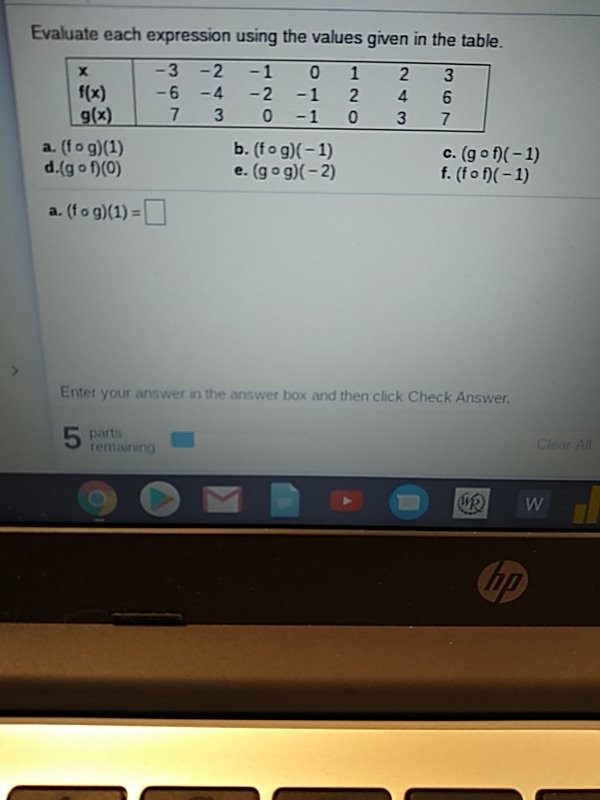
State Whether The Statement Is True Or False

The assertion that voter fraud is rampant in U.S. elections has become a persistent claim, often repeated despite evidence to the contrary. This statement, frequently amplified by political figures and spread through social media, has eroded public trust in the democratic process and fueled concerns about election integrity.
This article aims to examine the veracity of this claim by scrutinizing available data, official reports, and expert analyses. We will delve into the nature of voter fraud, analyze its documented frequency, and assess whether it constitutes a significant threat to the integrity of American elections.
The Nature of Voter Fraud
Voter fraud encompasses a range of illegal activities intended to manipulate election outcomes. These activities can include impersonating another voter, voting more than once, submitting fraudulent registration forms, or tampering with ballots.
It is important to distinguish between actual voter fraud and simple errors or administrative mishaps in voter registration or ballot counting.
Assessing the Evidence
Numerous studies and investigations have been conducted to assess the prevalence of voter fraud. A comprehensive review by the Brennan Center for Justice found that instances of voter fraud are extremely rare.
The report analyzed millions of votes cast in various elections and concluded that the rate of voter fraud is consistently below 0.0001%. This indicates that out of every million votes cast, only a tiny fraction involve fraudulent activity.
Lorraine Minnite, a professor at Rutgers University and an expert on election administration, analyzed voter fraud claims in her book The Myth of Voter Fraud. She concluded that most allegations are unsubstantiated and based on anecdotal evidence or politically motivated claims.
Official Investigations and Reports
Official investigations by state and federal agencies have consistently found little evidence of widespread voter fraud. The Government Accountability Office (GAO) has conducted multiple studies on election administration, finding that voter fraud is not a significant problem.
Following the 2020 election, numerous lawsuits and audits were conducted, particularly in closely contested states. These investigations, including those in Arizona, Georgia, and Wisconsin, largely confirmed the accuracy and integrity of the election results.
Even investigations led by partisan entities found little to no evidence of systemic fraud that would have altered the outcome of the election. For example, the Arizona Senate's audit of Maricopa County, though controversial in its methodology, ultimately confirmed Joe Biden's victory.
Federal Prosecutions
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) is responsible for prosecuting election-related crimes. The DOJ's record on voter fraud prosecutions further supports the conclusion that it is not a widespread problem.
Data shows that the number of convictions for voter fraud is relatively low, and most cases involve individual instances of illegal voting rather than large-scale conspiracies.
A report by the Public Interest Legal Foundation (PILF), a conservative legal group that advocates for election integrity, identified a relatively small number of proven voter fraud cases compared to the total number of votes cast in elections.
The Impact of Voter Fraud Claims
Despite the lack of evidence, claims of widespread voter fraud have had a significant impact on public perception and election administration. These claims have fueled distrust in elections, leading to increased polarization and political division.
Furthermore, allegations of voter fraud have been used to justify stricter voting laws, such as voter ID requirements and restrictions on early voting. Critics argue that these laws disproportionately affect minority voters and those with disabilities, effectively suppressing voter turnout.
Myrna Pérez, director of the Voting Rights and Elections Program at the Brennan Center for Justice, has argued that restrictive voting laws are often based on unfounded claims of voter fraud and that they undermine the fundamental right to vote.
Different Perspectives on Election Integrity
While evidence suggests that voter fraud is rare, concerns about election integrity remain valid. Some argue that even isolated instances of voter fraud can undermine public confidence in the democratic process.
Proponents of stricter voting laws contend that they are necessary to prevent fraud and ensure the accuracy of elections. They argue that measures like voter ID requirements are reasonable safeguards that do not unduly burden voters.
However, opponents of these laws maintain that they are discriminatory and unnecessary, given the lack of evidence of widespread fraud. They argue that efforts to improve election integrity should focus on expanding access to the ballot box and modernizing election administration.
Conclusion
Based on the available evidence, the statement that voter fraud is rampant in U.S. elections is false. While isolated instances of voter fraud do occur, they are extremely rare and do not significantly affect election outcomes.
Claims of widespread voter fraud, often lacking factual basis, can erode public trust in elections and lead to unnecessary restrictions on voting rights. Efforts to enhance election integrity should be evidence-based and focused on promoting both security and accessibility.
Moving forward, it is crucial to rely on credible sources of information and to engage in informed discussions about election administration. Fostering a fact-based understanding of election integrity is essential for maintaining a healthy democracy.

![State Whether The Statement Is True Or False [ANSWERED] State whether the following statement is true or false 2 The](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20220626195937198691-4653246.jpg?h=512)





![State Whether The Statement Is True Or False [ANSWERED] A State whether the sentence or statement is TRUE or FALSE 1](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20220425192308606715-4270279.jpg?h=512)
![State Whether The Statement Is True Or False [ANSWERED] State whether the following statement is true or false All](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20231002233314231259-5864185.jpg?h=512)
![State Whether The Statement Is True Or False [Solved] State whether the statement is true or false 1 Chatbots are](https://website-assets.studocu.com/img/document_thumbnails/f76127570ee40526bab939225cf5d624/thumb_300_667.png)