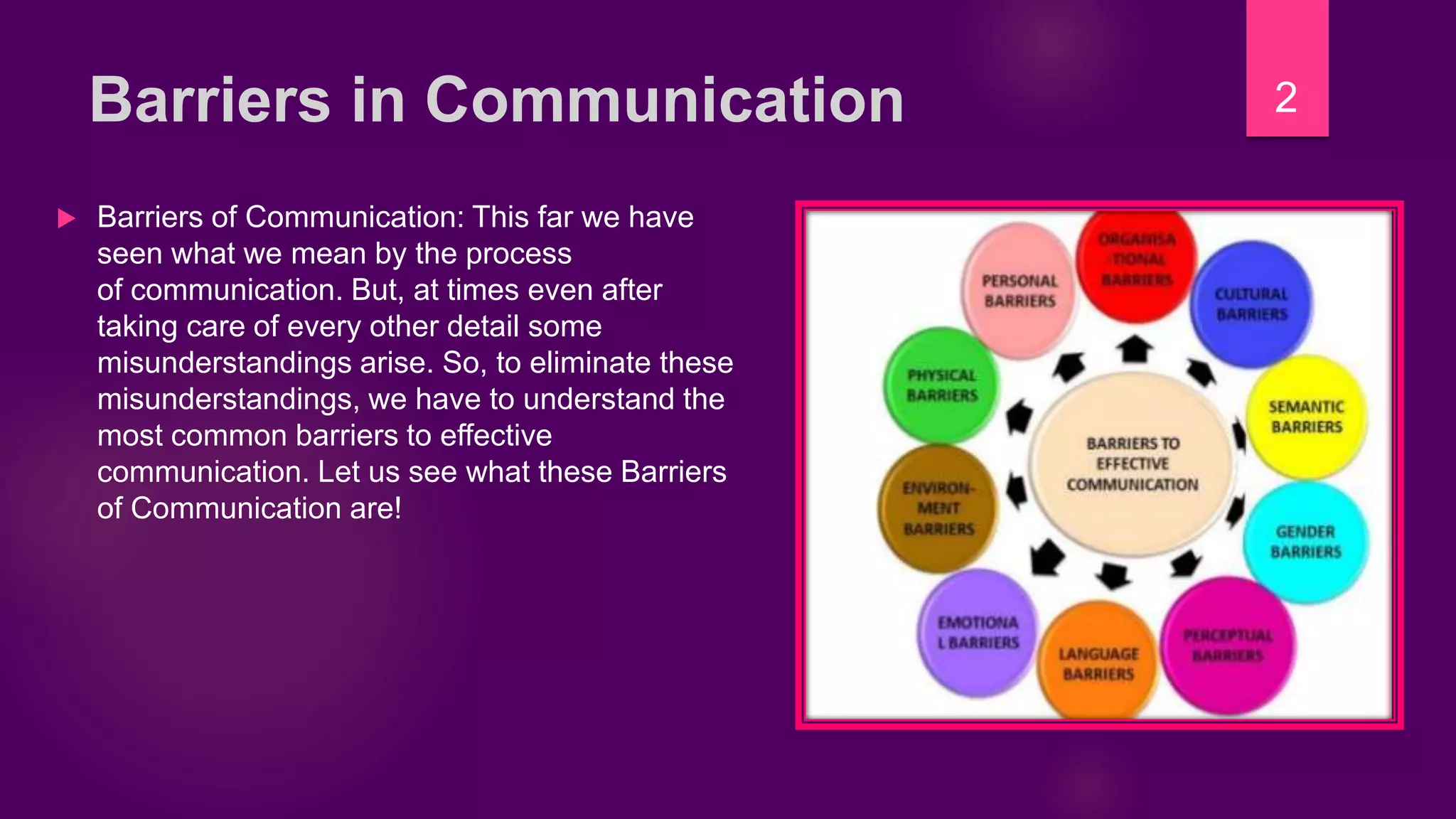
What Are Some Barriers To Communication
Effective communication is the cornerstone of human interaction, enabling us to build relationships, share information, and collaborate effectively. However, the path to clear and successful communication is often fraught with obstacles. These barriers can hinder the flow of information, leading to misunderstandings, frustration, and even conflict.
Understanding these barriers is crucial for individuals and organizations seeking to improve their communication strategies. This article examines some of the most prevalent barriers to communication, exploring their nature and impact on various aspects of life.
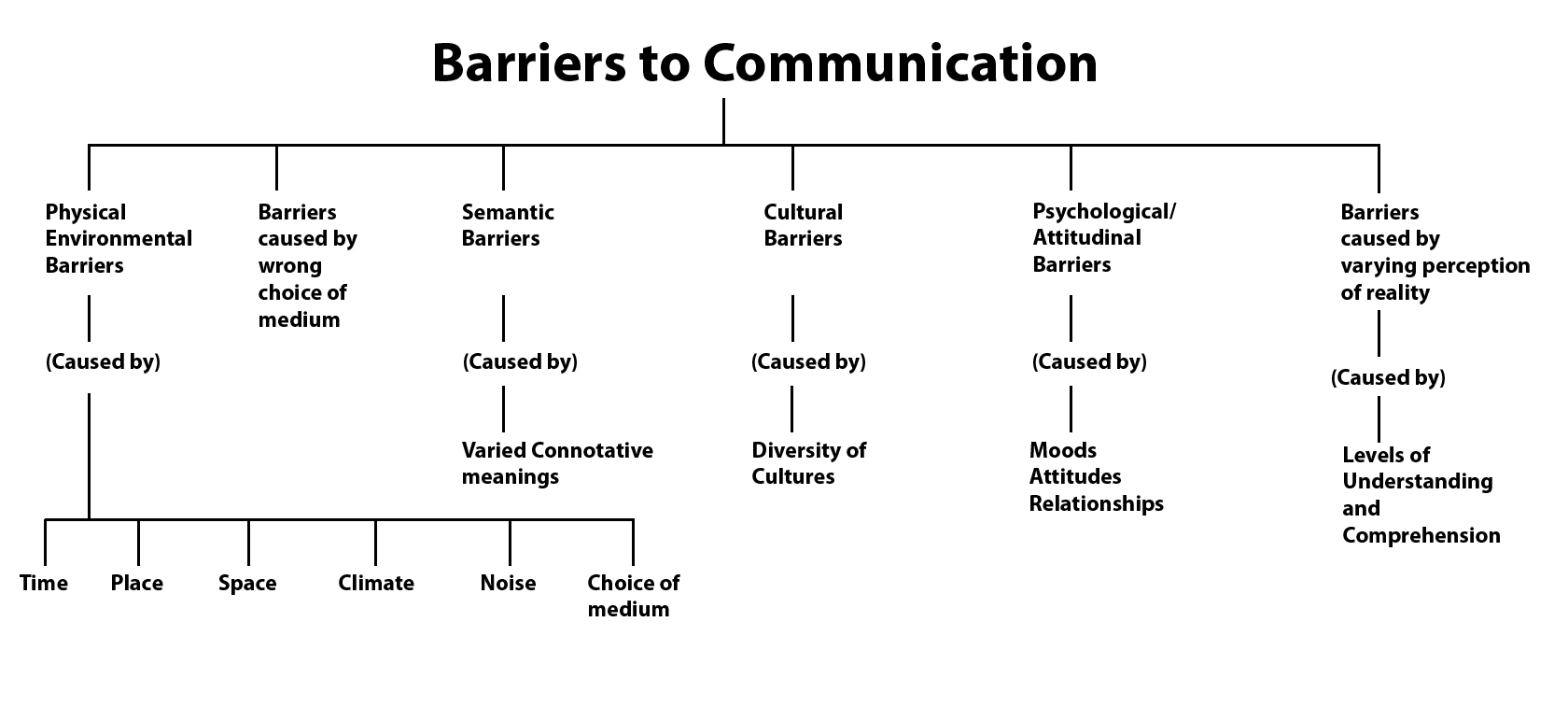
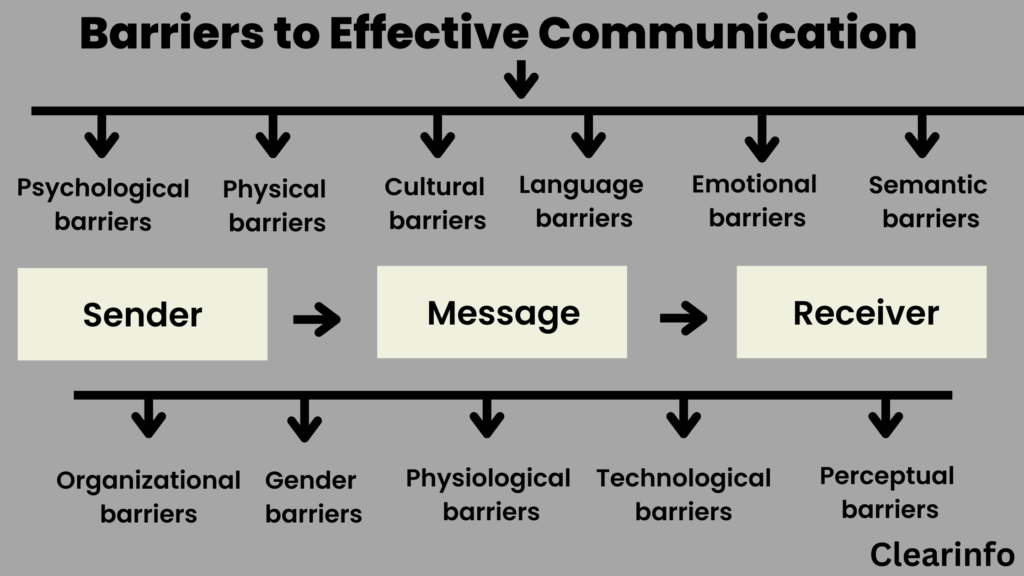
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers are perhaps the most obvious and easily identifiable. These encompass environmental factors that impede communication, such as noise, distance, and physical obstructions.
For example, loud machinery in a factory setting can make it difficult for workers to hear instructions or communicate effectively. Similarly, the vast distances separating individuals or teams working remotely can create challenges in maintaining consistent and clear communication.
Poor infrastructure, like unreliable internet connections, particularly in rural areas, significantly impacts online communication and collaboration. These barriers often require practical solutions, such as noise-canceling equipment or improved infrastructure.
Semantic Barriers
Semantic barriers arise from differences in the meaning of words and symbols. Language is inherently complex, and words can have multiple interpretations depending on context, culture, and individual experience.
Jargon, technical terminology, and ambiguous language can all contribute to semantic barriers. For instance, a doctor using highly technical medical terms when explaining a diagnosis to a patient may create confusion and anxiety.
According to a study by the National Institutes of Health, clear and simple language improves patient understanding and adherence to treatment plans. Similarly, cultural differences in language and communication styles can lead to misunderstandings in intercultural interactions. Clear, concise language and cultural sensitivity are essential to overcome these barriers.
Psychological Barriers
Psychological barriers stem from individuals' mental and emotional states. These barriers can significantly distort the message received, regardless of how clearly it is communicated.
Preconceived notions, biases, and stereotypes can act as filters, influencing how people interpret information. For example, if someone has a negative perception of a particular group, they may be less receptive to messages from members of that group.
Stress, anxiety, and emotional distress can also impede effective communication. A person experiencing high levels of stress may have difficulty focusing on the message being conveyed. Active listening, empathy, and self-awareness are key in mitigating psychological barriers.
Physiological Barriers
Physiological barriers are related to the physical condition of the sender or receiver. These barriers can include hearing impairments, visual impairments, speech impediments, or any other physical limitations that affect the ability to communicate effectively.
For example, someone with a hearing impairment may struggle to understand spoken messages, especially in noisy environments. Similarly, someone with a speech impediment may find it challenging to express themselves clearly.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), millions of people worldwide live with hearing loss, highlighting the widespread impact of this barrier. Assistive devices, such as hearing aids, and inclusive communication strategies are crucial for overcoming physiological barriers.
Organizational Barriers
Organizational barriers arise within the structure and culture of an organization. These barriers can include hierarchical structures, complex communication channels, and a lack of transparency.
For example, in organizations with rigid hierarchies, employees may be reluctant to share feedback or raise concerns with superiors, leading to a breakdown in communication. A lack of clear communication channels can also create confusion and inefficiency.
A study by PwC revealed that organizations with effective communication strategies are more likely to achieve their business objectives. Fostering a culture of open communication, implementing clear communication channels, and empowering employees to share their ideas are essential for breaking down organizational barriers.
The Impact of Communication Barriers
The consequences of communication barriers can be far-reaching, impacting individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. Misunderstandings can lead to damaged relationships, decreased productivity, and increased conflict.
In healthcare, communication barriers can have life-threatening consequences, leading to medication errors or delayed treatment. In business, poor communication can result in missed opportunities, project failures, and decreased profitability.
Addressing these barriers is not just about improving efficiency; it’s about fostering trust, building stronger relationships, and creating a more inclusive and understanding world.
Overcoming barriers to communication requires a multifaceted approach that addresses physical, semantic, psychological, physiological, and organizational factors. By understanding these barriers and implementing effective communication strategies, individuals and organizations can foster clearer, more meaningful interactions and achieve greater success in their endeavors. Prioritizing clear, empathetic, and inclusive communication is an investment in a more connected and collaborative future.