What Security Type For Wireless Network
Urgent security alert: Unsecured wireless networks are a major threat. Immediate action is required to safeguard personal and business data.
This article provides a concise guide to selecting the right wireless security protocol. It's vital to protect your network from unauthorized access and data breaches.
Understanding the Risks
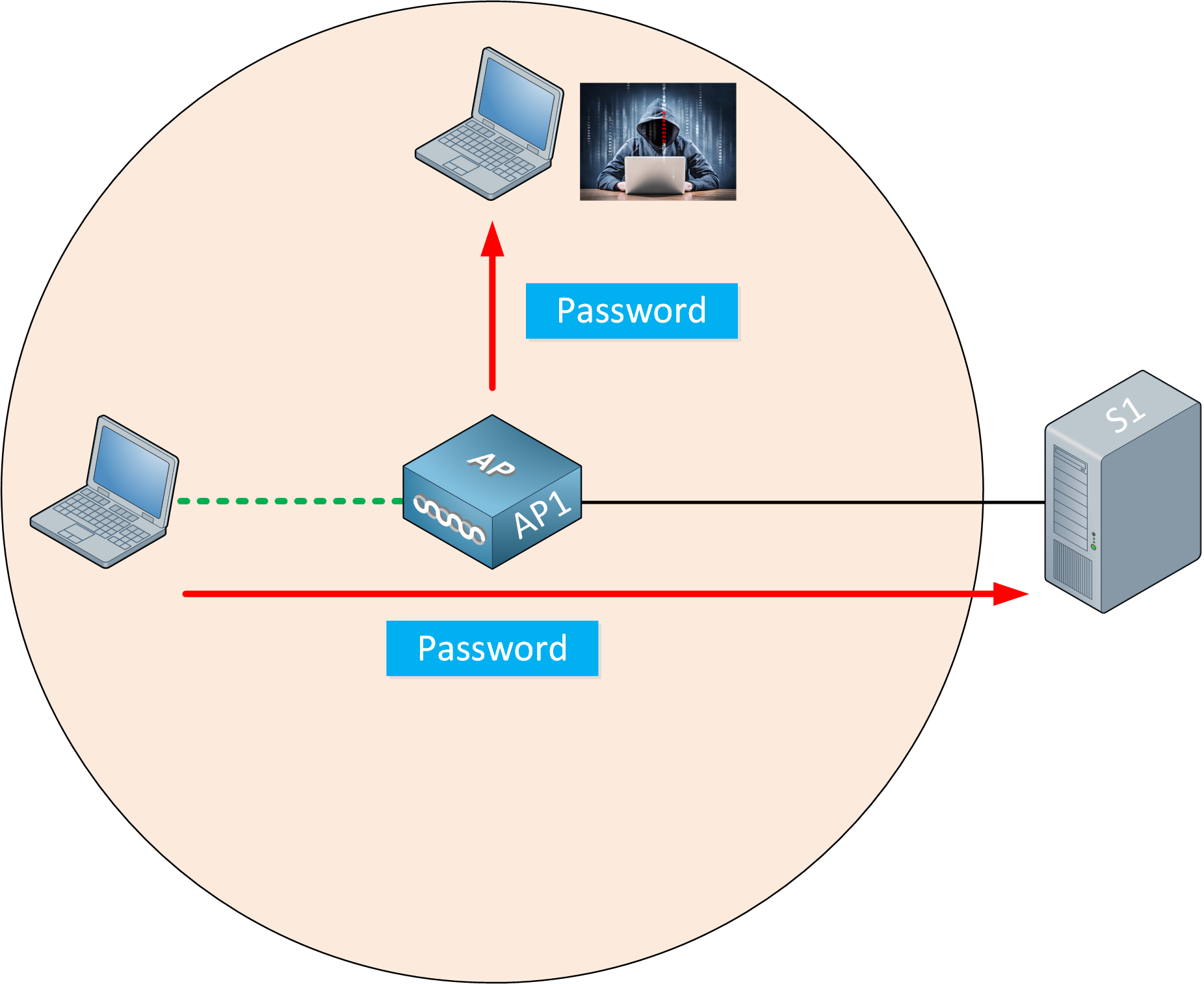
Unprotected Wi-Fi networks are easily exploited by hackers. They can steal passwords, intercept sensitive information, and even launch attacks on other devices connected to the network.
According to a 2023 report by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime damages are predicted to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. Securing your Wi-Fi is a crucial step in mitigating this risk.
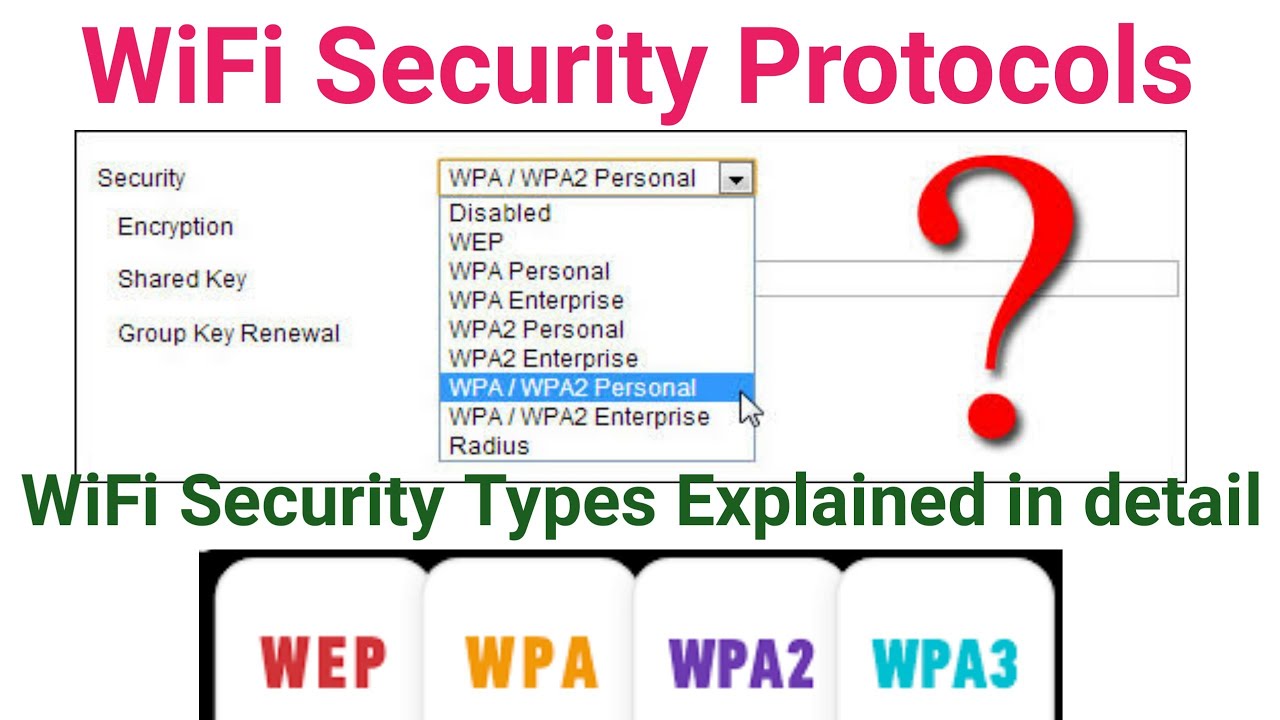
Wireless Security Protocols: A Comparison
Several security protocols exist, each offering varying levels of protection. Knowing the differences is essential for making an informed decision.
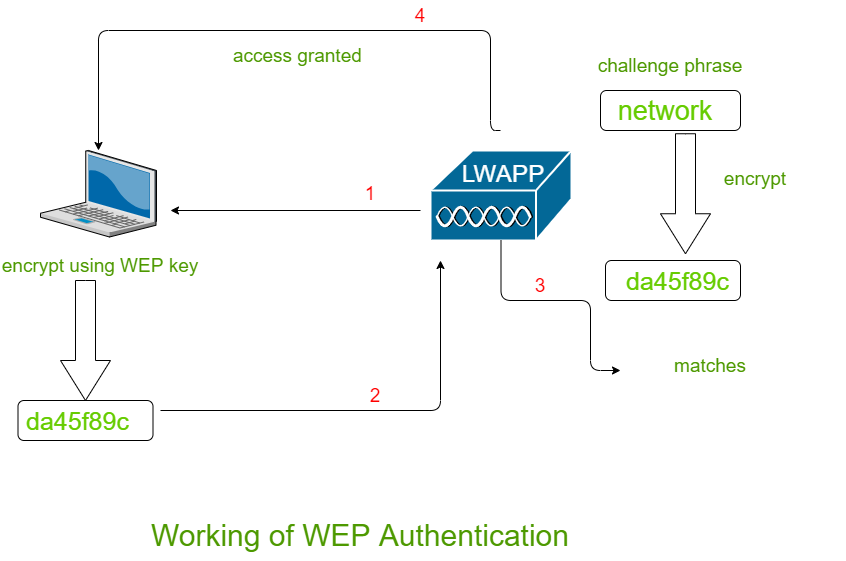
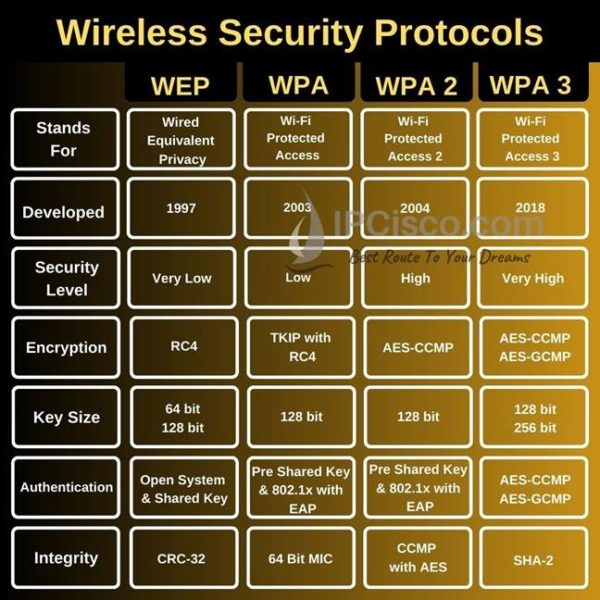
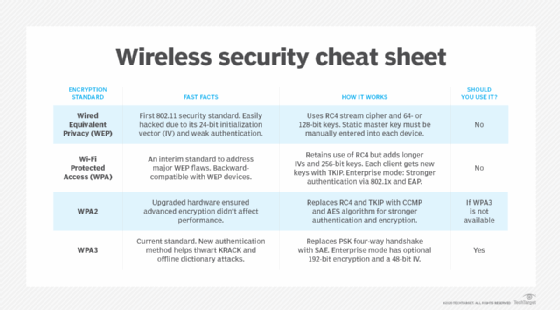
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
WEP is an outdated and highly vulnerable protocol. It should no longer be used under any circumstances.
Its easily crackable encryption makes it a prime target for attackers. Avoid WEP at all costs.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
WPA was designed as an interim solution to replace WEP. While better than WEP, it still has vulnerabilities.
WPA's TKIP encryption has known weaknesses. Consider upgrading to a more secure option if you are still using it.
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2)
WPA2 is a significant improvement over WPA, using the more secure AES encryption. It was the standard for many years.
However, WPA2 with TKIP is still vulnerable. Ensure your router is configured to use WPA2 with AES (also known as WPA2-PSK (AES)).
In 2017, vulnerabilities were discovered in the WPA2 protocol itself (KRACK attacks). Firmware updates were released to address these issues; ensure your router firmware is up-to-date.
WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3)
WPA3 is the latest and most secure wireless security protocol. It offers enhanced protection against password guessing and simplified Wi-Fi onboarding.
WPA3 utilizes Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE), also known as Dragonfly handshake. This makes it significantly harder to crack passwords.
It also provides individual data encryption, enhancing privacy on open Wi-Fi networks. Upgrade to WPA3 if your router and devices support it.
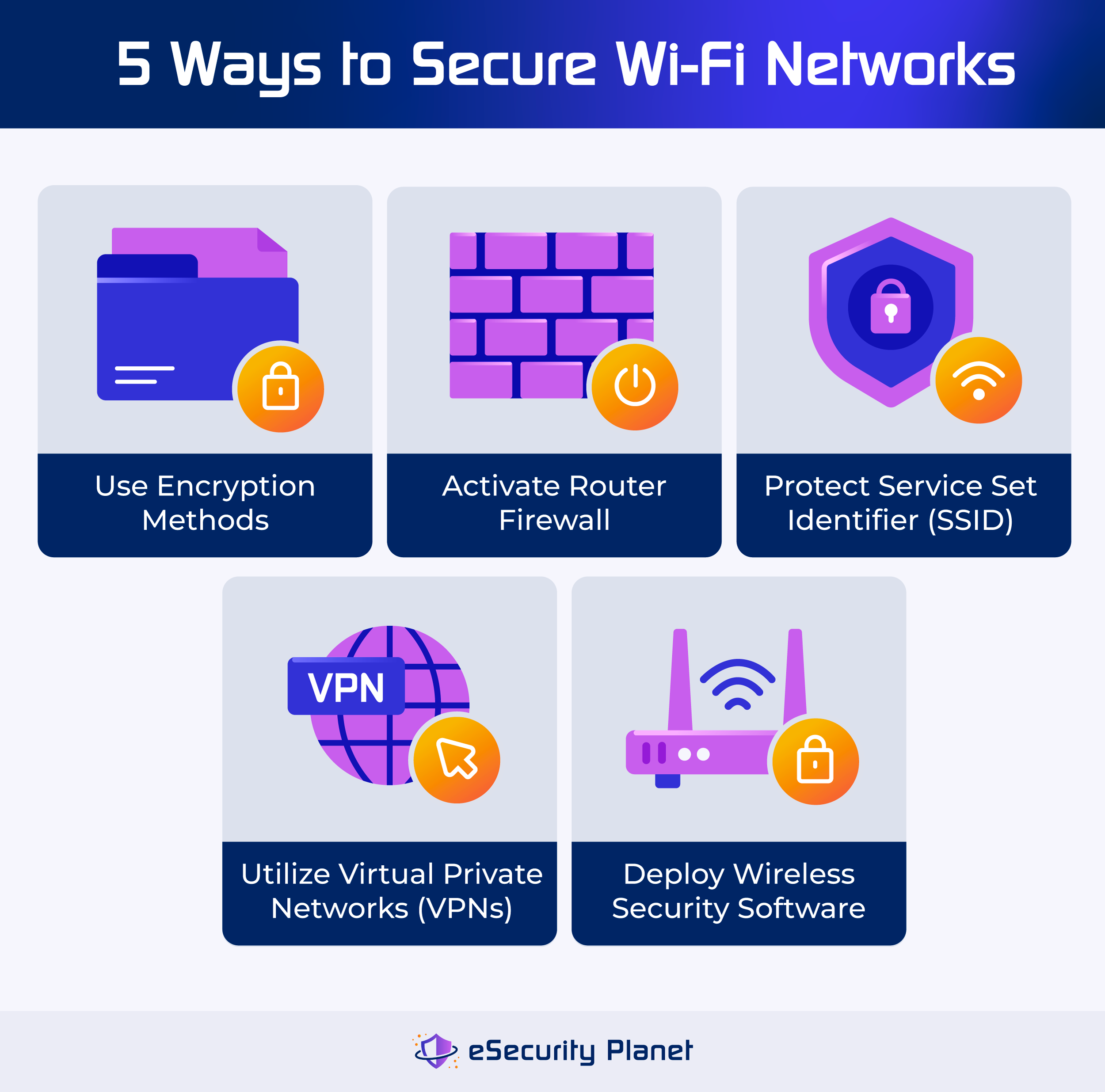
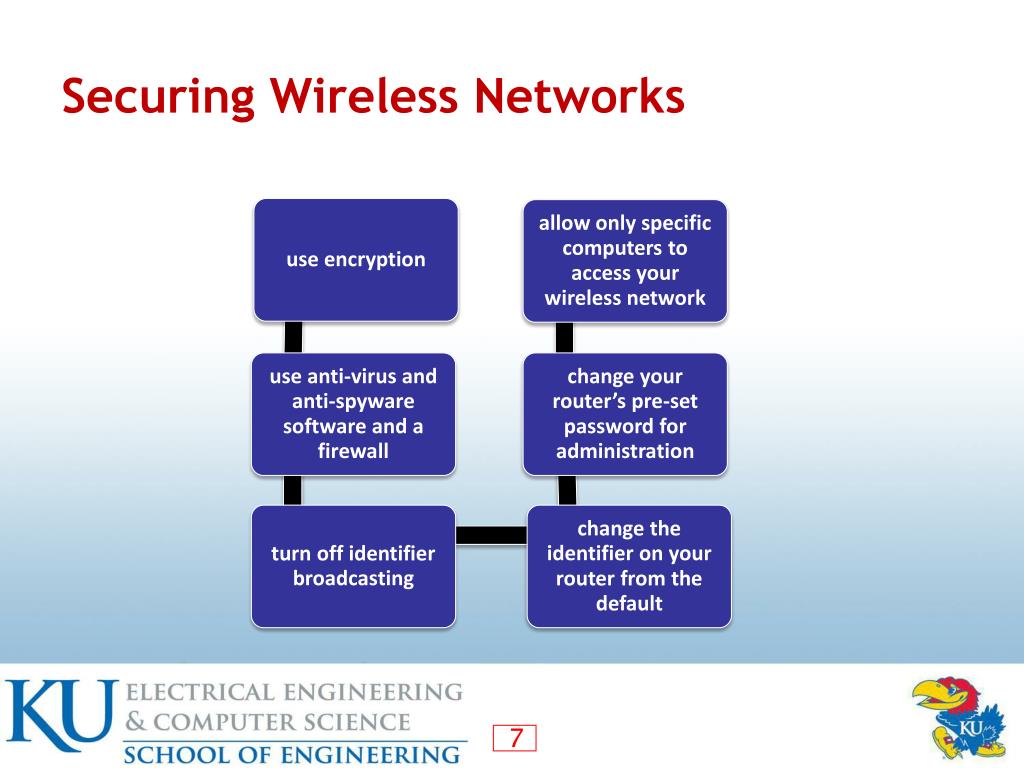
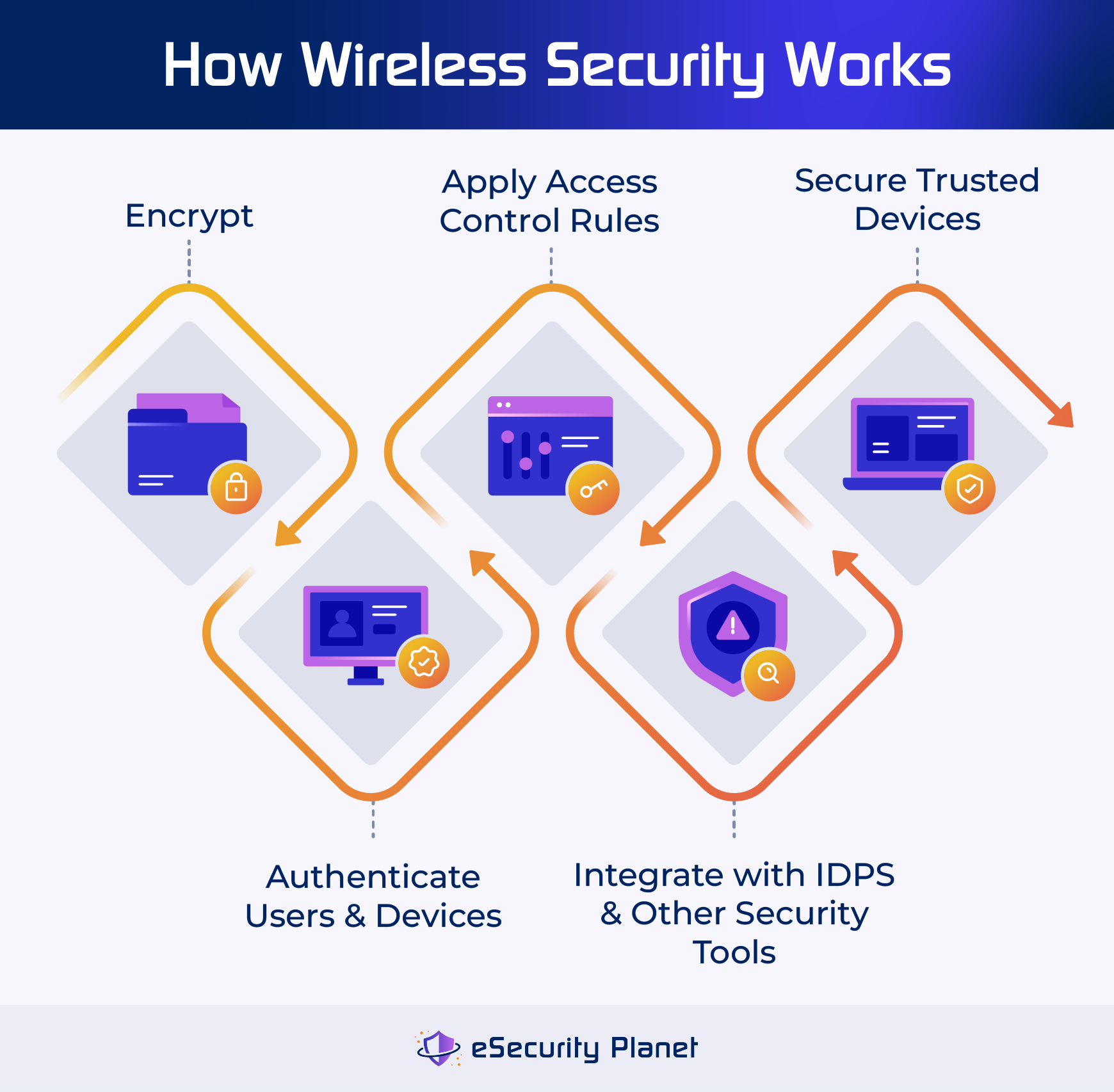
How to Secure Your Wireless Network
First, access your router's configuration page. This usually involves typing your router's IP address into a web browser (check your router's manual for the correct address).
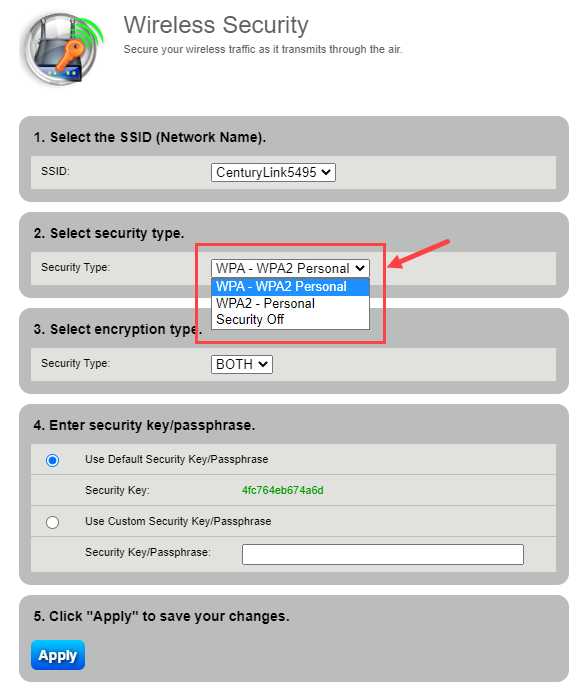
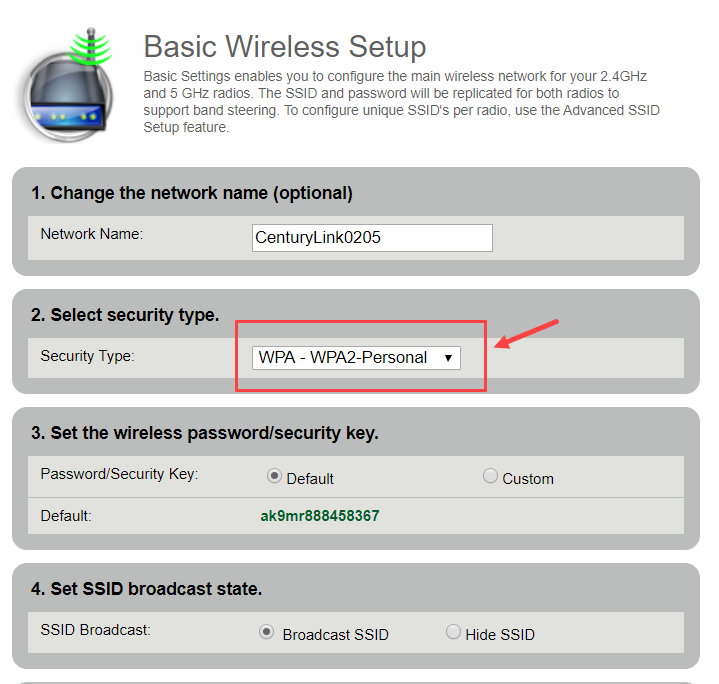
Navigate to the wireless settings and select WPA3 (if available). If not, choose WPA2-PSK (AES).
Create a strong, unique password. Avoid using easily guessable words or phrases.
Keep your router's firmware updated. Manufacturers regularly release updates to patch security vulnerabilities.
Next Steps
Immediately check your router's security settings and implement the strongest protocol available. Prioritize WPA3, followed by WPA2-PSK (AES).
Regularly review your network security and update your password. Stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices.
Consult with a cybersecurity professional if you need further assistance. Protecting your wireless network is a critical investment in your security.