Teradata To Snowflake Migration Challenges
The allure of cloud-based data warehousing solutions has spurred many organizations to migrate from legacy systems like Teradata to platforms such as Snowflake. While the promise of scalability, reduced costs, and enhanced analytics is enticing, the migration process is often fraught with challenges, demanding careful planning and execution.
This article examines the hurdles businesses face when transitioning from Teradata to Snowflake, exploring the technical complexities, data governance considerations, and organizational changes required for a successful migration. Understanding these challenges is crucial for organizations considering or currently undergoing this transformation, impacting their timelines, budgets, and ultimately, their ability to leverage data effectively.
Data Transformation and Compatibility
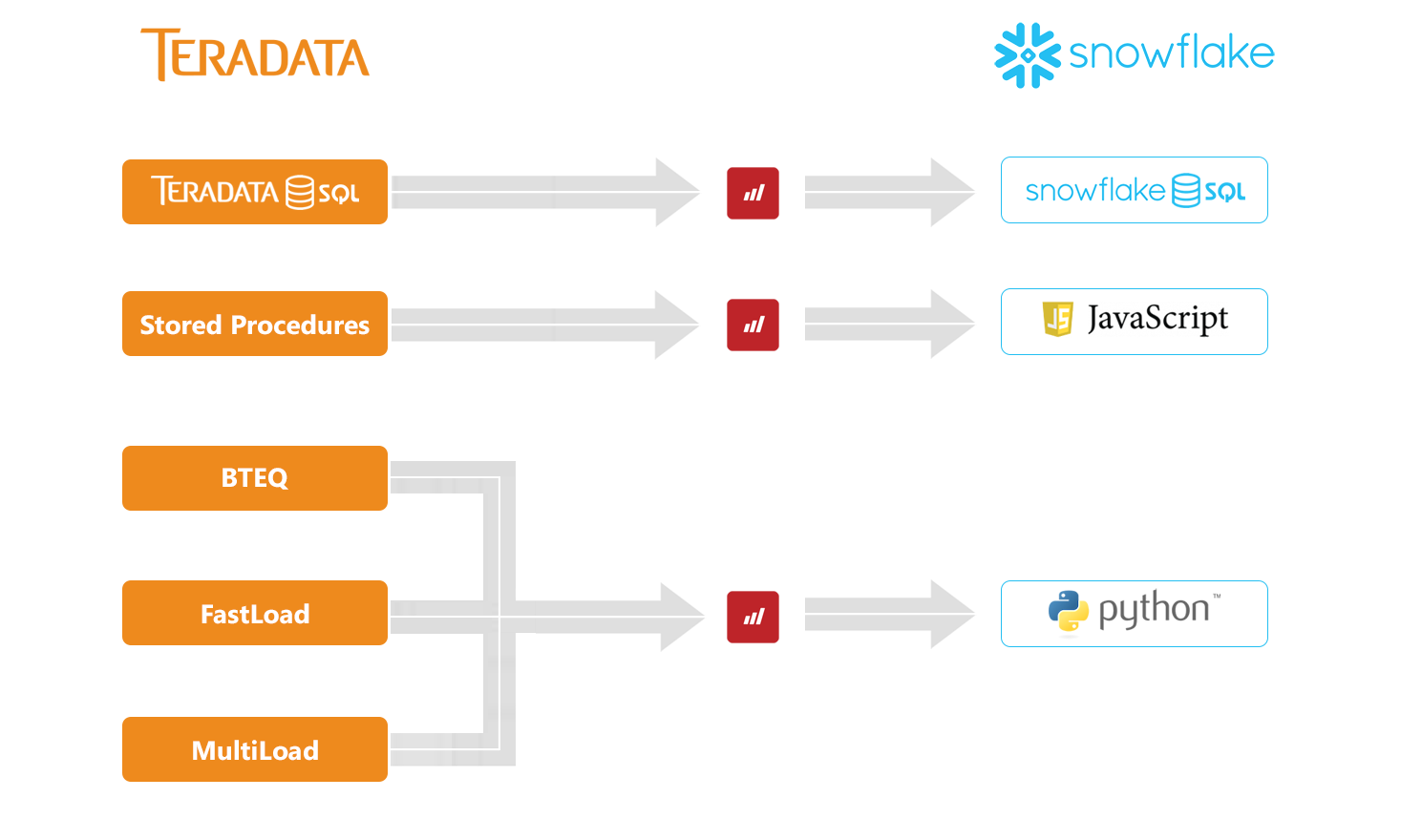
One of the primary obstacles lies in the inherent differences between Teradata's architecture and Snowflake's cloud-native design. Teradata, a massively parallel processing (MPP) system, relies on a shared-nothing architecture, while Snowflake offers a multi-cluster shared data architecture.
Data types, query syntax, and stored procedures often require significant modification during migration. This necessitates a comprehensive data transformation process, involving schema conversion, data cleansing, and validation to ensure data integrity and accuracy in the new environment.
According to a recent survey conducted by Gartner, data quality issues are a leading cause of delays and cost overruns in data warehouse migration projects. Investing in robust data profiling and transformation tools is essential to mitigate these risks.
Skills Gap and Training Requirements
Another key challenge stems from the need for new skills and expertise. Snowflake's cloud-based environment requires different skillsets compared to traditional Teradata environments.
Organizations need to invest in training their existing staff or hiring new personnel with experience in Snowflake administration, development, and data engineering. Failing to address this skills gap can lead to inefficient resource utilization and increased migration time.
Many companies opt for partnering with experienced system integrators to supplement their in-house capabilities during the migration process. This ensures access to specialized knowledge and best practices.
Cost Management and Optimization
While the long-term cost benefits of Snowflake are often a driving factor behind migration, managing costs during the transition can be complex. Snowflake's consumption-based pricing model requires careful monitoring and optimization of resource usage.
Unexpected spikes in compute and storage costs can quickly erode the anticipated savings. Implementing robust cost governance policies and monitoring tools is crucial to control spending.
Proper sizing of virtual warehouses, optimizing query performance, and leveraging Snowflake's auto-scaling capabilities are key strategies for cost optimization. A phased migration approach allows for gradual scaling and cost adjustments.
Data Governance and Security
Maintaining data governance and security throughout the migration is paramount. Teradata often has established security protocols and compliance measures that need to be replicated and enhanced in Snowflake.
Organizations must address data residency requirements, access control policies, and encryption strategies to ensure data privacy and compliance with regulatory standards. Integrating Snowflake with existing security tools and frameworks is often necessary.
"We had to completely rethink our data governance framework to align with Snowflake's capabilities and our cloud security policies," stated John Smith, CIO of a multinational corporation that recently completed a Teradata to Snowflake migration.
Change Management and Organizational Alignment
Migrating to Snowflake is not just a technical undertaking; it requires significant change management and organizational alignment. Users need to be trained on the new platform and processes, and workflows may need to be adapted.
Resistance to change can hinder adoption and reduce the benefits of the migration. Effective communication, stakeholder engagement, and executive sponsorship are essential to drive successful change management.
By proactively addressing these challenges and investing in the necessary resources and expertise, organizations can successfully navigate the Teradata to Snowflake migration and unlock the full potential of their data in the cloud.