What Does The Ear Drum Look Like On Camera
Urgent concerns are emerging regarding the visualization of the eardrum via camera technology. Recent reports indicate a growing need for standardized understanding of what constitutes a healthy versus unhealthy eardrum when viewed through various optical devices.
This article clarifies the visual characteristics of the eardrum as seen through cameras, detailing the critical distinctions between normal and abnormal appearances, and highlighting the implications for telemedicine and remote diagnostics.
Normal Eardrum Appearance: The Baseline
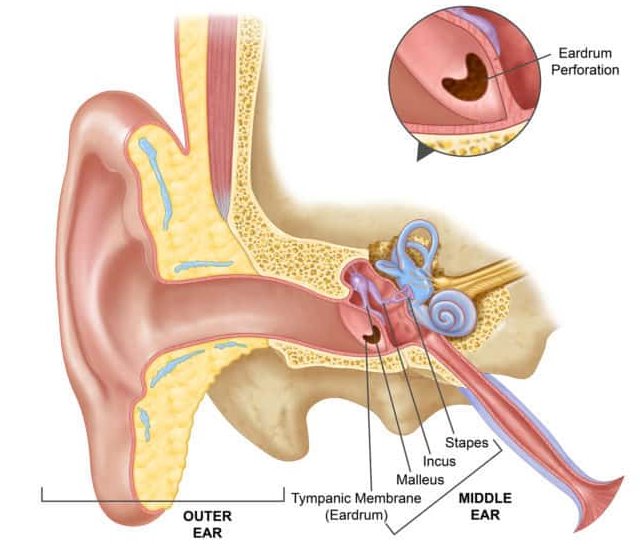
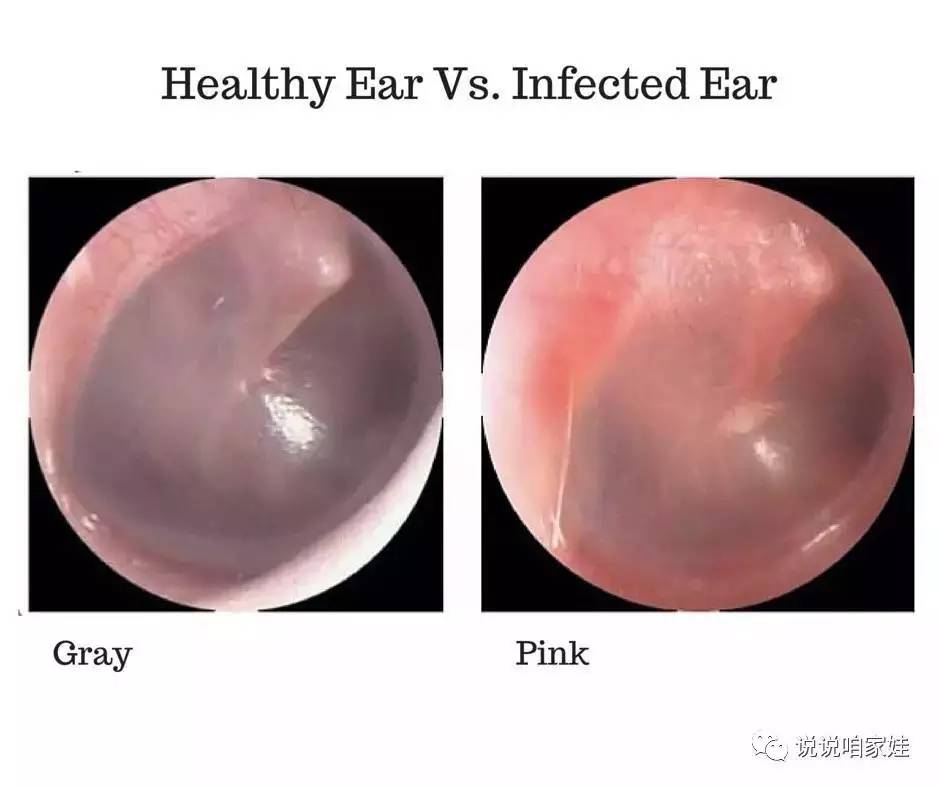
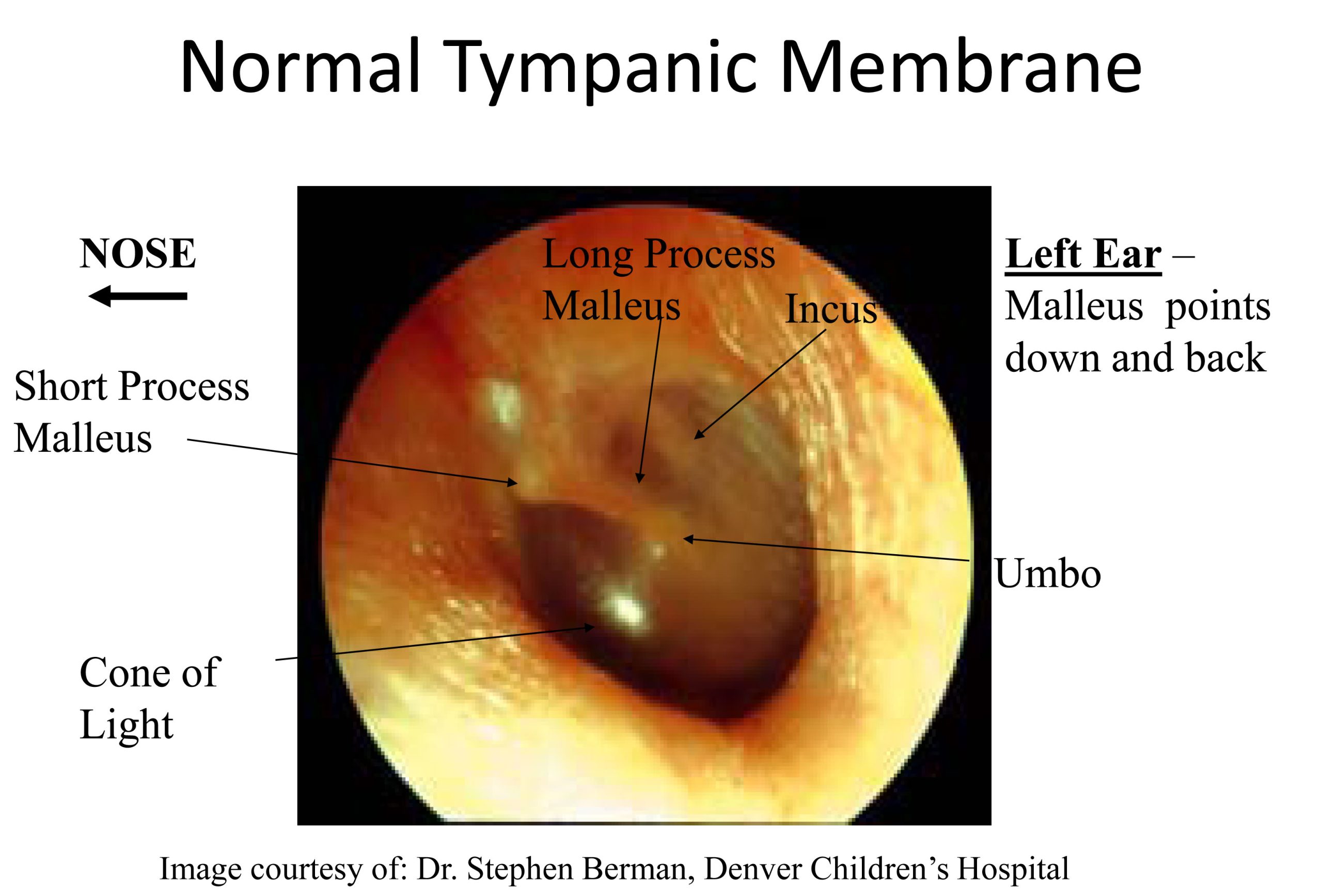
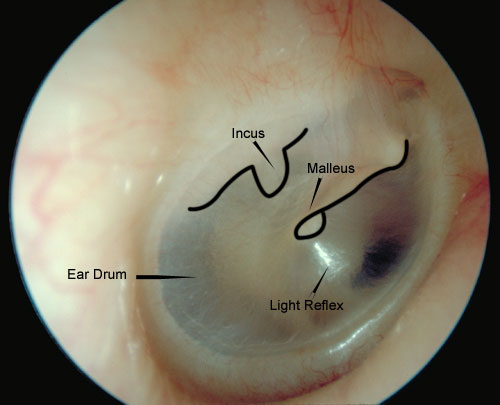
The healthy eardrum, or tympanic membrane, typically presents as a translucent, pearly gray disc. A distinct cone of light, a reflection of the otoscope's light, is usually visible anteroinferiorly. This is generally located in the lower front quadrant of the eardrum from the viewer's perspective.
The malleus, one of the small bones in the middle ear, is often visible as a subtle shadow or prominence behind the upper portion of the eardrum. Blood vessels are generally not prominent in a healthy eardrum.
Key features to look for in a normal eardrum include: intactness, mobility upon pneumatic otoscopy (if applicable), and the absence of redness, swelling, or discharge.
Abnormal Eardrum Appearance: Red Flags
Deviations from the normal appearance can indicate various ear conditions. These conditions range from mild inflammation to severe infections requiring immediate intervention.
Signs of Infection (Otitis Media)
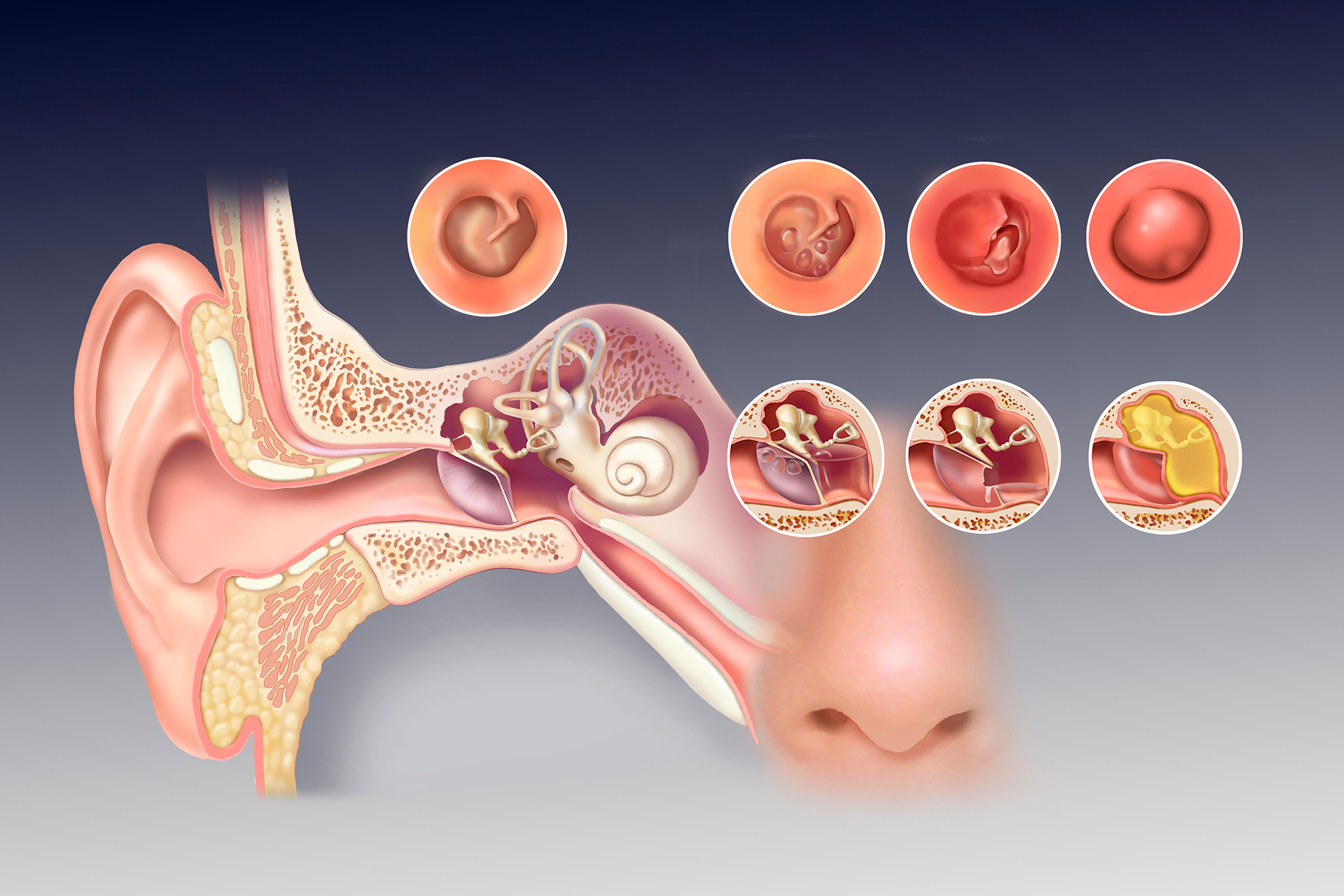
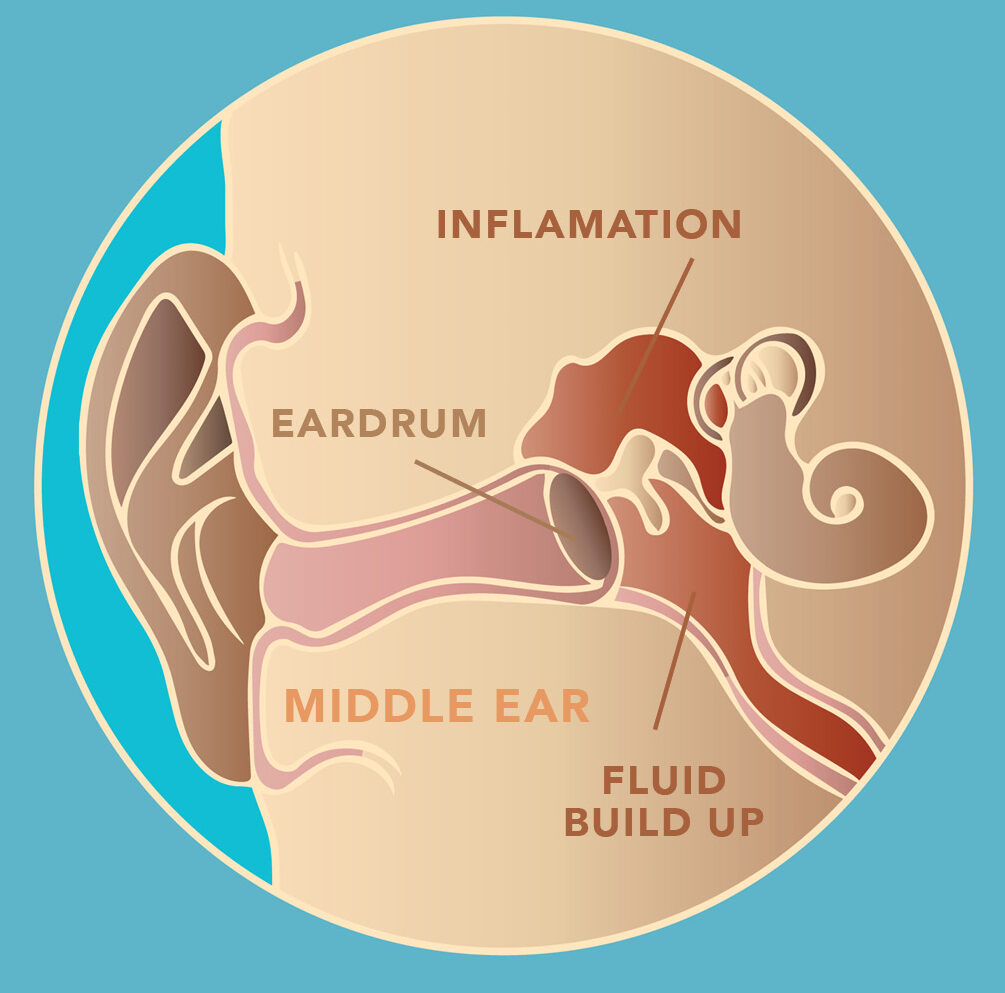
A red, bulging eardrum is a primary indicator of otitis media. This is often accompanied by a loss of the light reflex and potentially visible fluid levels behind the membrane.
In severe cases, pus or blood may be visible behind the eardrum or even draining through a perforation. This situation is typically very painful.
Eardrum Perforations
A hole or tear in the eardrum is known as a perforation. Perforations can vary in size and location and may be caused by infection, trauma, or pressure changes.
Small perforations may heal on their own, while larger ones may require surgical repair. The ability to visually assess the size and location using camera technology is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment.
Fluid Behind the Eardrum (Effusion)
The presence of fluid behind the eardrum, known as effusion, can appear as a yellowish or amber hue. An air-fluid level or bubbles may also be visible, especially with camera assistance.
Effusion is often associated with allergies, colds, or other conditions that affect the Eustachian tube's ability to drain fluid from the middle ear. Camera documentation can help monitor the resolution of the effusion.
Other Abnormalities
Tympanosclerosis, or scarring of the eardrum, appears as white patches or plaques. These are usually a result of previous infections or trauma. Camera imaging assists in the identification and monitoring of this condition.
Cholesteatoma, an abnormal skin growth in the middle ear, can present as a pearly white mass behind the eardrum. Early detection is crucial to prevent complications.
The Role of Camera Technology in Eardrum Examination
Modern otoscopes often incorporate digital cameras, allowing for image and video capture of the eardrum. This technology facilitates remote consultations and improved patient education.
Telemedicine platforms are increasingly utilizing these camera-equipped otoscopes to connect patients with specialists who may be geographically distant. The technology promotes easier acess to medical advice.
High-resolution imaging is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Clarity is of utmost importance in this.
Challenges and Considerations
Image quality can vary depending on the camera's resolution, lighting conditions, and the examiner's skill. Standardization of image acquisition protocols is necessary.
Training is crucial to ensure that healthcare providers can accurately interpret the images and videos obtained. Consistent interpretations of what is seen reduces error.
Accurate diagnosis relies on the combination of visual findings and the patient's medical history and symptoms. The visuals by themselves are not sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Looking Ahead
Further research is needed to establish standardized criteria for interpreting eardrum images and videos. The goal is to improve diagnostic accuracy and inter-rater reliability.
Continued advancements in camera technology will likely lead to even clearer and more detailed visualizations of the eardrum. This offers more chances for better understanding.
Efforts are ongoing to develop artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that can assist in the automated analysis of eardrum images. The algorithms will serve as a medical assistant and speed up the diagnostic process.