Support Cells In The Central Nervous System Are Collectively Called

The central nervous system's unsung heroes, support cells, are vital for neuronal function and overall brain health. Understanding these cells is crucial for developing effective treatments for neurological disorders.
These essential support cells, vital for neuronal health and function, are collectively known as glial cells, or simply glia. This knowledge is fundamental for researchers and clinicians tackling neurological diseases, making ongoing research into glial cell function paramount.
Glia: The Central Nervous System's Support Network
Glia, derived from the Greek word for "glue," highlights their traditional role as structural support.
However, their functions extend far beyond mere scaffolding, playing active roles in neuronal communication, maintenance, and defense.
Types of Glial Cells
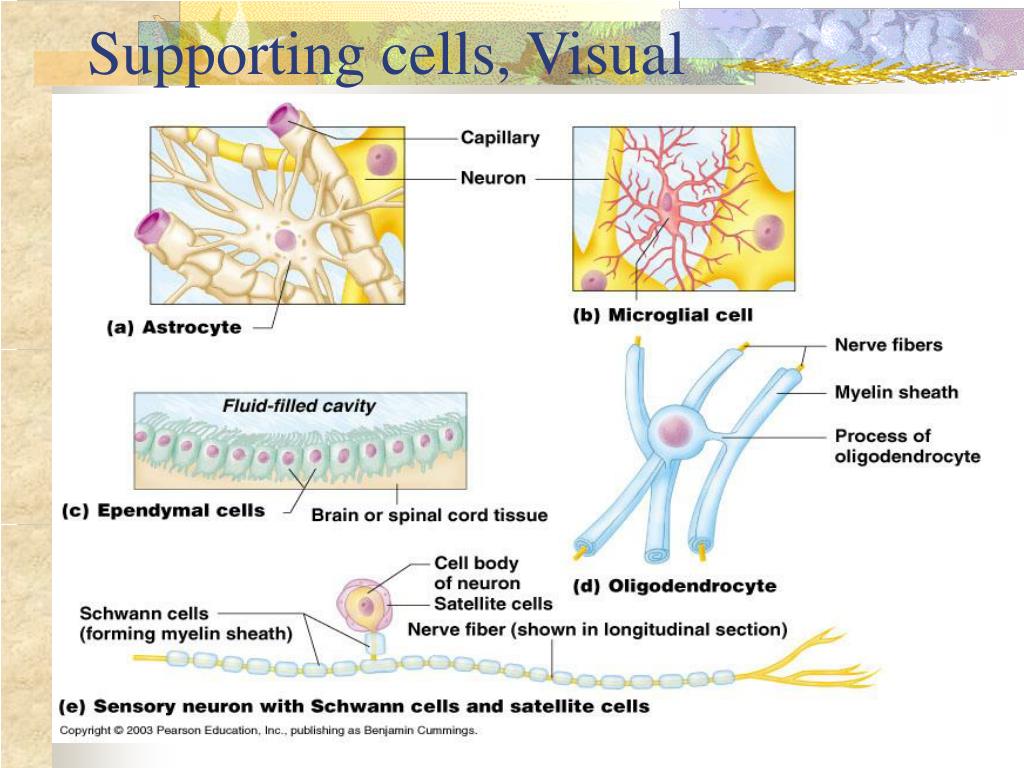
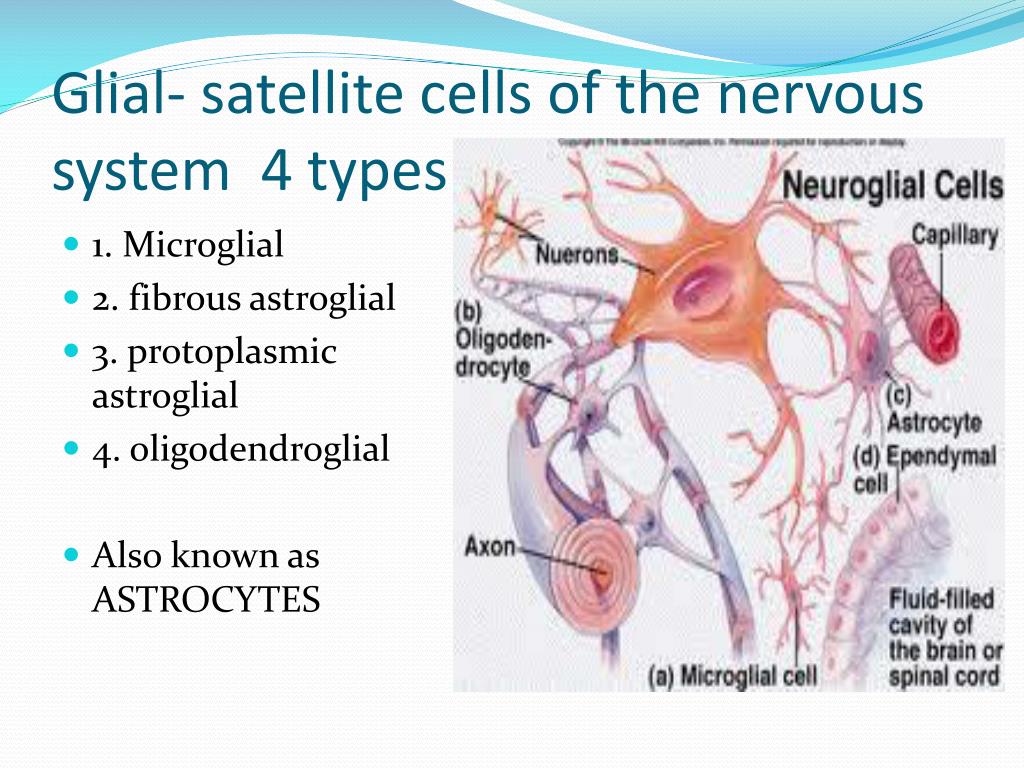
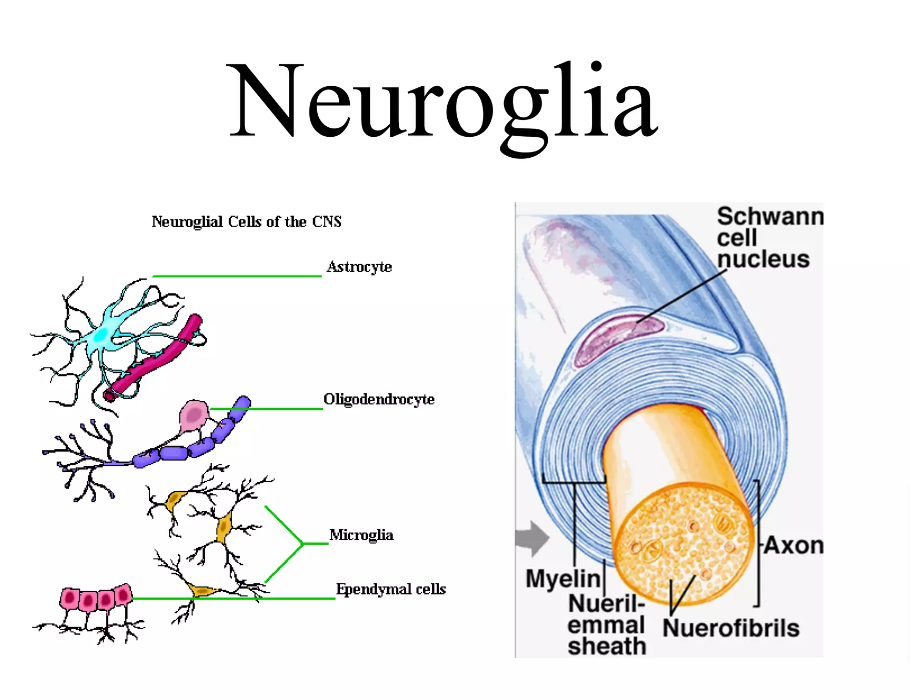
Several distinct types of glial cells populate the central nervous system, each with specialized functions.
Astrocytes, the most abundant type, regulate the chemical environment around neurons, provide nutrients, and maintain the blood-brain barrier. Dysfunctional astrocytes are implicated in various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and stroke.
Oligodendrocytes are responsible for myelinating axons in the central nervous system, speeding up nerve impulse transmission. Damage to oligodendrocytes, as seen in multiple sclerosis (MS), severely disrupts neurological function.
Microglia act as the brain's resident immune cells, scavenging debris and fighting infection. While crucial for maintaining brain health, chronic microglial activation can contribute to neuroinflammation and neuronal damage.
Ependymal cells line the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord, producing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and facilitating its circulation. These cells play a crucial role in maintaining a stable brain environment.
Functions Beyond Support: Active Roles in Brain Activity
Glia actively participate in synaptic transmission, modulating neuronal excitability and influencing network activity.
Astrocytes, for instance, release gliotransmitters that can either enhance or inhibit neuronal signaling.
Recent research suggests that glia play a critical role in learning and memory processes. Their involvement highlights the complexity of brain function, extending beyond neuronal activity alone.
Implications for Neurological Disorders
Dysregulation of glial function is implicated in a wide range of neurological disorders.
From neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's to psychiatric conditions like schizophrenia and depression, glial cells are increasingly recognized as key players in disease pathogenesis.
Targeting glial cells is emerging as a promising therapeutic strategy for neurological disorders.
Researchers are exploring ways to modulate glial activity to promote neuronal survival, reduce inflammation, and restore brain function.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Research into glial cell biology is rapidly expanding, driven by technological advancements and a growing appreciation of their importance.
Single-cell sequencing and advanced imaging techniques are providing unprecedented insights into glial cell heterogeneity and function.
Efforts are underway to develop drugs that specifically target glial cells, aiming to correct their dysfunction in neurological disorders.
Understanding the intricate roles of glia in the central nervous system is paramount for developing effective therapies for a wide range of neurological diseases.
Continued research into glial cell biology holds immense promise for improving the lives of millions affected by these debilitating conditions.