Remittance Processor Job Description

The global remittance industry, a critical lifeline for families and economies worldwide, is experiencing a surge in demand for skilled professionals. Among the most sought-after roles is that of a Remittance Processor, a position vital for ensuring the smooth and secure transfer of funds across borders. Understanding the nuances of this job is crucial for both those seeking employment in the sector and for businesses reliant on efficient remittance services.
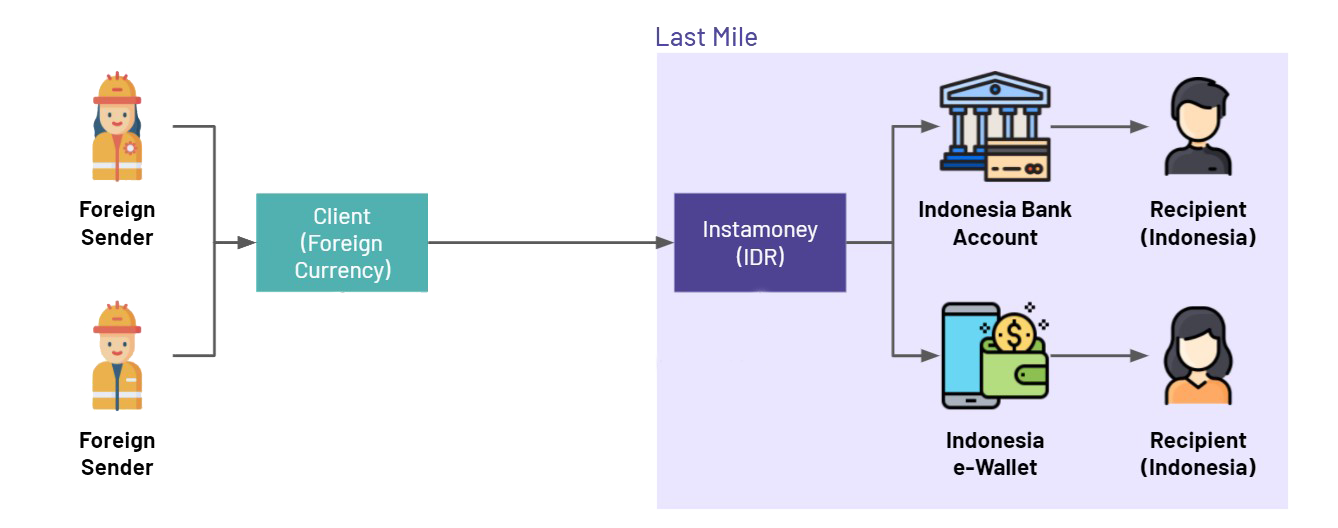
At its core, the Remittance Processor role involves facilitating the international transfer of money from senders to recipients. This article will delve into the specifics of this job description, including the responsibilities, required skills, and potential career paths.
Key Responsibilities of a Remittance Processor
The responsibilities of a Remittance Processor are multifaceted and demanding. They must be meticulous in adhering to regulations, especially those related to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance.
These regulations are designed to prevent illicit financial activities. The processor must verify the identity of both the sender and the recipient, and carefully scrutinize transaction details.
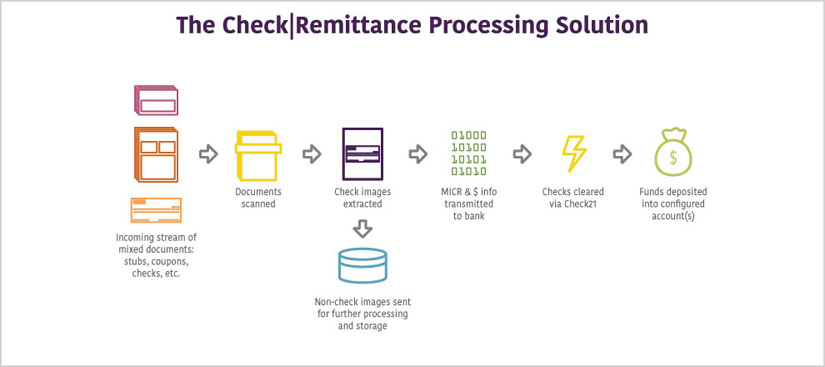
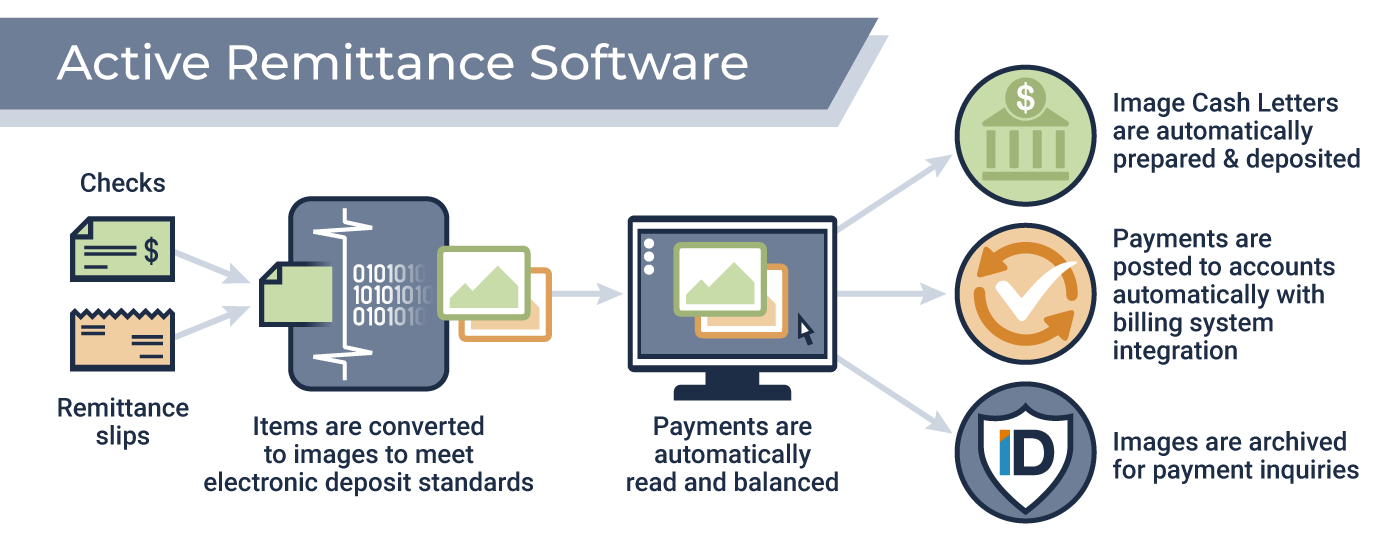
Daily tasks typically include processing remittance requests. This involves verifying documentation, inputting data into remittance processing systems, and ensuring accuracy in all transactions.
They also need to communicate with customers to resolve any issues or discrepancies. This could involve clarifying transaction details, providing updates on processing status, or assisting with troubleshooting problems.
Furthermore, processors monitor transactions for suspicious activity and report any concerns to the appropriate authorities. This is a critical function in preventing fraud and maintaining the integrity of the remittance system.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
A successful Remittance Processor requires a specific skill set. Strong attention to detail and accuracy are paramount, as even minor errors can have significant consequences in financial transactions.
Excellent communication skills are essential for interacting with customers and colleagues. The ability to clearly explain procedures and resolve issues is vital.
Proficiency in computer skills and data entry is also necessary. Processors often work with specialized remittance software and must be comfortable using technology to manage transactions.
Employers typically seek candidates with a high school diploma or equivalent. Some positions may require a degree in finance, accounting, or a related field.
Experience in banking, customer service, or a similar industry is often preferred. Familiarity with AML and KYC regulations is a major advantage.
Regulatory Compliance and the Role of the Processor
The remittance industry is heavily regulated, and Remittance Processors play a crucial role in ensuring compliance. They are the first line of defense against money laundering and other financial crimes.
Processors must stay up-to-date on the latest regulations and guidelines. This requires ongoing training and a commitment to understanding complex legal requirements.
According to a 2023 report by the World Bank, remittances to low- and middle-income countries reached an estimated $669 billion, highlighting the importance of a secure and compliant remittance ecosystem.
Failing to adhere to these regulations can result in significant penalties for both the individual processor and the remittance company. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an inter-governmental body, sets international standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
Career Paths and Opportunities
The Remittance Processor role can be a stepping stone to other opportunities within the financial services industry. With experience and further training, processors can advance to roles such as Senior Remittance Processor, Compliance Officer, or Remittance Manager.
The growing demand for remittance services is creating more job opportunities in this field. Technological advancements are also changing the landscape, with new roles emerging in areas such as digital remittances and mobile money transfers.
Individuals with a strong work ethic and a commitment to compliance can build a rewarding career in the remittance industry. The ability to facilitate vital financial flows across borders is a valuable and in-demand skill.
A 2022 report by Pew Research Center indicates that a significant portion of remittances are used for basic needs such as food, healthcare, and education in recipient countries, underscoring the societal impact of efficient and reliable remittance services.
Conclusion
The Remittance Processor job is a critical function in the global financial system. These professionals are essential for ensuring the secure and efficient transfer of money across borders, supporting families and economies around the world.
By understanding the responsibilities, skills, and regulatory requirements of this role, individuals can pursue a rewarding career in the remittance industry. Businesses can also better appreciate the importance of investing in skilled and knowledgeable processors.