What Is Street Smart And Book Smart

In a world that increasingly values formal education, the dichotomy between street smarts and book smarts remains a captivating and crucial discussion. While academic achievements are readily quantifiable through grades and degrees, the intangible qualities of street smarts, honed through lived experience, often prove equally, if not more, valuable in navigating the complexities of life.
This article explores the nuances of these two distinct forms of intelligence, examining their characteristics, strengths, and limitations. We delve into how each contributes to success, adaptability, and overall well-being. We also consider the interplay between them, and how a balance can lead to a well-rounded individual.
Defining Book Smarts
Book smarts refer to the knowledge and skills acquired through formal education, reading, and academic study. It encompasses a mastery of theoretical concepts, facts, and information that are typically assessed through standardized tests and academic performance.
Individuals with strong book smarts often excel in structured learning environments. They are adept at analyzing information, solving problems using established methodologies, and retaining vast amounts of data. This kind of smart can lead to specialized jobs and opportunities.
However, book smarts can sometimes be limited by a lack of practical experience or an inability to adapt theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. This can cause struggle when they leave the structured, controlled environment of the classroom.
Understanding Street Smarts
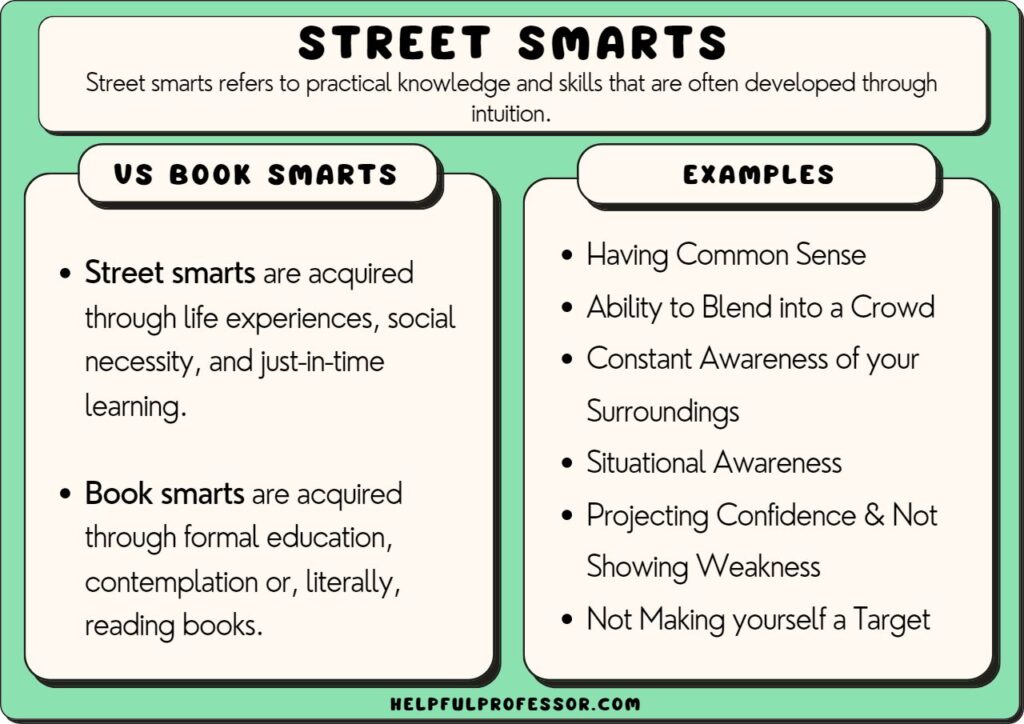
In contrast to book smarts, street smarts represent a practical intelligence developed through navigating real-life situations, particularly in challenging environments. It is the ability to understand people, anticipate problems, and effectively manage unpredictable circumstances.
Street smarts involve a high degree of emotional intelligence, resourcefulness, and adaptability. This kind of person often has quick thinking skills, and can solve problems without being given the structure of a classroom.
People who are street smart may not possess extensive formal education, but they have honed their survival and problem-solving skills through direct experience. These skills can be beneficial in many areas of life.
Strengths and Limitations
Book smarts offer a structured framework for understanding the world, providing a foundation for critical thinking and analytical skills. However, it can sometimes lack the flexibility and adaptability required to thrive in unpredictable situations.
Street smarts, on the other hand, excel in navigating ambiguity and uncertainty. Their quick wit and understanding of human behavior can be invaluable in high-pressure situations. On the other hand, this type of smart can lack proper training in some fields.
A key limitation of street smarts is that it may rely heavily on intuition and anecdotal evidence, potentially leading to biases or flawed decision-making. A person who is only street smart may have a harder time getting a job, as they lack degrees and certifications.
The Interplay and Balance
Ideally, a balanced approach that combines both book smarts and street smarts provides the most comprehensive foundation for success. Book smarts offers a theoretical framework, while street smarts provides the practical skills to apply that knowledge effectively.
Emotional intelligence, a key component of street smarts, complements the analytical abilities fostered by book smarts. Together, they foster well-rounded decision making. Emotional intelligence is required to read nonverbal cues and body language of people.
Many successful individuals across various fields demonstrate a blend of both qualities. They leverage their formal education while also drawing upon their real-world experiences and intuitive understanding of people and situations.
Looking Ahead
As the world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to navigate diverse social environments and adapt to unforeseen challenges is more critical than ever. Recognizing the value of both street smarts and book smarts is essential for personal and professional growth.
Educational institutions and employers should strive to cultivate both forms of intelligence. Incorporating real-world applications into academic curricula and providing opportunities for experiential learning can help bridge the gap between theory and practice. This can help create well-rounded members of society.
Ultimately, the most effective approach involves continuous learning and adaptation. By embracing both formal knowledge and practical experience, individuals can develop a holistic understanding of the world and achieve greater success in their personal and professional lives. The most important aspect is that both kinds of intelligence are fostered.