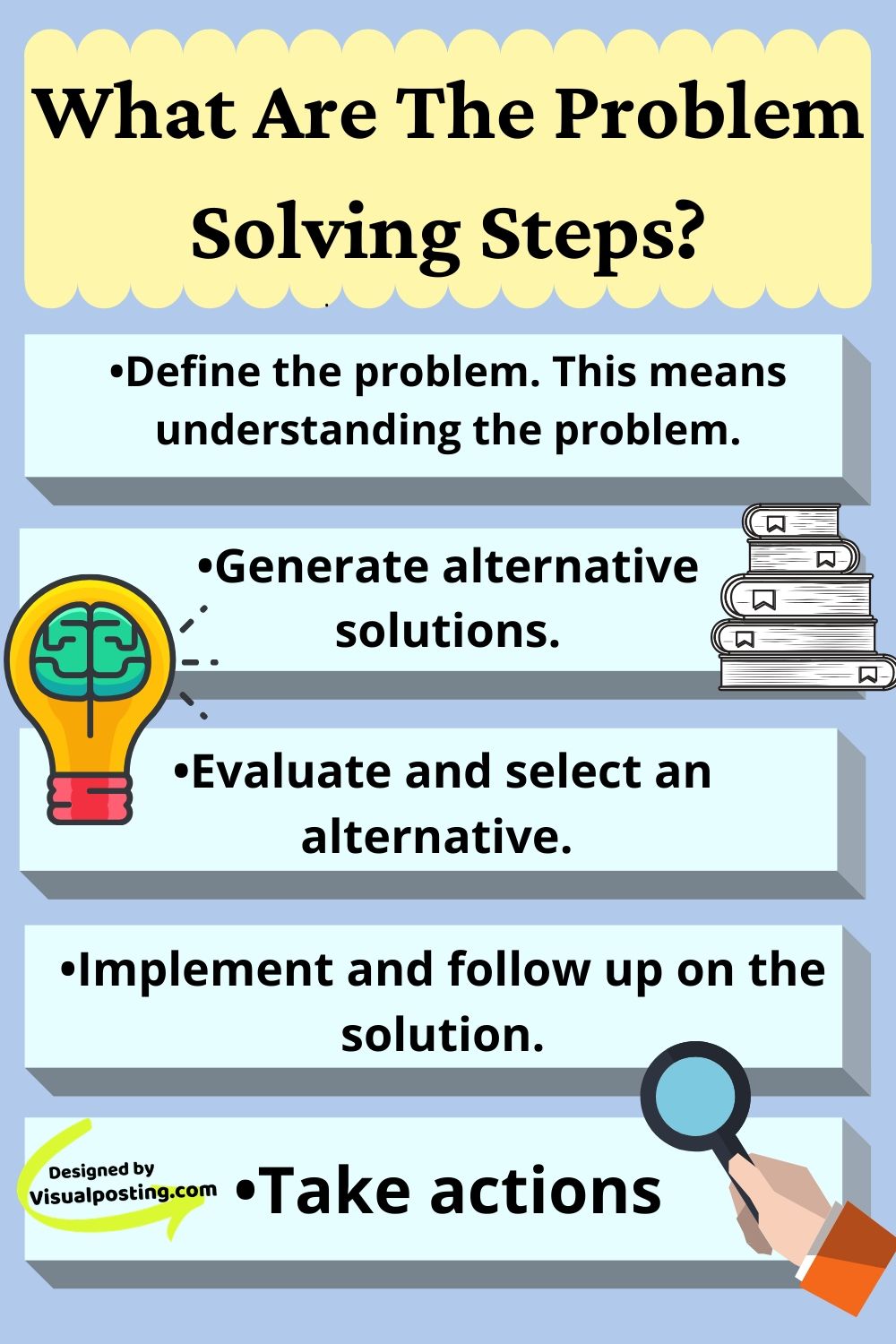
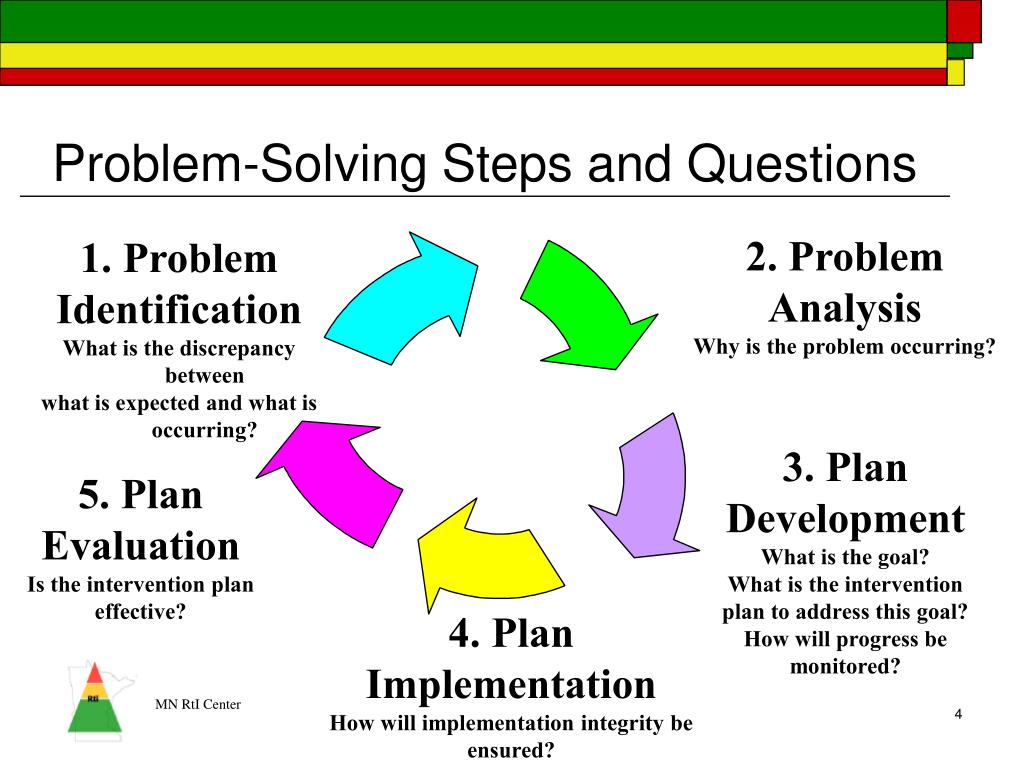
Identification: This is the crucial first step. Businesses must accurately pinpoint the root cause of a problem, not just its symptoms.
Analysis: Once identified, the problem needs thorough examination. Data collection, process mapping, and root cause analysis are essential tools at this stage.
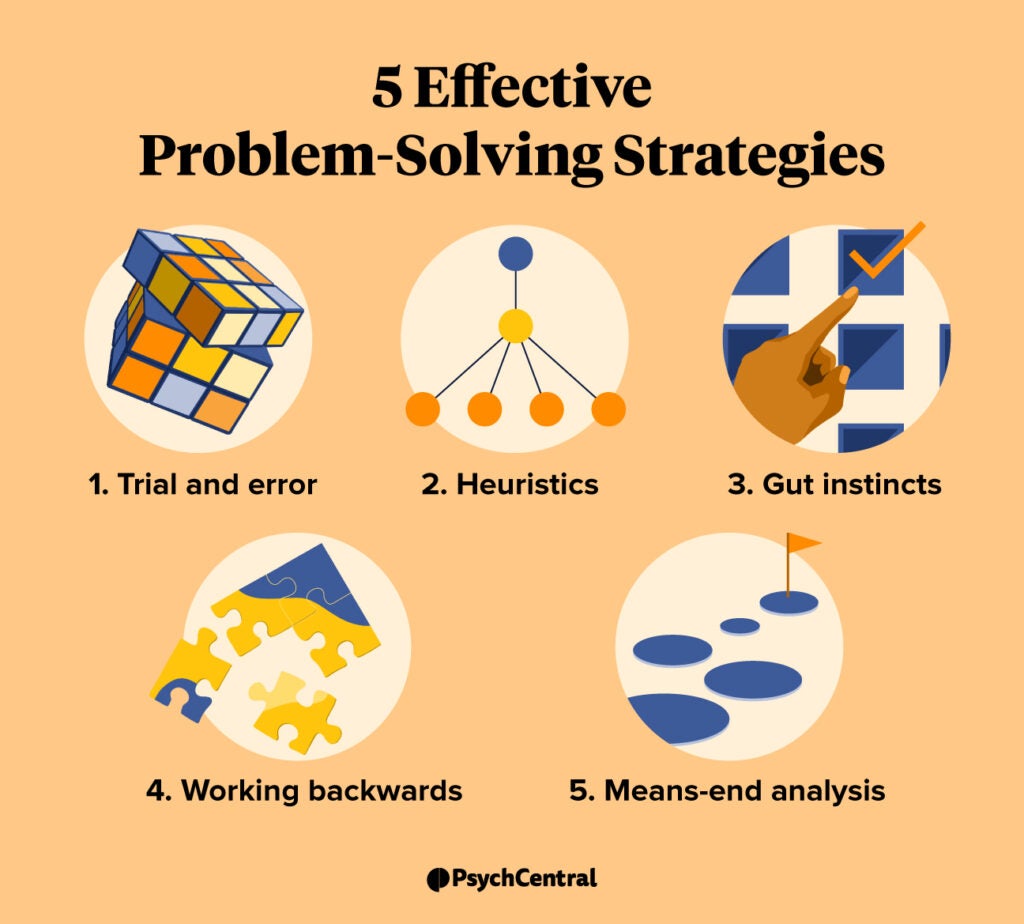
Solution Generation: Creativity and strategic thinking are key here. Teams must brainstorm and evaluate multiple solutions, considering both short-term and long-term impacts.
Implementation: A well-defined plan for putting the solution into action is vital. This includes assigning responsibilities, setting timelines, and allocating resources.
Evaluation: Post-implementation, it’s imperative to assess the effectiveness of the solution. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be monitored to determine if the problem has been adequately resolved and to identify areas for further improvement.
The 'Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How' of Business Problem Solving
Who: Everyone in an organization should be equipped with basic problem-solving skills. From frontline employees to senior management, everyone plays a role.
What: It encompasses any obstacle hindering operational efficiency, profitability, market share, or employee satisfaction. The 'what' is highly variable depending on the company.
Where: Problem-solving occurs in every department and at every organizational level. It's a pervasive function of a healthy business.
When: Problem-solving is an ongoing process. It is needed continuously, not just during crises.
Why: Failure to address problems effectively leads to stagnation, financial losses, and competitive disadvantage. Successful businesses are adept at identifying and resolving problems quickly.
How: A structured approach, involving data analysis, collaborative brainstorming, and strategic implementation, is the 'how'. Techniques like Six Sigma and Lean Management provide structured frameworks.
Impact of Effective Problem Solving
Effective problem-solving drives innovation. By tackling challenges head-on, businesses discover new opportunities and develop novel solutions.
Operational efficiency improves drastically when problems are resolved swiftly and efficiently. This translates to cost savings and increased productivity.
Employee morale increases in a problem-solving culture. Employees feel empowered when their contributions are valued in finding solutions.
Ongoing Developments and Next Steps
Companies are increasingly investing in training programs to enhance their employees' problem-solving abilities. This includes workshops on critical thinking, data analysis, and collaborative problem-solving techniques.
Technology plays an increasingly important role in problem-solving. Artificial intelligence and data analytics are being used to identify patterns, predict potential problems, and generate solutions.
The ongoing evolution of business requires a continuous refinement of problem-solving strategies. Companies must remain adaptable and embrace new approaches to stay ahead of the curve.