Distribution And Conservation Of Threatened Plants In China

China's botanical heritage, a tapestry woven with millennia of evolution, is fraying at the edges. Countless plant species, some found nowhere else on Earth, are silently slipping towards extinction, victims of habitat loss, climate change, and unsustainable exploitation. The race to document, protect, and propagate these threatened flora is a national imperative, demanding innovative strategies and unwavering commitment.
At the heart of this crisis lies a complex web of interconnected challenges. China's rapid economic development has fueled widespread land conversion, shrinking natural habitats and fragmenting ecosystems. This article delves into the current status of threatened plant species in China, examining the critical efforts underway to ensure their survival through strategic distribution and robust conservation measures. It will explore the roles of governmental organizations, research institutions, and local communities in this vital endeavor, highlighting both the successes achieved and the formidable obstacles that remain.
The Scale of the Problem: A Botanical Crisis
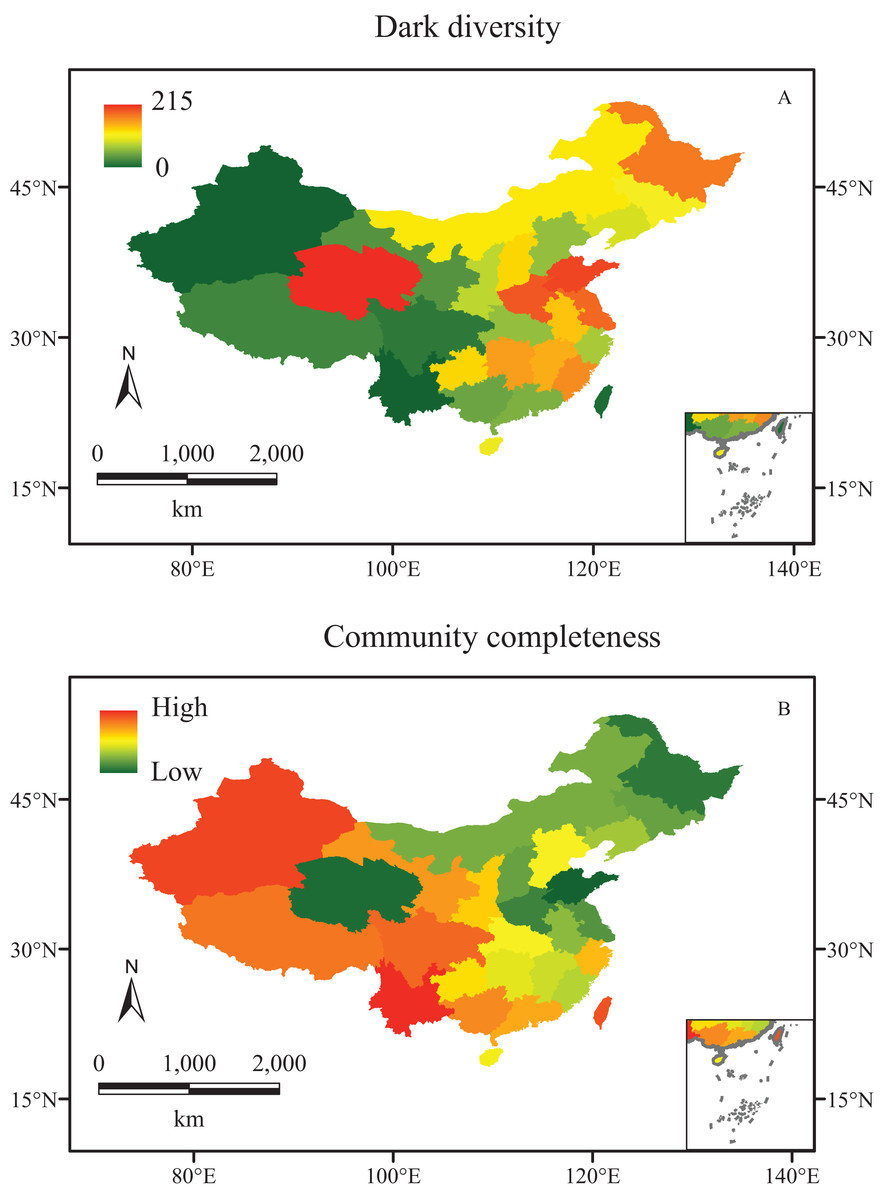
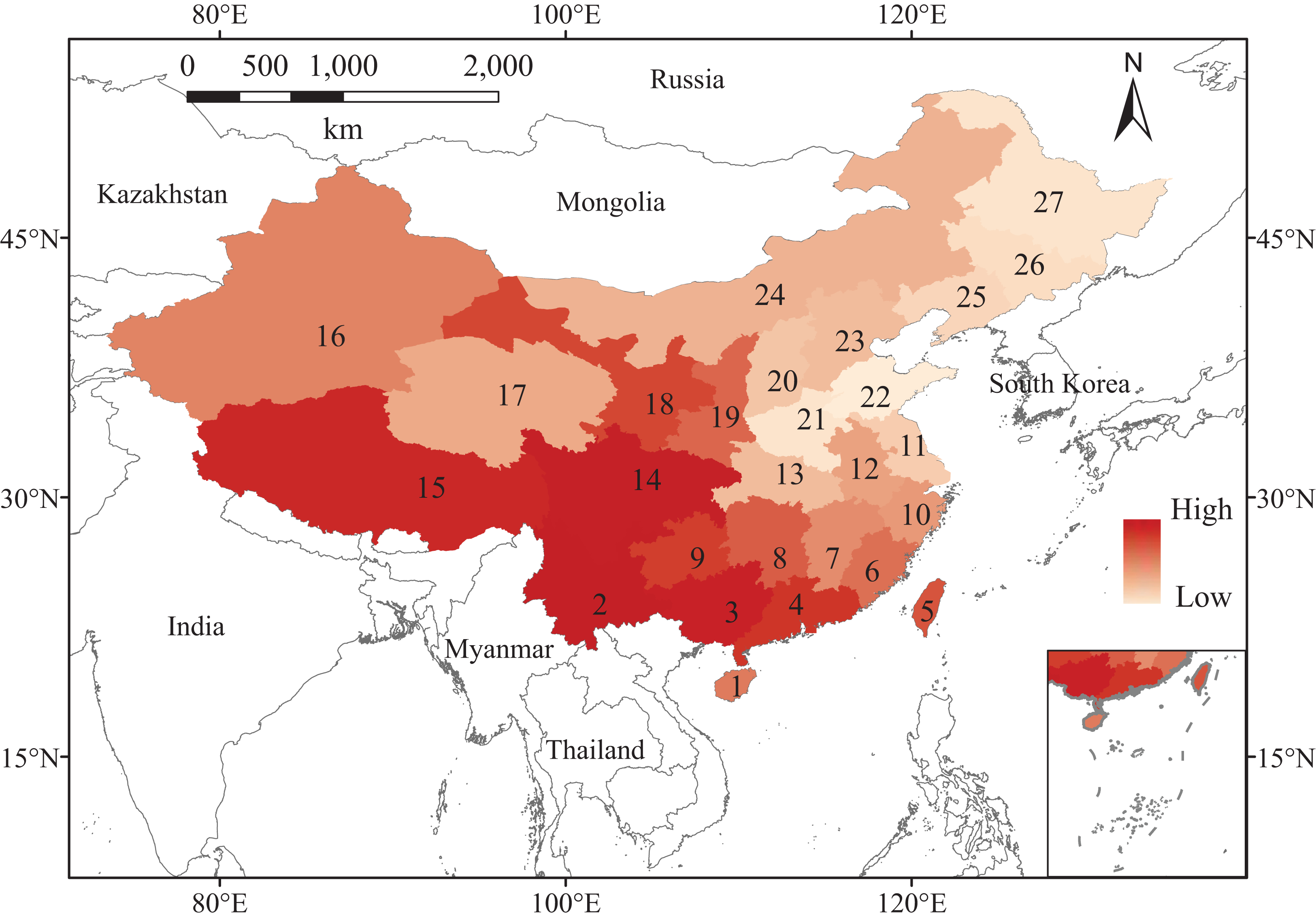
China is a megadiverse country, harboring an estimated 30,000 vascular plant species, representing about 10% of the world's total. However, this botanical richness is under severe threat. The IUCN Red List identifies hundreds of Chinese plant species as endangered or critically endangered, and the true number of threatened plants is likely much higher.
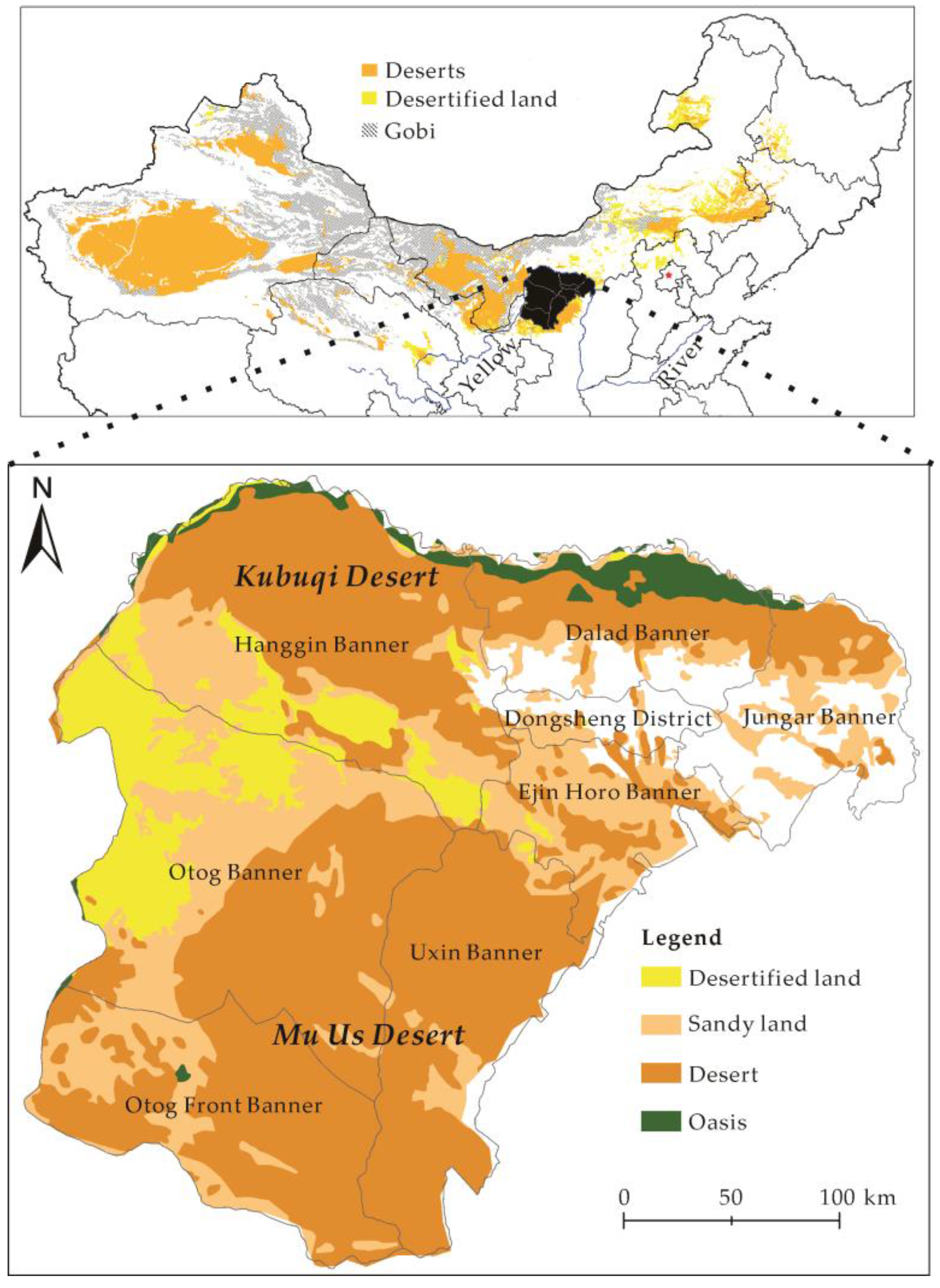
Habitat loss due to agricultural expansion, urbanization, and infrastructure development is the primary driver of plant extinctions. Illegal logging, over-collection of medicinal plants, and the introduction of invasive species exacerbate the problem. Climate change adds another layer of complexity, altering temperature and precipitation patterns, and shifting suitable habitats beyond the reach of many species.
Conservation Strategies: A Multifaceted Approach
China has implemented various conservation strategies to protect its threatened flora. These efforts range from in-situ conservation, which focuses on protecting plants in their natural habitats, to ex-situ conservation, which involves preserving plants outside their natural environment.
In-situ conservation is primarily achieved through the establishment of protected areas, such as national parks, nature reserves, and botanical gardens. These areas provide safe havens for threatened plants, allowing them to thrive without the pressures of human development.
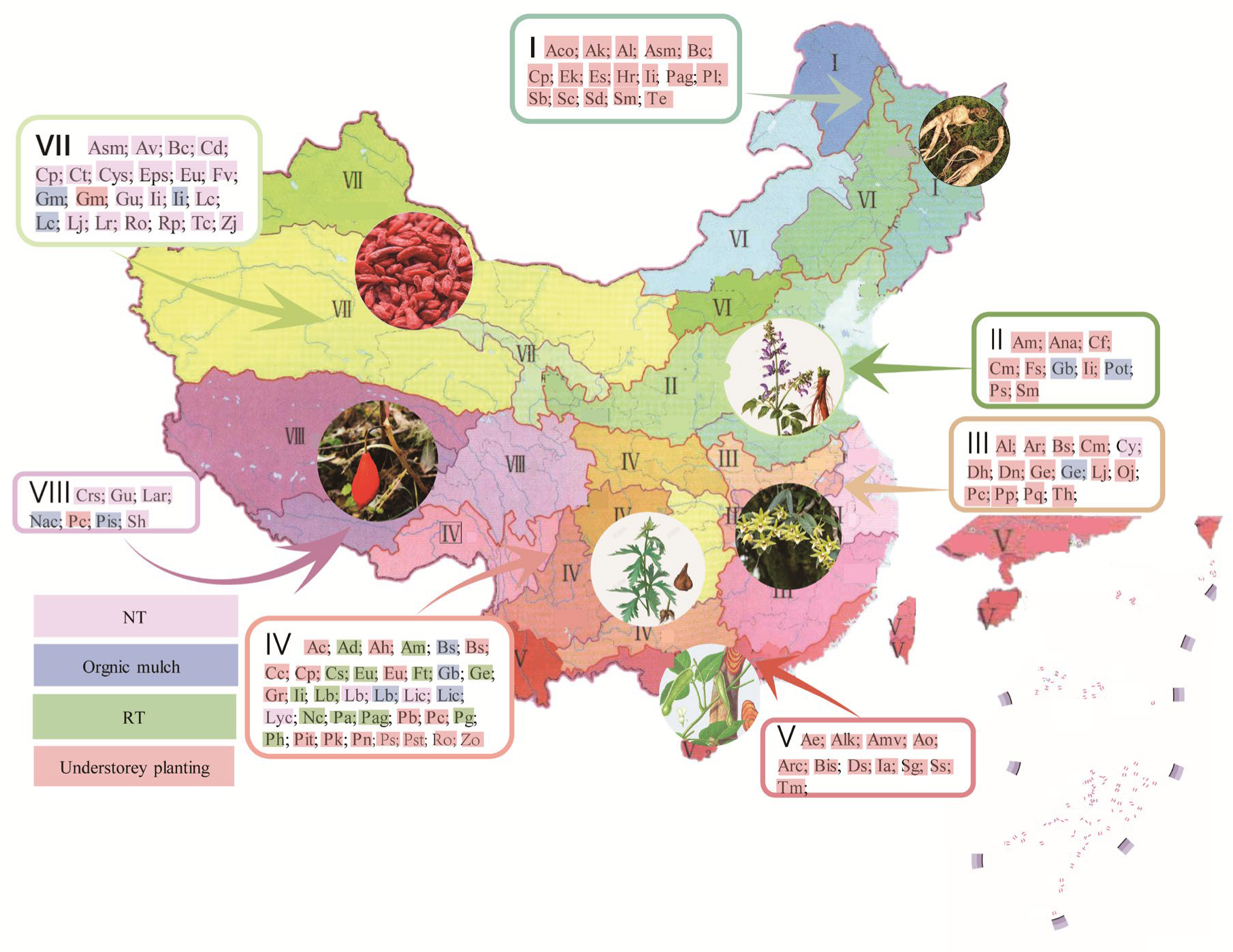
Ex-situ conservation involves the collection, storage, and propagation of threatened plant species in seed banks, botanical gardens, and research institutions. The Kunming Institute of Botany, for example, plays a crucial role in seed banking and plant propagation, safeguarding genetic diversity for future generations.
Distribution and Reintroduction: Restoring Lost Landscapes
A crucial aspect of plant conservation is the distribution and reintroduction of threatened species into suitable habitats. This process involves carefully selecting appropriate sites, propagating plants in nurseries, and then transplanting them back into the wild.
The reintroduction of Davidia involucrata (Dove Tree), a vulnerable species native to central and southwestern China, serves as a successful example. Through collaborative efforts between research institutions and local communities, the Dove Tree has been successfully reintroduced into several protected areas.
Careful monitoring is essential to ensure the success of reintroduction programs. Factors such as habitat suitability, plant health, and interactions with other species must be closely monitored to assess the long-term viability of the reintroduced populations.
The Role of Local Communities: Guardians of Biodiversity
Engaging local communities in plant conservation is essential for long-term success. Local communities often possess invaluable knowledge about plant species and their habitats, and their participation can significantly enhance conservation efforts.
Community-based conservation programs empower local residents to become stewards of their natural environment. These programs often involve training, education, and economic incentives to encourage sustainable resource management.
In some regions, local communities are involved in the cultivation of medicinal plants, providing a sustainable alternative to wild harvesting. This approach not only protects wild populations but also provides income opportunities for local residents.
Challenges and Future Directions: A Path Forward
Despite the progress made, significant challenges remain in the conservation of threatened plants in China. Funding limitations, insufficient expertise, and a lack of public awareness continue to hinder conservation efforts.
Climate change poses a particularly daunting challenge, as it alters habitats and threatens to disrupt ecosystems. Adapting conservation strategies to account for climate change is crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of threatened plants.
Moving forward, a more integrated and collaborative approach is needed. This includes strengthening partnerships between governmental organizations, research institutions, local communities, and international organizations.
Increased investment in research, education, and public awareness campaigns is essential. By fostering a greater understanding of the importance of plant conservation, we can create a more sustainable future for China's botanical heritage.
Looking ahead, the development of innovative technologies, such as remote sensing and genetic analysis, will play an increasingly important role in plant conservation. These technologies can help us to better understand plant distributions, monitor habitat changes, and identify genetically distinct populations.
The conservation of threatened plants in China is a complex and multifaceted challenge. It requires a long-term commitment, a collaborative approach, and a willingness to adapt to changing circumstances. By embracing these principles, we can ensure that China's rich botanical heritage continues to thrive for generations to come.