What Is The Ultimate Source Of Genetic Variability

In the intricate tapestry of life, genetic variability stands as the driving force behind evolution, adaptation, and the sheer diversity observed in the natural world. Understanding its ultimate source is a fundamental question in biology, captivating researchers for decades and leading to breakthroughs that reshape our understanding of life itself.
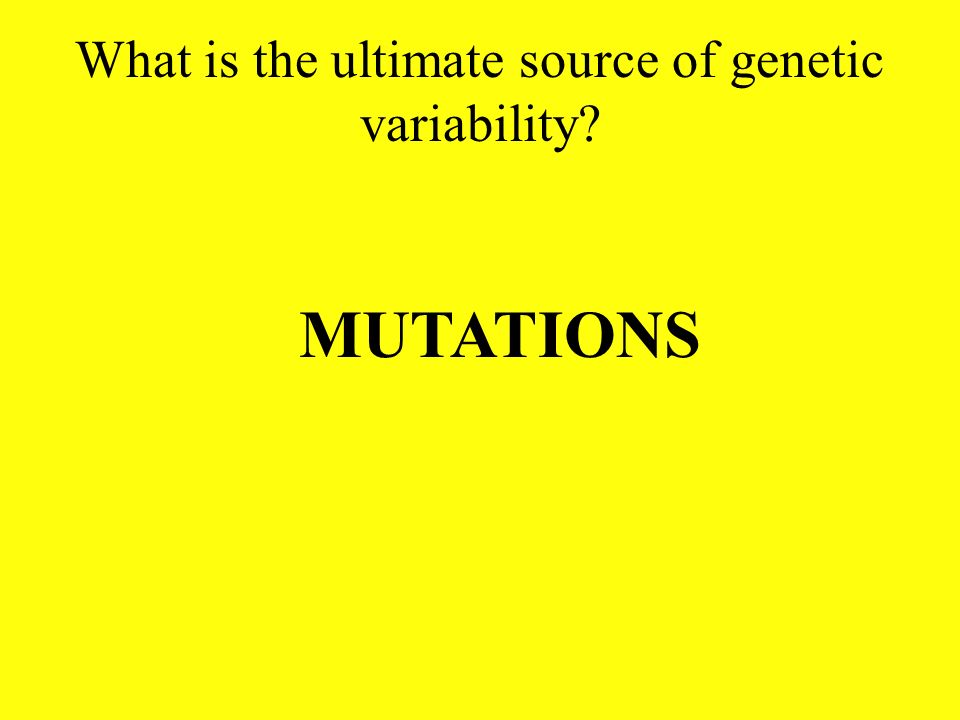
At its core, the ultimate source of genetic variability lies in the phenomenon of mutation. This article delves into the mechanisms and significance of mutation as the wellspring of all new genetic variations.
The Primacy of Mutation
Mutation, in its simplest form, is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism. These changes can be spontaneous, arising from errors during DNA replication, or induced by external factors such as radiation or certain chemicals. They are the raw material upon which natural selection acts.
Mutations can manifest in various ways, ranging from single-base substitutions to large-scale chromosomal rearrangements. These alterations in the genetic code provide the initial variation upon which other evolutionary processes operate. Without mutation, all life would be essentially clones.
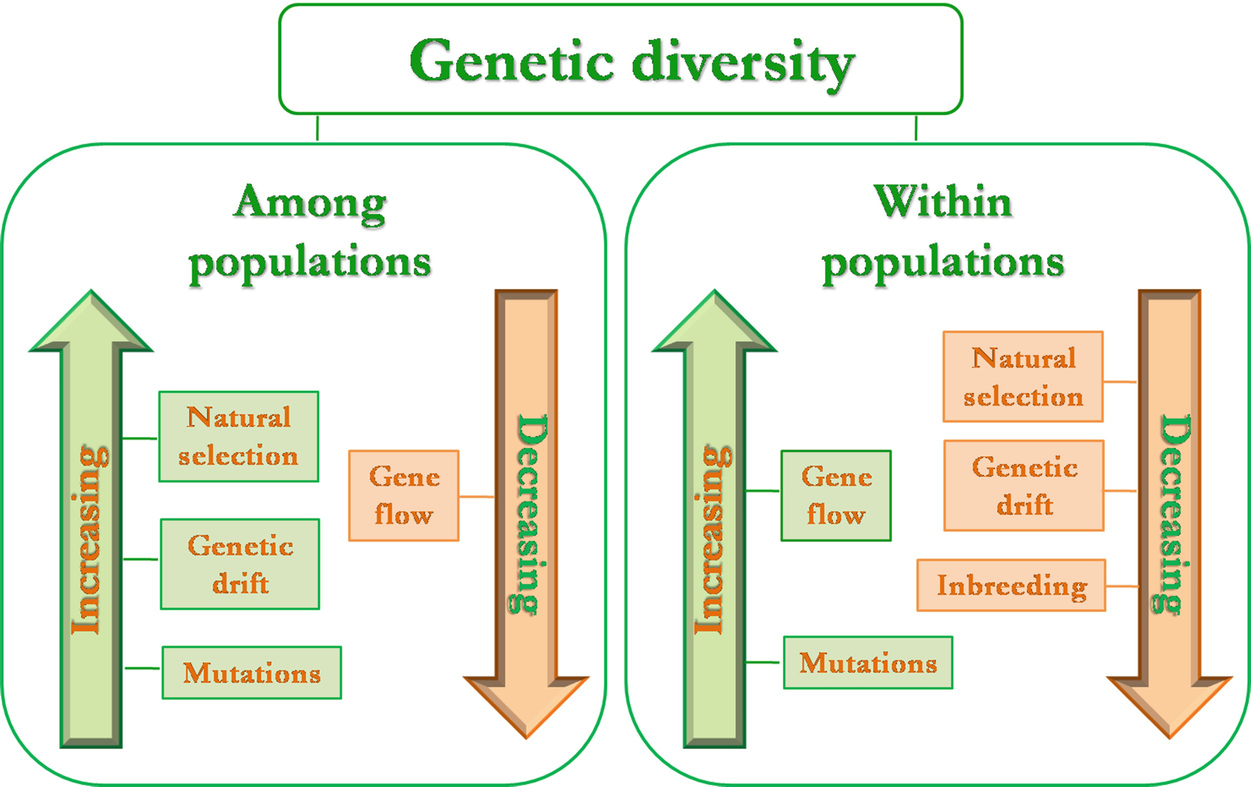
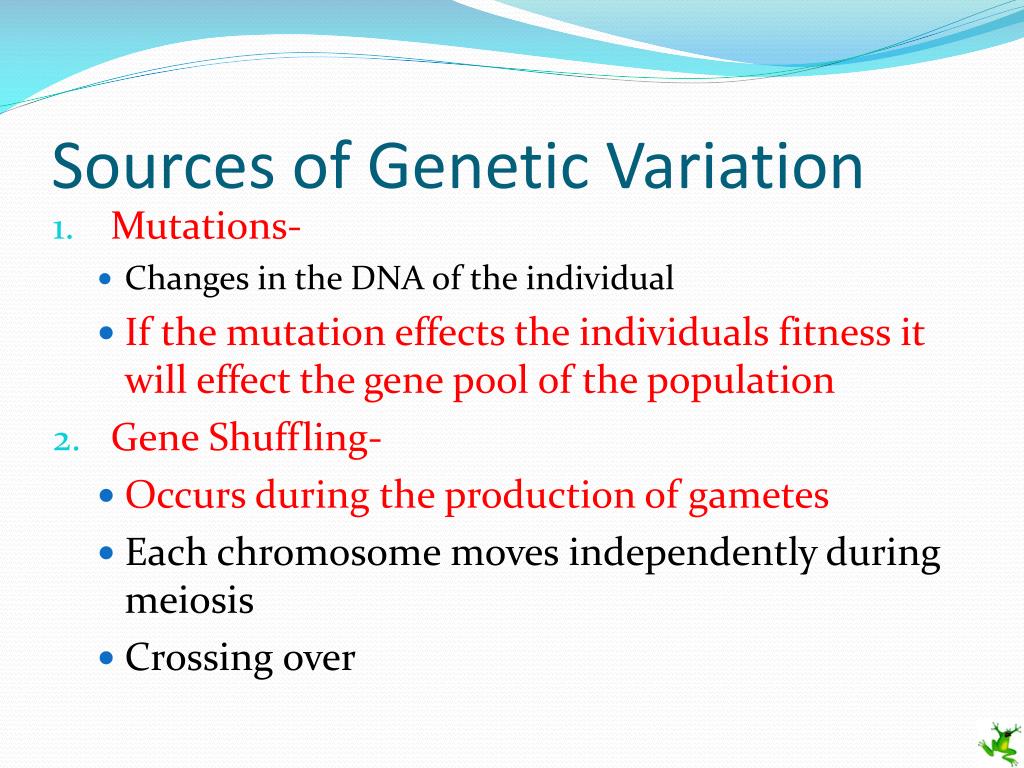
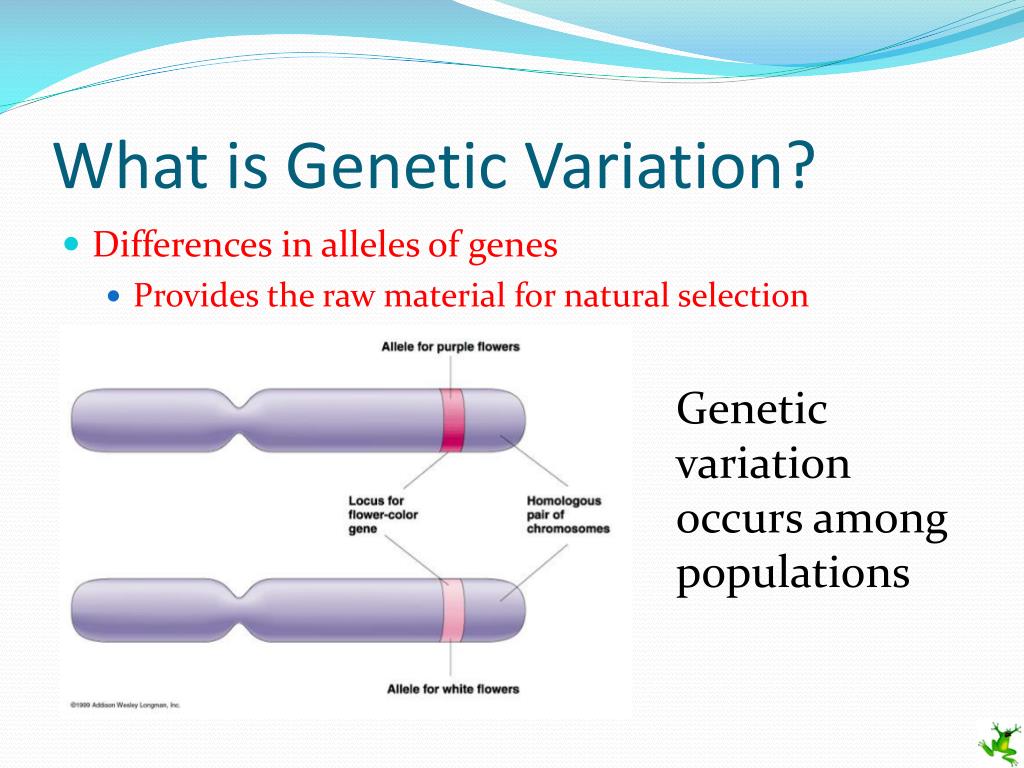
It is important to note that the term "ultimate source" refers to the origin of new genetic information. While other mechanisms, like genetic recombination, play crucial roles in shuffling existing genetic material, they do not create novel variations.
Types of Mutations
Mutations are not all created equal; their impact on an organism can vary greatly. Point mutations, which involve changes to a single nucleotide, are the most common type.
These can be further classified as substitutions, insertions, or deletions. Frameshift mutations, caused by insertions or deletions that are not multiples of three, can have devastating effects, disrupting the reading frame of a gene and leading to a completely different protein sequence.
Chromosomal mutations, on the other hand, involve larger-scale changes to the structure or number of chromosomes. These can include deletions, duplications, inversions, or translocations of entire chromosomal segments.
The Role of Other Mechanisms
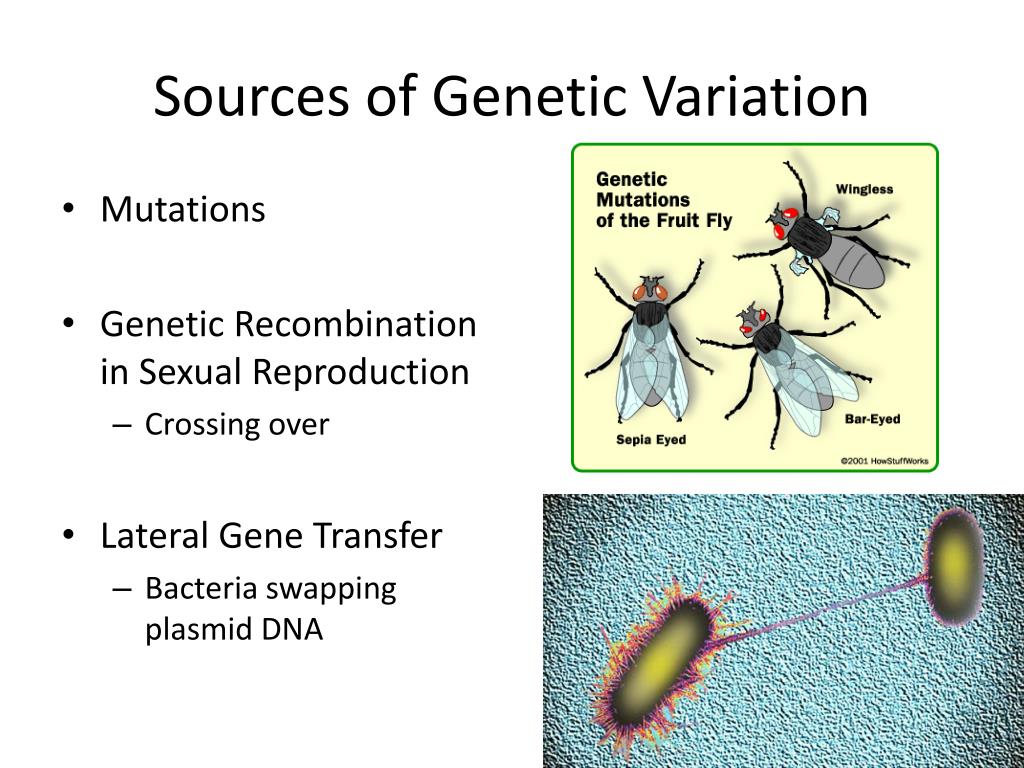
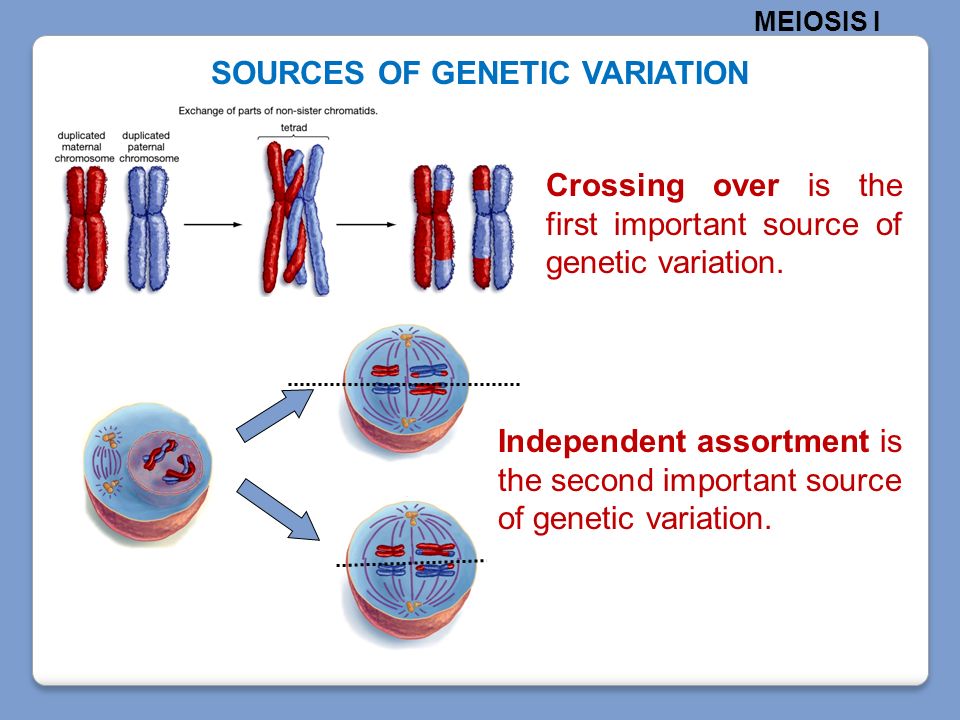
While mutation is the ultimate source, other mechanisms play essential roles in amplifying and redistributing genetic variability. Genetic recombination, which occurs during meiosis, shuffles existing genetic material between homologous chromosomes, creating new combinations of alleles.
This process, known as crossing over, does not generate new genetic information but rather rearranges existing variations. Similarly, gene flow, the movement of genes between populations, can introduce existing variations into new geographic areas.
These mechanisms are essential for increasing the frequency of beneficial mutations and spreading them throughout a population. However, without mutation, these other processes would have no raw material to work with.
The Significance of Mutation
The significance of mutation extends far beyond the realm of academic biology. It is the foundation upon which evolutionary adaptation is built, allowing organisms to respond to changing environments and exploit new ecological niches.
Understanding mutation is crucial for addressing many pressing challenges facing humanity. For instance, antibiotic resistance in bacteria arises through mutations that confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs.
Similarly, cancer is often caused by mutations that disrupt normal cell growth and division. By studying the mechanisms of mutation, scientists can develop strategies to combat these diseases and improve human health.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), research into mutation is crucial for understanding the development of inherited diseases. It also helps in the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Furthermore, mutation plays a critical role in agriculture. Plant breeders and animal breeders rely on induced mutations to create new varieties with desirable traits, such as increased yield or disease resistance. These innovations are crucial for feeding a growing global population.
The Future of Mutation Research
The study of mutation is an ongoing endeavor, with new discoveries constantly reshaping our understanding. Advances in genomics and molecular biology have provided powerful tools for studying mutation at the level of individual nucleotides and entire genomes.
Researchers are now able to identify and characterize mutations with unprecedented accuracy and speed. Furthermore, new technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing offer the potential to precisely manipulate the genome and introduce specific mutations, both for research purposes and for therapeutic applications.
One of the most promising areas of research is the study of mutational landscapes. This involves mapping the rates and patterns of mutation across the genome, which can provide insights into the mechanisms that regulate mutation and the factors that influence its distribution.
This knowledge could be used to develop strategies for preventing or correcting mutations in situations where they are harmful, such as in the context of cancer or inherited diseases.
A Human Perspective
Consider the story of a young girl diagnosed with cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene. For her and countless others, understanding mutation isn't just an academic exercise; it's a matter of life and death.
Research into the underlying causes of these mutations and the development of gene therapies offer hope for a future where these conditions can be effectively treated or even cured. This deeply personal connection underscores the profound impact that mutation research has on individuals and families around the world.
Ultimately, the story of mutation is a story of resilience, adaptation, and the remarkable capacity of life to evolve and thrive in the face of adversity.
Mutation, the source of raw material for natural selection and the engine of adaptation, stands as the ultimate source of genetic variability, driving the magnificent diversity of life on Earth. It continues to be a critical area of research, shaping our understanding of biology and holding the key to addressing some of humanity's most pressing challenges.