The Net Assets Of A Corporation Are Equal To

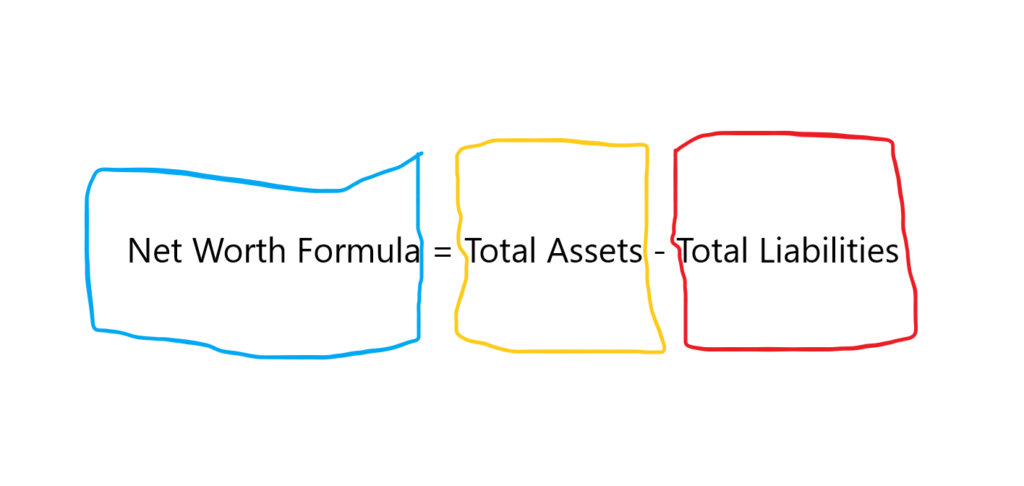
In the complex world of corporate finance, understanding the fundamental equation of a company's financial health is paramount. This equation, often understated yet critically important, boils down to a simple concept: the net assets of a corporation are equal to the difference between its total assets and its total liabilities.
This balance reveals the company's equity, representing the ownership stake and the value remaining after settling all debts. Misunderstanding this equation can lead to flawed investment decisions, inaccurate financial reporting, and ultimately, a distorted picture of a company's true worth.
Decoding the Equation: Assets, Liabilities, and Equity
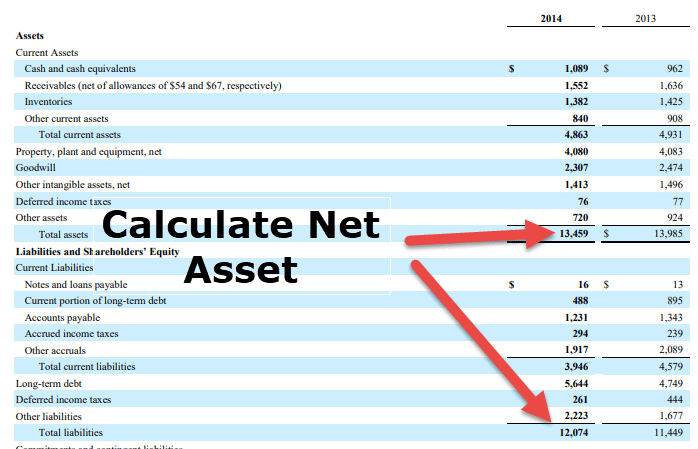
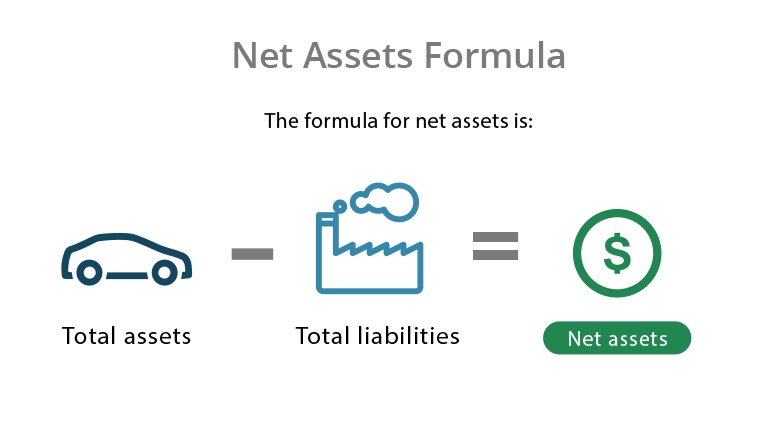
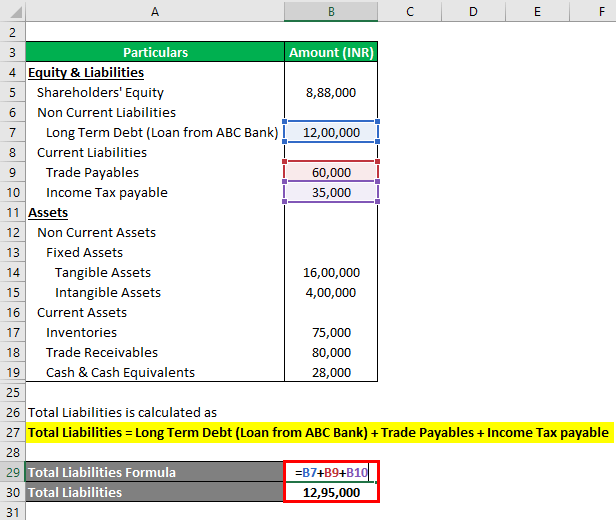
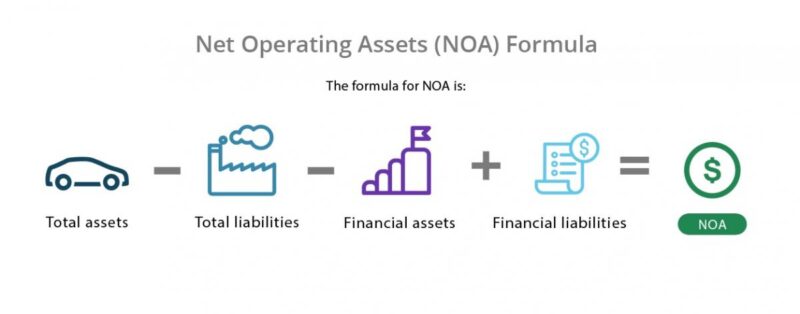
At its core, the accounting equation that defines net assets is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. Consequently, rearranging this gives us: Assets - Liabilities = Equity. This equity, also known as net assets, represents the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities.
Assets are everything a company owns that has economic value. These include cash, accounts receivable (money owed to the company), inventory, property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), and intangible assets like patents and trademarks. Assets are categorized as either current (expected to be converted to cash within a year) or non-current (long-term assets).
Liabilities represent a company's obligations to others. These include accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), salaries payable, loans, deferred revenue, and bonds payable. Similar to assets, liabilities are also categorized as current (due within a year) or non-current (long-term debts).
Equity, often referred to as shareholders' equity or owner's equity, represents the owners' stake in the company. It includes contributed capital (money invested by shareholders) and retained earnings (accumulated profits that have not been distributed as dividends).
The Importance of Accurate Valuation
Accurate valuation of both assets and liabilities is crucial for a correct calculation of net assets. Overstating assets or understating liabilities will lead to an inflated equity value, which can mislead investors and creditors. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) emphasizes the importance of transparent and accurate financial reporting to maintain market integrity.
Consider the case of Enron, whose accounting scandals involved manipulating asset values and hiding liabilities through special purpose entities. This ultimately led to a dramatic overstatement of equity and the company's collapse. This serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of inaccurate asset and liability reporting.
Fair value accounting, which requires certain assets and liabilities to be recorded at their market value, can be particularly challenging. Determining fair value often involves subjective estimates, particularly for assets that are not actively traded. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) provide guidelines for fair value measurement, but their application can still be complex.
Perspectives on Net Asset Valuation
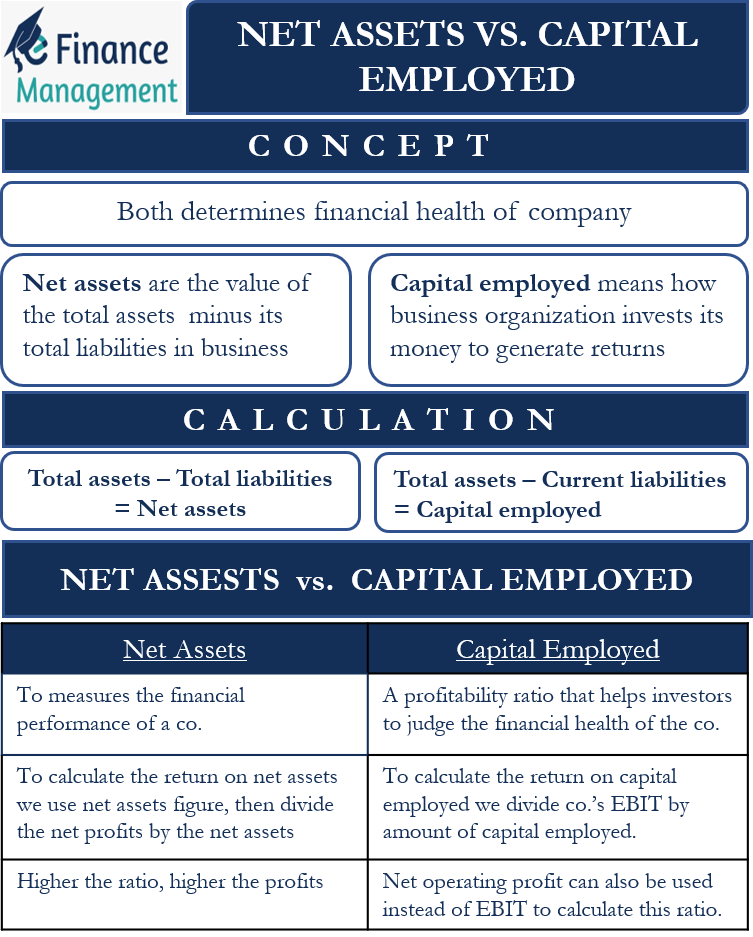
Different stakeholders may have different perspectives on the significance of net asset valuation. Investors often use net asset value (NAV) as a benchmark to assess the intrinsic value of a company, especially in asset-intensive industries like real estate or manufacturing. A high NAV suggests that the company may be undervalued by the market.
Creditors, on the other hand, are more concerned with the company's ability to repay its debts. They will scrutinize the asset composition and the level of liabilities to assess the company's solvency. A low net asset value relative to liabilities may indicate a higher risk of default.
Management uses net asset valuation to track the company's performance over time and to make strategic decisions about capital allocation. A growing net asset value indicates that the company is creating wealth for its shareholders.
Adjusted Net Asset Value (ANAV)
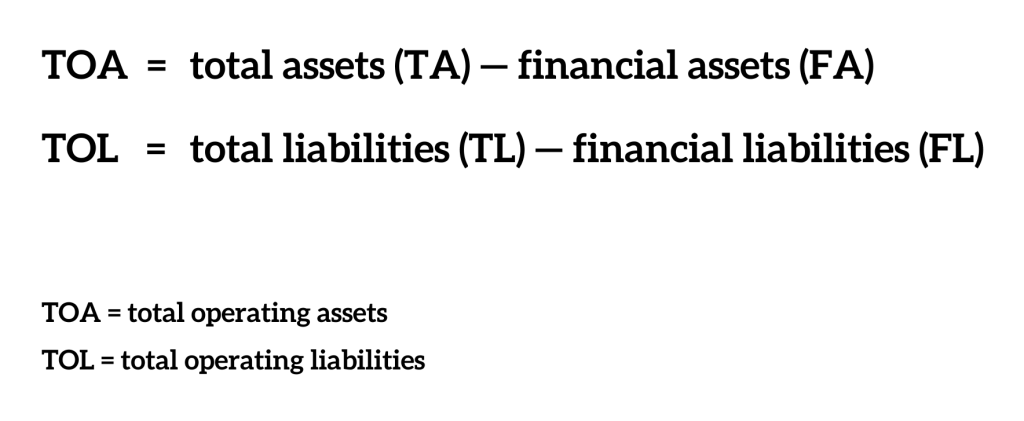
In some cases, analysts may calculate an adjusted net asset value (ANAV) to account for off-balance-sheet assets and liabilities. This involves making adjustments to the reported asset and liability values to reflect their true economic value. ANAV can provide a more comprehensive picture of a company's financial position.
The Impact of Intangible Assets
Intangible assets, such as brand reputation, intellectual property, and goodwill, can significantly impact a company's net asset value. However, valuing these assets can be challenging, as they lack physical substance. The accounting treatment of intangible assets varies depending on their nature and how they were acquired.
Internally developed intangible assets, like brand reputation, are generally not recognized on the balance sheet unless they meet specific criteria. Acquired intangible assets, on the other hand, are typically recorded at their fair value at the time of acquisition.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Net Asset Valuation
As businesses become increasingly digital and asset-light, the traditional concept of net asset valuation may become less relevant for some industries. The value of many companies now lies in their data, algorithms, and network effects, which are difficult to quantify using traditional accounting methods.
However, net asset valuation will continue to be a crucial tool for assessing the financial health of asset-intensive businesses and for understanding the underlying value of companies in general. The ongoing development of accounting standards and valuation techniques will help to improve the accuracy and relevance of net asset valuation in the years to come.
Understanding that a corporation's net assets are equal to its total assets minus its total liabilities provides a critical foundation for financial literacy. It's a key metric for investors, creditors, and company management alike, offering insights into a company's financial stability and overall value, remaining a cornerstone of financial analysis in a constantly evolving business landscape.