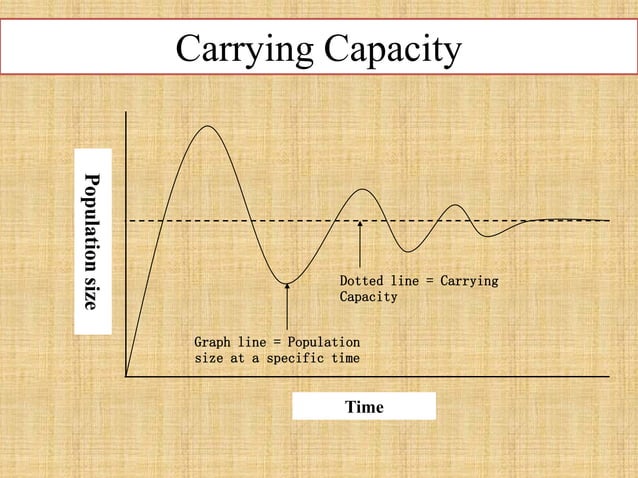
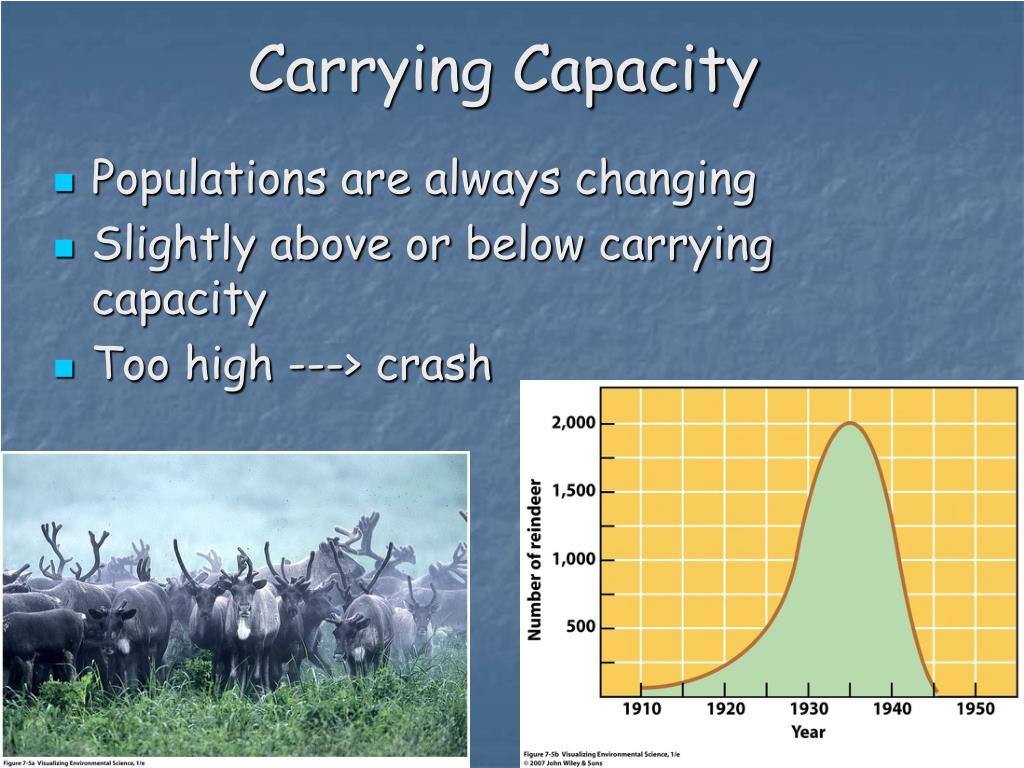
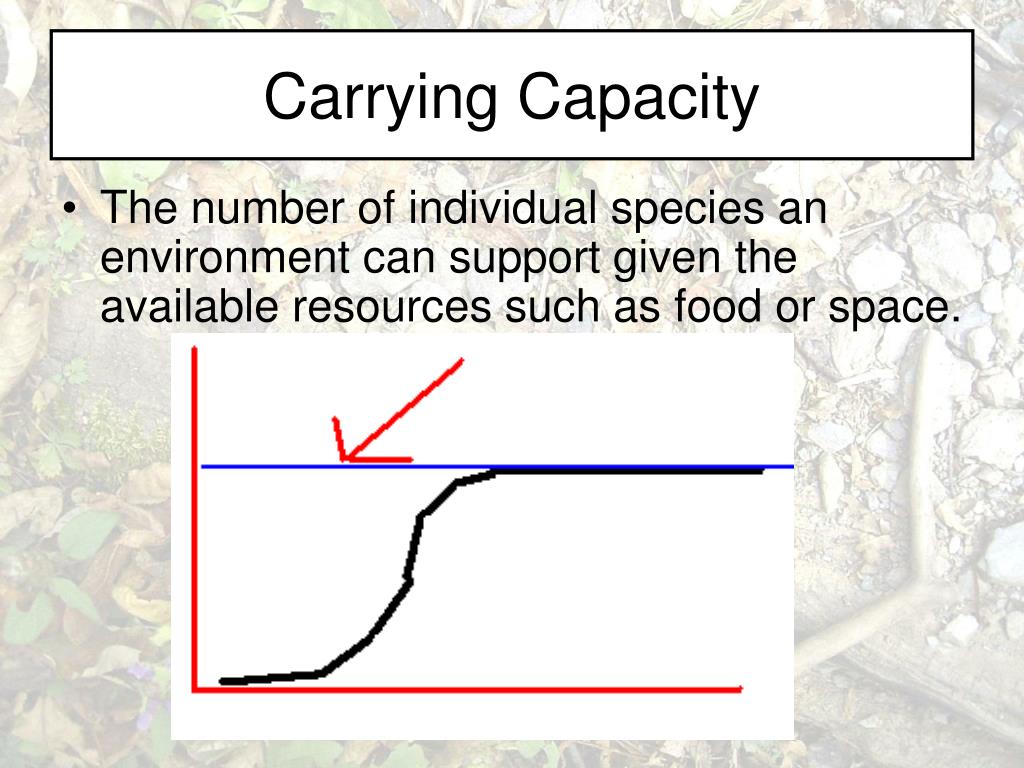
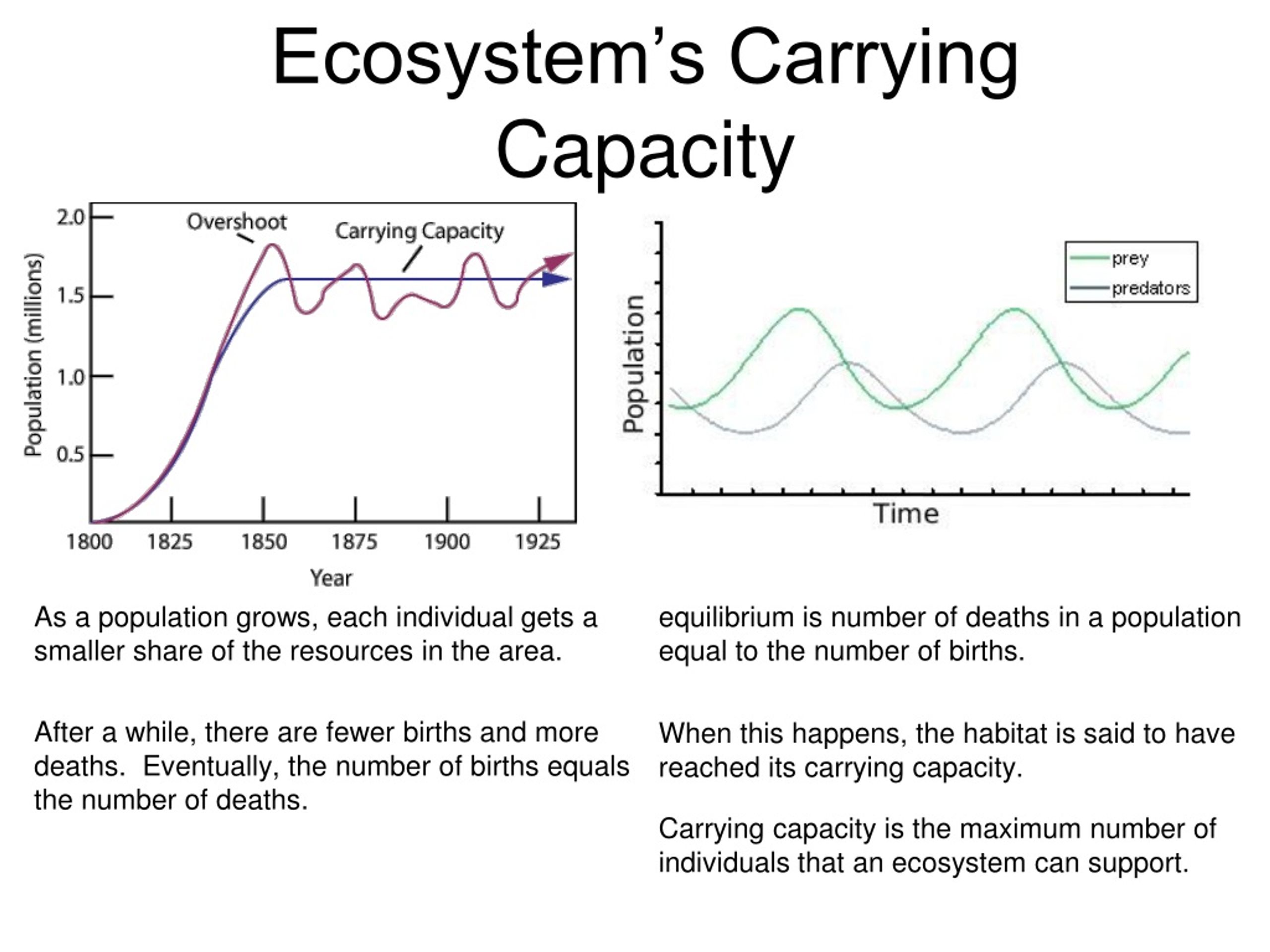
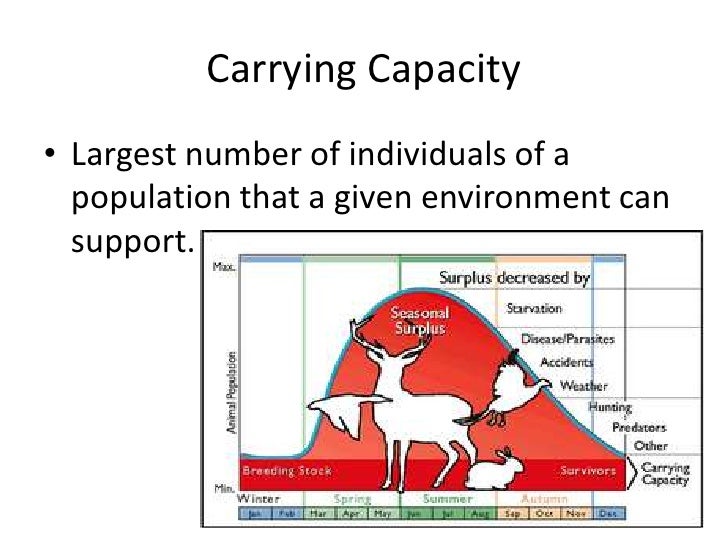
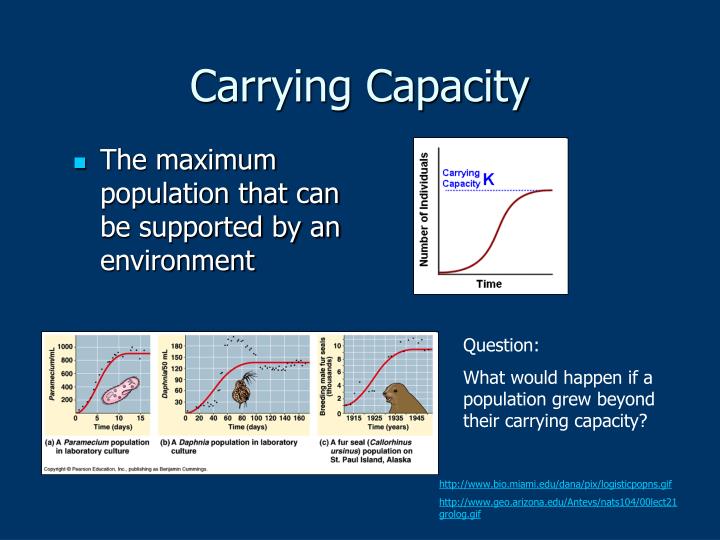
The Carrying Capacity Of An Environment May Be Decreased By
Environmental carrying capacities globally are plummeting at an alarming rate, threatening biodiversity and human well-being. Resource depletion, habitat destruction, and pollution are key drivers behind this dangerous trend.
The Earth's carrying capacity, the maximum population size of a species that the environment can sustain indefinitely, is being compromised. This degradation has severe repercussions for both natural ecosystems and human societies that rely on them.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion are shrinking and fragmenting habitats. This leaves species with less territory, limiting their access to food, water, and mates.
A 2020 report by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) revealed a 68% average decline in population sizes of mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish between 1970 and 2016, largely due to habitat loss. Critical habitats, such as the Amazon rainforest, are particularly vulnerable, with ongoing deforestation rates exceeding sustainable levels.
According to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), habitat destruction is a primary driver of species extinction. Without intact ecosystems, species face heightened competition and reduced breeding success.
Resource Depletion
Overconsumption of natural resources, including water, minerals, and fossil fuels, is straining environmental carrying capacities. The demand for these resources continues to rise with increasing global population and economic development.
Water scarcity is becoming an increasingly pressing issue, with the World Resources Institute (WRI) projecting that by 2030, water demand will exceed supply by 56% globally. Over-extraction of groundwater and unsustainable agricultural practices are contributing to this crisis.
The exploitation of mineral resources, such as rare earth elements used in electronics, often leads to habitat destruction and pollution. Mining operations can contaminate water sources and release harmful chemicals into the environment.
Pollution and Climate Change
Pollution, in its various forms, significantly degrades environmental quality and reduces carrying capacity. This includes air pollution, water pollution, and plastic pollution.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that air pollution is responsible for millions of deaths annually. Industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural runoff contribute to air and water contamination.
Climate change, driven by greenhouse gas emissions, is altering ecosystems and exacerbating existing environmental stresses. Rising temperatures, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events are forcing species to migrate or face extinction.
Impact on Food Security
Reduced carrying capacity directly impacts food security. Declining fish stocks due to overfishing and habitat destruction threaten global food supplies.
Soil degradation, caused by unsustainable agricultural practices, reduces crop yields and limits food production. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), one-third of the world's soils are degraded.
Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, can decimate crops and livestock, leading to food shortages and price increases.
Disease Outbreaks
Environmental degradation increases the risk of disease outbreaks. Habitat loss forces animals into closer contact with humans, increasing the likelihood of zoonotic disease transmission.
Deforestation and urbanization disrupt natural ecosystems, altering the distribution of disease vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks.
Changes in climate patterns can expand the geographic range of infectious diseases, putting more populations at risk, according to reports by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Urgent Action Needed
Addressing the decline in environmental carrying capacity requires immediate and coordinated action. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable resource management, and protecting and restoring habitats.
Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to implement policies and practices that prioritize environmental sustainability. This includes investing in renewable energy, adopting circular economy models, and promoting responsible consumption.
Conservation efforts, such as protected areas and species recovery programs, are crucial for preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem services. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) plays a critical role in assessing the conservation status of species and guiding conservation action.
Next Steps: Global leaders are scheduled to meet at the upcoming UN Climate Change Conference (COP28) to discuss enhanced climate action. Monitoring of biodiversity loss and habitat degradation will continue, with updated reports expected from the WWF and UNEP in the coming year. Further research is underway to better understand the complex interactions between environmental degradation and human health.