What Is The Underlying Concept Of Level Premiums
The promise of consistent, predictable insurance costs can be a powerful draw, especially amidst the swirling uncertainties of life. But behind the seemingly simple concept of level premiums lies a complex financial arrangement, one that requires careful consideration from both insurers and policyholders. Understanding the mechanics of level premiums is crucial for making informed decisions about long-term financial security, preventing potential surprises down the road.
This article delves into the underlying concept of level premiums in insurance, examining how they work, the financial principles behind them, and the potential benefits and drawbacks for consumers and insurers. It explores the long-term implications and factors that influence the attractiveness of level premiums in different insurance contexts, providing a comprehensive overview of this widely used pricing strategy.
The Core Principle: Smoothing Costs Over Time
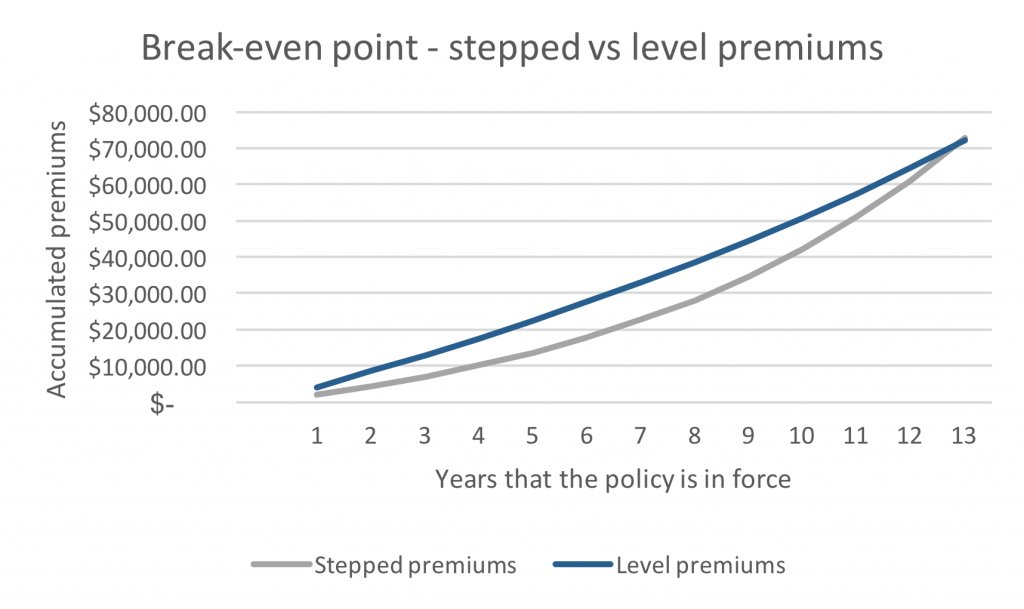
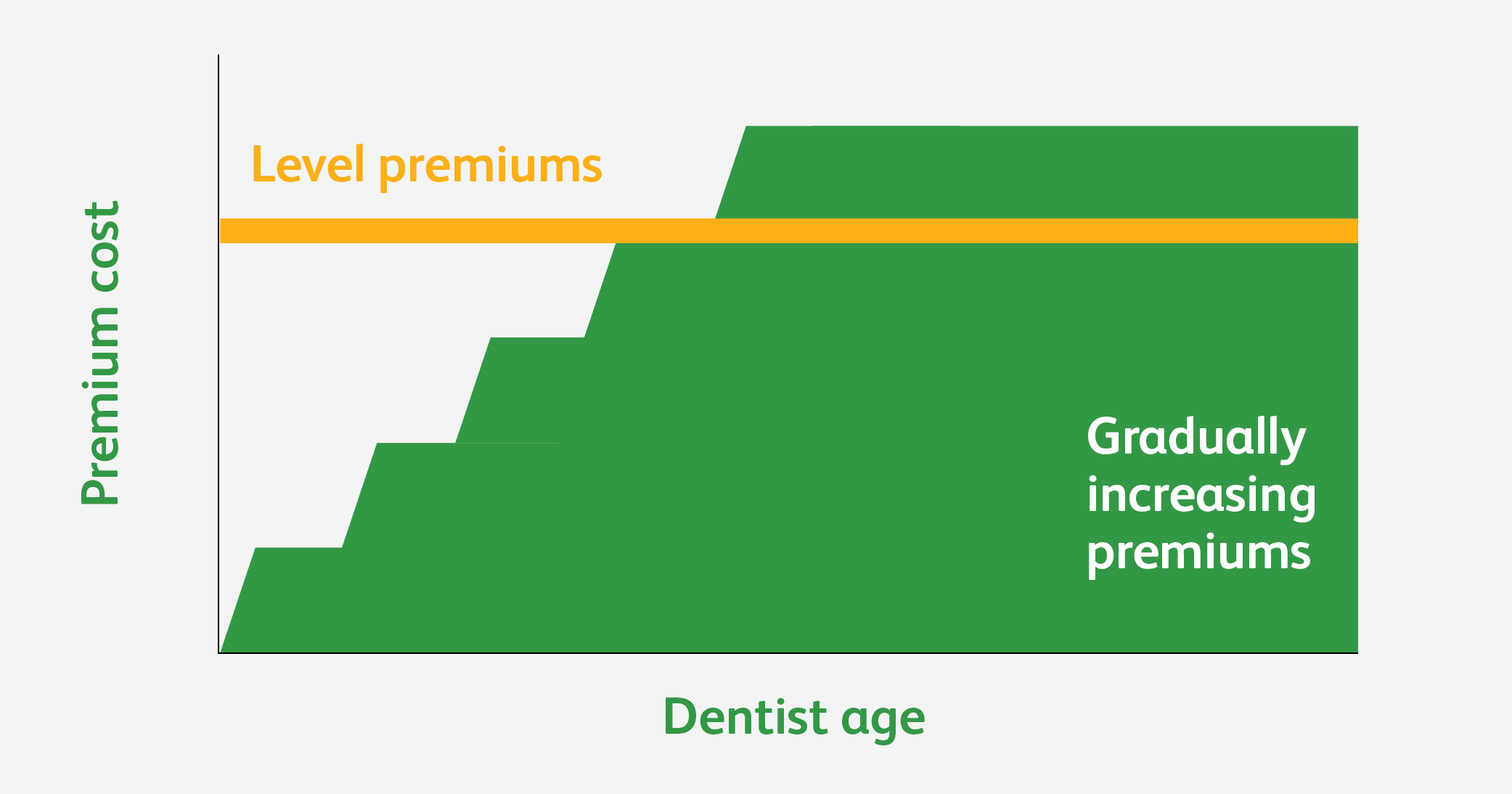
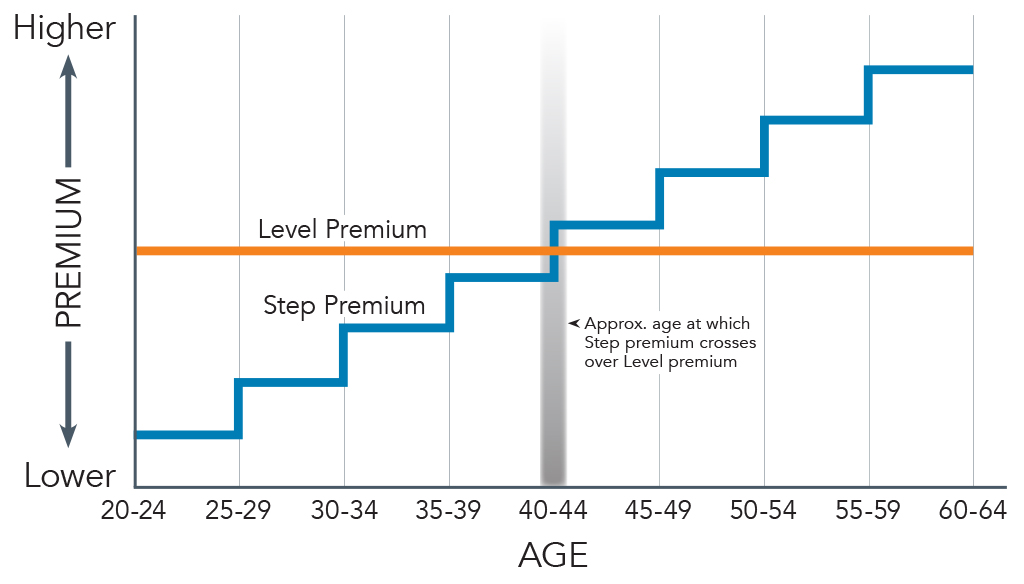
At its heart, a level premium is designed to maintain a constant premium payment for a specified period, usually the entire term of the insurance policy. This contrasts with other premium structures, such as yearly renewable term, where premiums increase annually as the policyholder ages and the risk of a claim rises.
The core principle involves overpaying in the early years of the policy to offset the underpayment in the later years when the actual cost of coverage is higher. This difference is not simply profit for the insurance company; it's carefully calculated and managed.
The insurance company invests the excess premiums collected during the initial years, and the investment earnings contribute to covering the higher cost of claims as the policyholder gets older.
How Level Premiums Work: A Financial Deep Dive
The calculation of level premiums is a complex actuarial process. Actuaries use mortality tables, interest rate assumptions, and expense projections to determine the appropriate level premium.
Mortality tables provide data on the probability of death at different ages. These projections enable actuaries to predict future claim costs.
Interest rate assumptions are crucial because the insurer relies on investment income generated from the excess premiums collected in early years. Lower interest rate environments require higher initial premiums to compensate.
Expense projections include administrative costs, commissions, and other operating expenses associated with managing the insurance policy.
Benefits for Policyholders: Predictability and Budgeting
The primary benefit of level premiums for policyholders is the predictability of costs. Knowing that the premium will remain the same for the policy's duration simplifies budgeting and financial planning.
This is particularly attractive for individuals and families who value stability and want to avoid unexpected increases in their insurance expenses.
Level premiums can also be beneficial if interest rates are low when the policy is purchased. In these cases, locking in a level premium can protect against future premium increases due to rising interest rates and higher associated costs.
Considerations for Policyholders: Potential Overpayment and Opportunity Cost
A potential drawback for policyholders is the initial overpayment compared to a policy with increasing premiums, like yearly renewable term. While premiums remain constant, policyholders essentially pay more upfront.
This means that the money paid in the early years could potentially be invested elsewhere or used for other financial goals. The opportunity cost of paying higher premiums initially must be considered.
Another consideration is the potential for needing to cancel the policy early. Cancelling a policy with level premiums, especially in the early years, might result in a lower cash value or even a loss compared to the premiums paid, depending on the policy's terms.
Benefits for Insurers: Predictable Cash Flow and Risk Management
Level premiums provide insurers with a predictable stream of income, which is essential for managing their financial obligations. This helps them better project their future cash flows.
The upfront collection of excess premiums allows insurers to build reserves and invest those reserves, generating additional income to cover future claims. This strengthens their overall financial stability.
Level premiums also help insurers manage the risk associated with rising healthcare costs or increasing mortality rates. By spreading the cost over the policy's duration, they are better insulated from unexpected spikes in claims.
Considerations for Insurers: Investment Risk and Lapse Rates
One of the biggest risks for insurers offering level premium policies is investment risk. If investment returns are lower than projected, the insurer may face difficulties in meeting its future obligations.
Another consideration is lapse rates, which is the rate at which policies are cancelled or terminated before maturity. High lapse rates, especially in the early years, can negatively impact the insurer's profitability.
Insurers must carefully manage these risks through prudent investment strategies and effective policy retention programs.
Level Premiums in Different Insurance Contexts
Level premiums are commonly used in various types of insurance, including life insurance, health insurance, and long-term care insurance. The specific application and advantages can vary depending on the type of coverage.
In life insurance, level premiums are often preferred for their predictability and long-term security. These policies are designed to provide financial protection for beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder's death.
In health insurance, level premiums can help stabilize healthcare costs for individuals and families. This is especially valuable for those with chronic conditions or those who anticipate needing significant medical care in the future.
The Future of Level Premiums: Adapting to Change
The continued attractiveness of level premiums depends on various factors, including interest rate environments, healthcare costs, and consumer preferences. As interest rates fluctuate and healthcare costs continue to rise, insurers will need to adapt their pricing strategies to ensure the sustainability of level premium products.
Technological advancements and evolving actuarial models may also play a role in refining the calculation of level premiums and improving their accuracy. New predictive models can help insurers more precisely estimate future claim costs.
Ultimately, the success of level premiums depends on the ability of insurers to balance the needs of policyholders for predictable costs with the financial realities of providing long-term insurance coverage. Continuing communication and transparency are key to sustaining trust in this complex financial arrangement.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/10OptionsStrategiesToKnow-02_2-6804019b335144f5b3cd32ffae8dae2b.png)