What Size Generator To Power A Refrigerator

Power outages can disrupt daily life, and ensuring essential appliances like refrigerators continue running is a primary concern for many households. Determining the correct generator size for a refrigerator requires careful consideration of wattage requirements and other factors.
The "nut graf": This article aims to provide homeowners with the information needed to select an appropriately sized generator to power their refrigerator during a power outage, focusing on wattage calculations, starting surges, and different types of generators available on the market. Understanding these factors is crucial to avoid overloading the generator and ensuring the refrigerator operates safely and efficiently.
Understanding Refrigerator Wattage
Refrigerators typically require two different wattage measurements: running wattage and starting wattage. Running wattage is the continuous power needed to keep the refrigerator operating once the compressor is running. Starting wattage is a much higher surge of power required to start the compressor motor, often two to three times the running wattage.
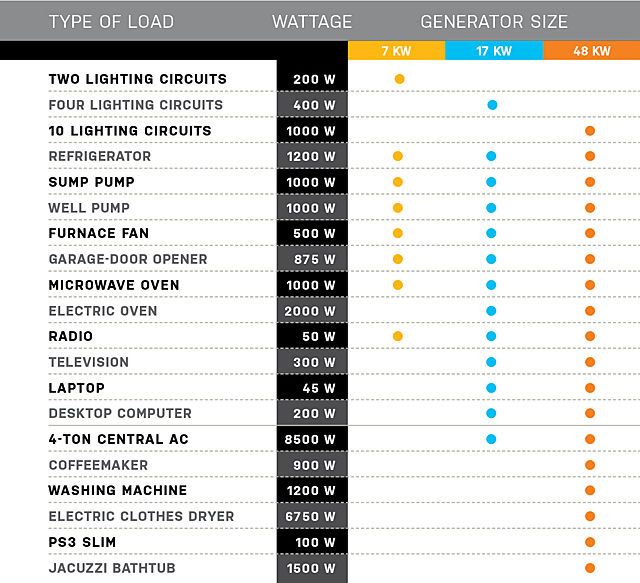
The running wattage for a standard refrigerator usually falls between 100 and 200 watts. However, older models or those with additional features like ice makers and water dispensers may require more. Check the appliance's nameplate, usually located on the back or inside the refrigerator, to find the exact wattage requirements.
The starting wattage is the most important factor when selecting a generator. A refrigerator with a running wattage of 150 watts might require a starting surge of 450-600 watts. This surge lasts only a few seconds, but the generator must be capable of providing this power.
Calculating Generator Size
To determine the appropriate generator size, start by identifying the refrigerator's starting wattage. Add the running wattage of any other essential devices you plan to power simultaneously, such as lights or a fan.
For example, if your refrigerator requires 600 starting watts and you want to run a 100-watt lamp, you'll need a generator capable of providing at least 700 watts. It's always advisable to add a safety margin of at least 10-20% to avoid overloading the generator.
Therefore, in the example above, a generator with a capacity of 800-840 watts would be a safe bet. Overloading a generator can damage both the generator and the connected appliances.
Types of Generators
Several types of generators are suitable for powering a refrigerator, each with different advantages and disadvantages. Inverter generators are known for their clean power output, making them ideal for sensitive electronics, including modern refrigerators with electronic controls.
Inverter generators are also typically quieter and more fuel-efficient than traditional generators. However, they may be more expensive and have lower power output than conventional models.
Conventional generators are generally more affordable and offer higher power output. However, they produce less clean power and can be noisier. These generators are better suited for older refrigerators without sensitive electronics.
Dual-fuel generators offer the flexibility of running on either gasoline or propane. This can be useful in situations where gasoline is scarce or propane is readily available.
Human Interest Angle: Peace of Mind During Outages
For many families, the ability to keep their refrigerator running during a power outage is about more than just convenience. It's about ensuring food safety and preventing spoilage, especially for families with young children or individuals with dietary restrictions.
Having a generator provides peace of mind, knowing that essential food supplies will remain safe and usable. This is particularly important in regions prone to severe weather events that can cause prolonged power outages.
Sarah Miller, a resident of coastal Florida, shared her experience after a hurricane. "After the storm, we were without power for five days. Our generator kept the refrigerator running, which saved us hundreds of dollars in spoiled food. It was a lifesaver."
Safety Considerations
When using a generator, safety is paramount. Always operate the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Never plug a generator directly into a wall outlet. This can backfeed electricity into the power grid, posing a serious risk to utility workers. Instead, use a heavy-duty extension cord to connect the refrigerator directly to the generator.
Regularly inspect the generator for any damage or leaks, and follow the manufacturer's instructions for maintenance and operation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right size generator to power a refrigerator requires careful consideration of wattage requirements, starting surges, and the type of generator. Understanding these factors can help homeowners select an appropriate generator that provides reliable power during outages.
By accurately calculating wattage needs and prioritizing safety, individuals can ensure their refrigerator continues running, preventing food spoilage and providing peace of mind during unexpected power disruptions. Investing in the right generator is an investment in preparedness and security.









![What Size Generator To Power A Refrigerator What Size Generator for Refrigerator & Freezer? [Expert Opinion]](https://biomachineslab.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/generator-for-refrigerator.jpg)