What Does The Process Of Controlling Costs Primarily Involve
In an era defined by economic uncertainty and fierce competition, the ability to effectively control costs is no longer just a desirable business practice – it's a fundamental imperative for survival and sustained success. From multinational corporations navigating complex global supply chains to small startups striving to gain a foothold, the pressure to optimize spending and maximize value is relentless.
However, cost control isn't simply about slashing budgets indiscriminately. It's a multifaceted process that requires a strategic approach, a deep understanding of underlying cost drivers, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
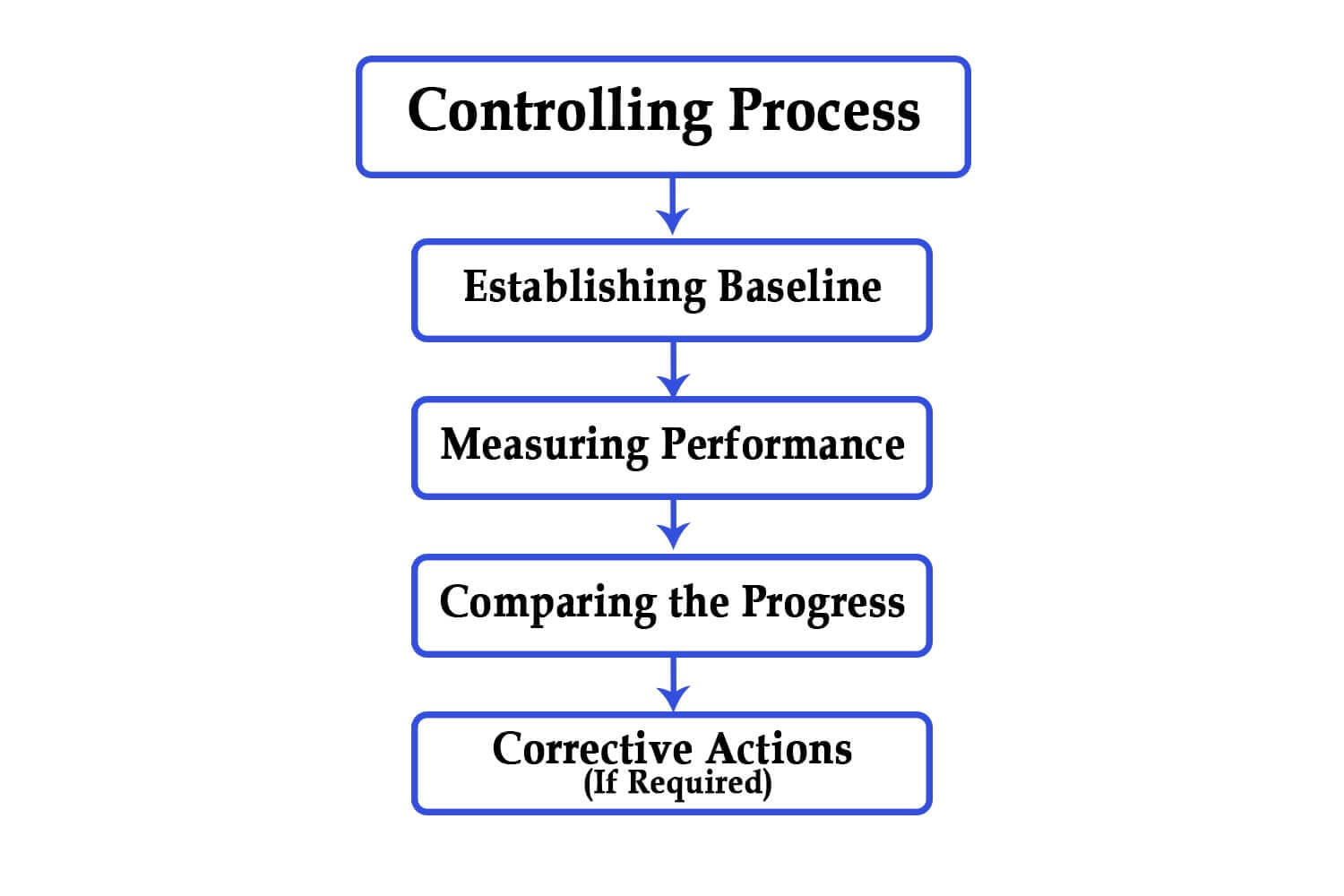
At its core, the process of controlling costs primarily involves a systematic and proactive approach to identifying, analyzing, and managing expenses. This includes setting clear financial goals, meticulously tracking expenditures, pinpointing areas of inefficiency, and implementing strategies to optimize resource allocation and minimize waste. Ultimately, it’s about creating a culture of cost consciousness throughout the organization.
The Foundation: Planning and Budgeting
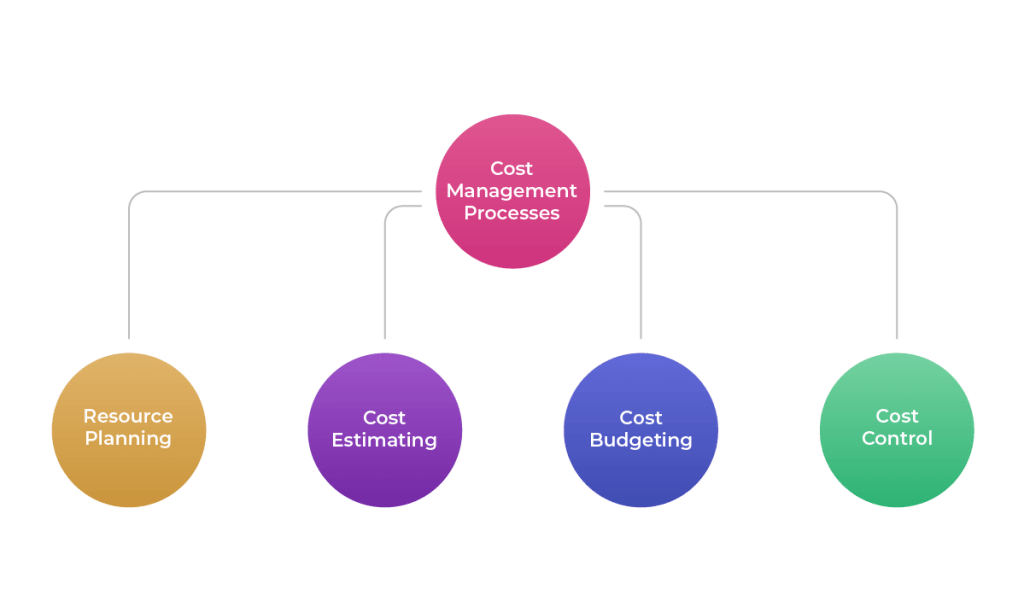
Effective cost control begins with robust planning and budgeting processes. A well-defined budget serves as a roadmap, outlining anticipated revenues and expenses for a specific period. "Budgeting provides a framework for aligning financial resources with strategic objectives," explains Dr. Anya Sharma, a Professor of Finance at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania.
This alignment ensures that spending is prioritized in areas that will generate the greatest return and contribute to long-term growth. This involves careful consideration of market conditions, competitive pressures, and internal capabilities.
Budgeting also requires a thorough understanding of cost behavior – how costs change in response to fluctuations in activity levels. This is crucial for developing realistic and adaptable financial plans.
The Core: Cost Identification and Analysis
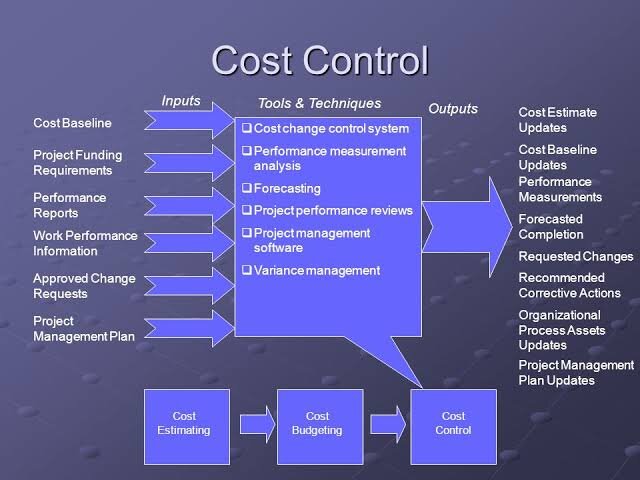
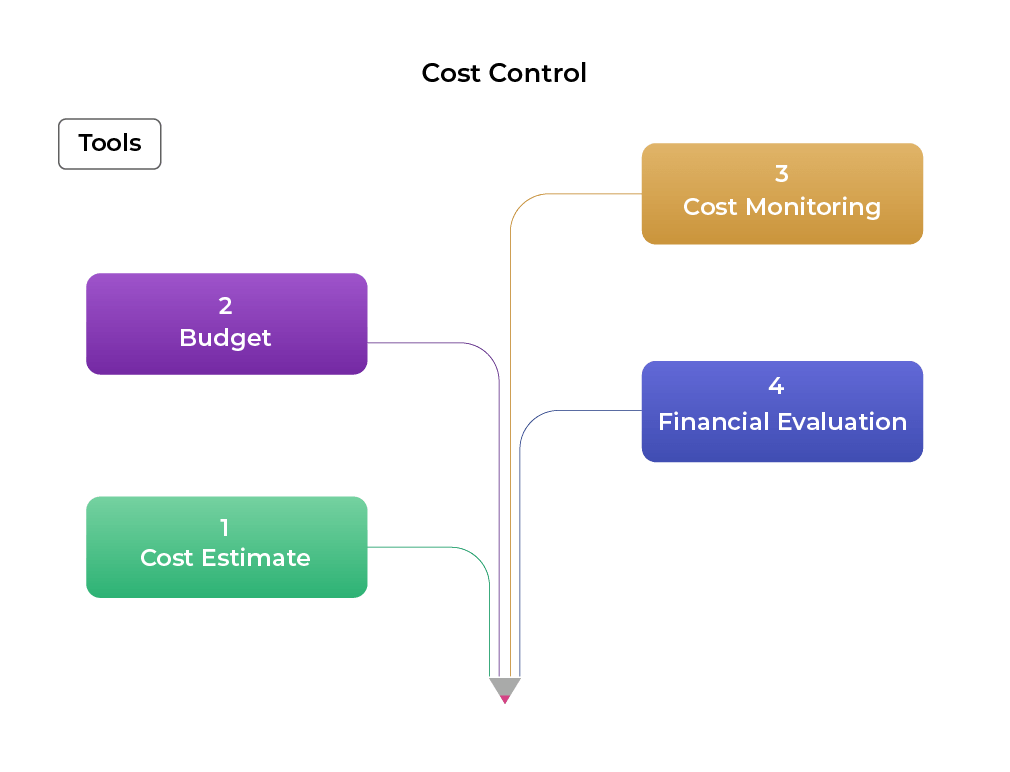
Once a budget is in place, the next step is to meticulously track and analyze actual expenditures. This involves identifying all relevant costs, categorizing them appropriately, and comparing them against the budgeted amounts.
Cost accounting systems play a vital role in this process. These systems provide detailed information about the cost of producing goods or services, allowing businesses to identify areas where costs are exceeding expectations.
Variances between actual and budgeted costs are carefully investigated to determine the underlying causes. This analysis helps to pinpoint inefficiencies, waste, or unexpected price increases.
The Engine: Implementation and Monitoring
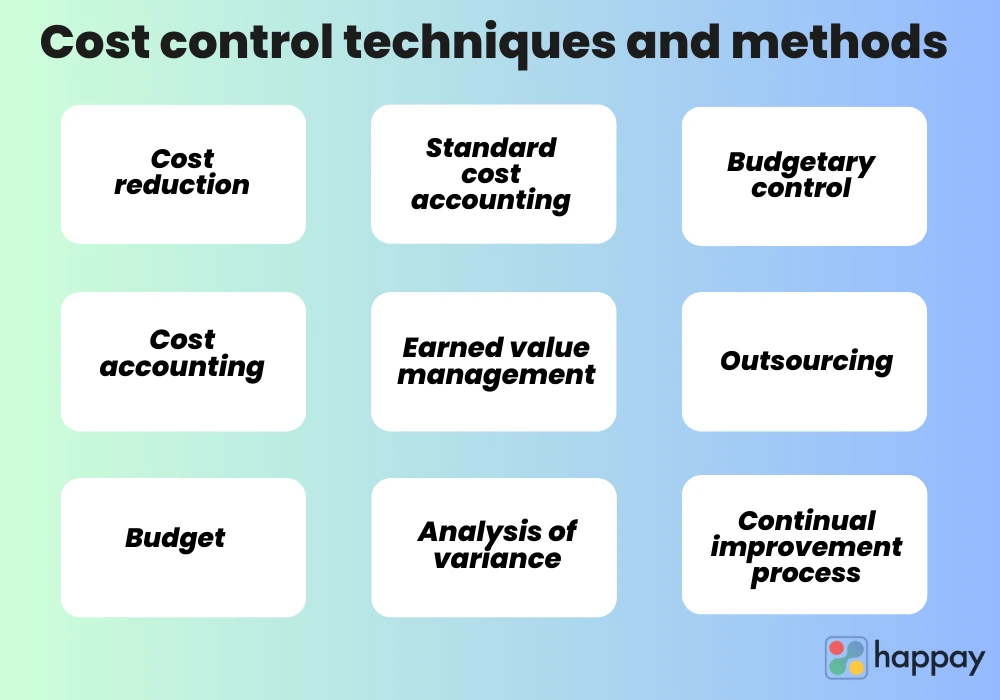
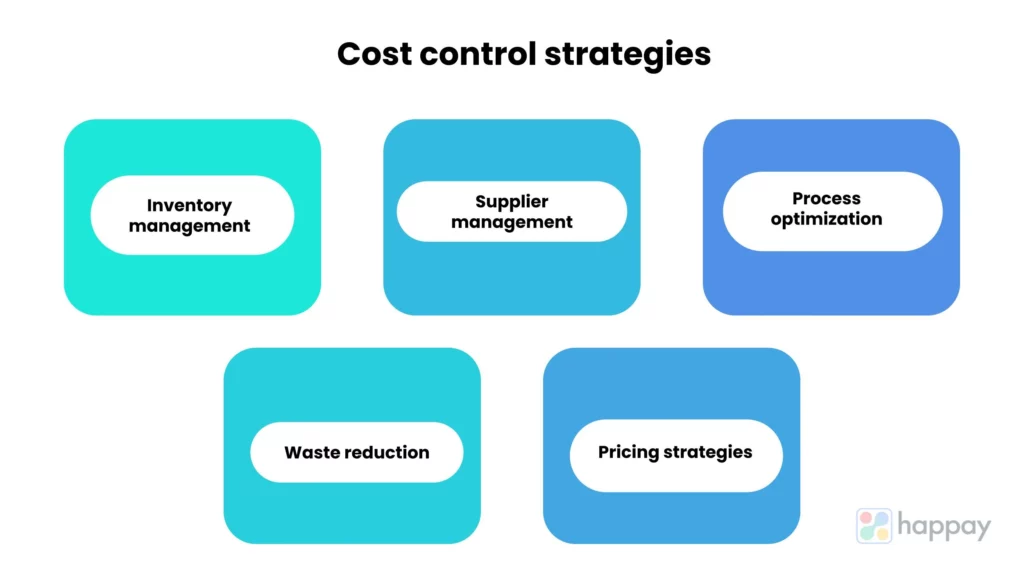
Identifying cost overruns is only the first step. The real challenge lies in implementing effective strategies to bring costs back under control. These strategies may include streamlining processes, negotiating better deals with suppliers, investing in technology to automate tasks, or reducing headcount.
Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure that these strategies are working as intended. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to track progress and identify any emerging issues.
Regular performance reviews are conducted to assess the effectiveness of cost control measures and make adjustments as needed. This iterative process ensures that cost management remains dynamic and responsive to changing circumstances.
The Human Factor: Culture and Communication
Effective cost control isn't just about numbers and spreadsheets; it's also about people and culture. Creating a culture of cost consciousness requires buy-in from all levels of the organization.
Open communication is key to fostering this culture. Employees need to understand the importance of cost control, how their actions impact the bottom line, and how they can contribute to the effort.
Incentive programs can be used to reward employees for identifying and implementing cost-saving ideas. This encourages a sense of ownership and accountability.
External Perspectives: Benchmarking and Best Practices
Looking beyond internal operations is also crucial for effective cost control. Benchmarking against industry peers can provide valuable insights into best practices and potential areas for improvement.
Professional organizations and industry associations often publish data on cost structures and performance metrics. This data can be used to identify areas where a company is lagging behind its competitors.
Adopting industry best practices can lead to significant cost savings and improved efficiency. This may involve implementing new technologies, adopting lean manufacturing principles, or outsourcing non-core activities.
The Future: Technology and Automation
The future of cost control is inextricably linked to technology and automation. Cloud-based accounting systems, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotic process automation (RPA) are transforming the way businesses manage their finances.
These technologies can automate manual tasks, improve accuracy, and provide real-time visibility into cost data. "AI-powered analytics can identify hidden cost drivers and predict future expenses with greater accuracy," says John Carter, a leading expert in financial technology.
Furthermore, blockchain technology has the potential to streamline supply chain management and reduce transaction costs. By embracing these technological advancements, businesses can gain a significant competitive advantage in the fight to control costs.
Looking Ahead: Adaptability and Resilience
In conclusion, the process of controlling costs is a dynamic and ongoing endeavor that requires a strategic approach, a commitment to continuous improvement, and a willingness to embrace change. It's not merely about cutting expenses; it's about optimizing resource allocation and maximizing value creation.
As the global economy becomes increasingly complex and unpredictable, the ability to effectively control costs will be essential for survival and sustained success. Adaptability and resilience will be the hallmarks of businesses that thrive in this challenging environment. The focus must be on building a cost-conscious culture that empowers employees to identify and implement cost-saving ideas, while leveraging technology to gain a competitive edge.
By embracing these principles, organizations can navigate economic uncertainties, achieve their financial goals, and create long-term value for their stakeholders. In a world of constant change, cost control remains a cornerstone of sustainable business performance.
![What Does The Process Of Controlling Costs Primarily Involve Cost Control: Monitor Project Spending & Profitability [2022] • Asana](https://assets.asana.biz/m/274ac5c55c96eea2/original/inline-work-management-cost-control-2-2x.jpg)
![What Does The Process Of Controlling Costs Primarily Involve Cost Control: Monitor Project Spending & Profitability [2022] • Asana](https://assets.asana.biz/m/385ee64bdac9a995/original/inline-work-management-cost-control-1-2x.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cost-control-FINAL-75f723c92bc3468f83a6541d107d7520.png)