When Did Asc 606 Go Into Effect
The year 2018 marked a significant turning point for revenue recognition in the business world, a shift driven by a new accounting standard that promised to reshape how companies reported their earnings. The ripple effects of this change are still being felt today, prompting ongoing discussions and adjustments across various industries.
At the heart of this transformation lies ASC 606, a comprehensive accounting standard officially known as *Revenue from Contracts with Customers*. It's vital to understand its effective dates, its purpose, and its continued impact on financial reporting. This article delves into the specifics of when ASC 606 went into effect, providing a detailed overview of its implementation timeline and its lasting influence on businesses globally.
The Effective Dates of ASC 606
The implementation of ASC 606 was staggered based on the type of entity adopting the standard. This phased approach aimed to provide companies with adequate time to understand and adapt to the new requirements.
For public business entities, certain not-for-profit entities, and certain employee benefit plans, ASC 606 was effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. In simpler terms, this meant that most publicly traded companies were required to adopt the standard for their fiscal years beginning on or after January 1, 2018.
Private companies and certain other entities had a later effective date. For these organizations, ASC 606 became effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019. This provided private companies with an additional year to prepare for the transition.
A Closer Look at the Timeline
To clarify the timing, consider a company with a December 31 year-end. A public company would have adopted ASC 606 starting with its 2018 financial statements. A private company, on the other hand, would have adopted it beginning with its 2019 financial statements.
Early adoption was permitted, meaning companies could choose to implement the standard before the mandatory effective dates. Several companies did opt for early adoption, often to align their financial reporting with industry peers or to present a more transparent financial picture to investors.
The Core Principles of ASC 606
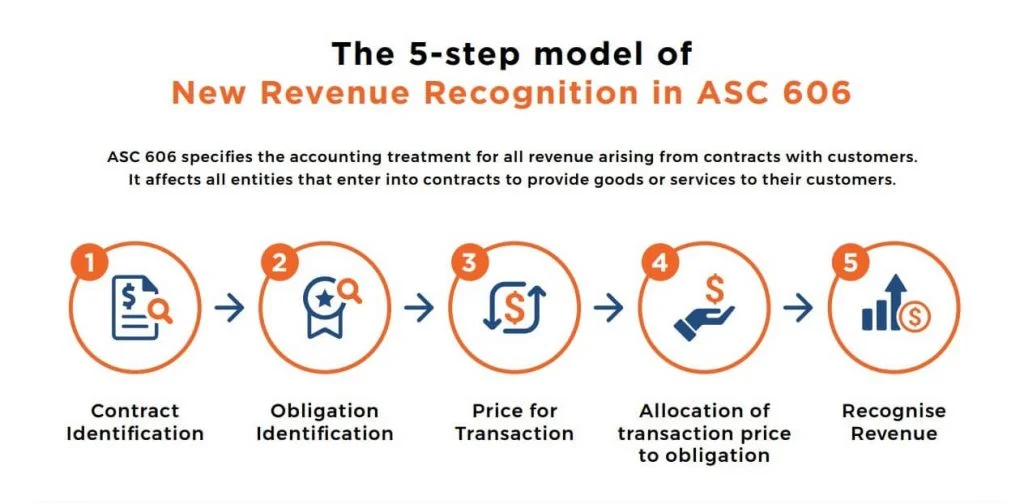
ASC 606 introduced a five-step model for revenue recognition. This framework provides a structured approach to determining when and how revenue should be recognized.
The five steps are: 1) Identify the contract(s) with a customer, 2) Identify the performance obligations in the contract, 3) Determine the transaction price, 4) Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations, and 5) Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation. Each of these steps requires careful consideration and judgment.
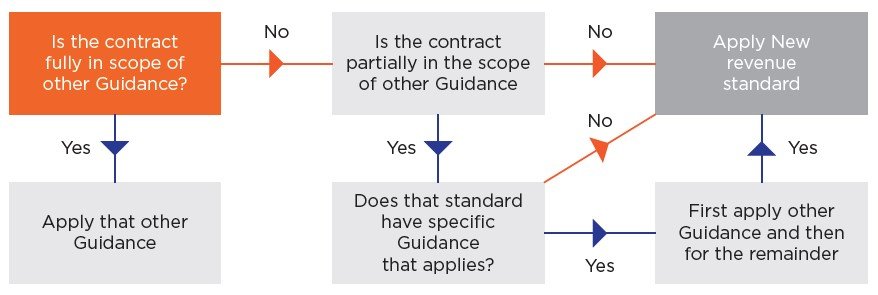
The core principle of ASC 606 is that revenue should be recognized to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. This principle emphasizes the substance of the transaction over its legal form.
Impact and Implementation Challenges
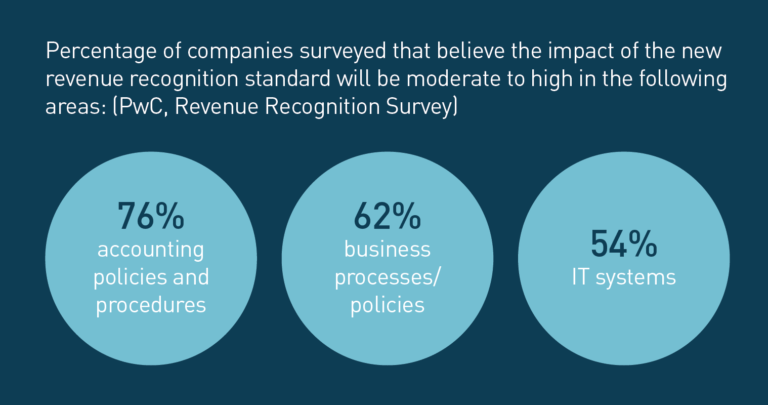
The implementation of ASC 606 presented numerous challenges for businesses across various sectors. Companies had to invest significant time and resources to understand the new requirements and update their accounting systems and processes.
One of the key challenges was identifying and analyzing all contracts with customers to determine the performance obligations and allocate the transaction price accordingly. This required a thorough review of existing contracts and the development of new accounting policies and procedures.
Another challenge was the increased use of judgment required under ASC 606. Companies had to make subjective assessments about the fair value of performance obligations and the likelihood of collecting consideration from customers. This introduced a greater degree of complexity and subjectivity into financial reporting.
Industry-Specific Considerations
The impact of ASC 606 varied significantly across different industries. Some sectors, such as software and telecommunications, were particularly affected due to the complex nature of their revenue arrangements.
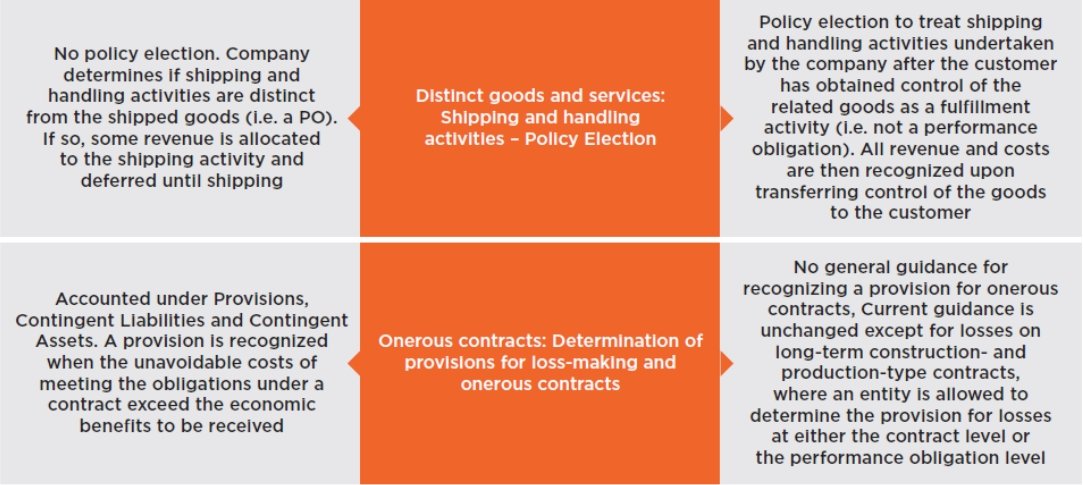
For example, software companies often have contracts that involve the delivery of software licenses, installation services, and ongoing maintenance and support. Under ASC 606, these different components had to be treated as separate performance obligations, each with its own revenue recognition schedule.
Telecommunications companies also faced challenges related to the allocation of revenue from bundled services. They had to determine the fair value of each service included in the bundle and allocate the transaction price accordingly.
The Ongoing Impact and Future Implications
While the initial implementation phase of ASC 606 has passed, its impact continues to be felt in the business world. Companies are still refining their accounting policies and procedures and working to improve the consistency and comparability of their financial reporting.
The standard has led to increased transparency and greater comparability of financial statements across different companies and industries. However, it has also increased the complexity of financial reporting and requires companies to exercise a greater degree of judgment.
Looking ahead, it is likely that ASC 606 will continue to evolve as companies and regulators gain more experience with its application. Further guidance and interpretations may be issued to address specific issues and improve the consistency of implementation.
Ultimately, ASC 606 represents a significant step forward in the evolution of revenue recognition standards. While its implementation has been challenging, it has also led to a more transparent and reliable financial reporting system, benefiting investors and other stakeholders alike.



![When Did Asc 606 Go Into Effect ASC 606 Revenue Recognition [Guide for Subscriptions] | Recurly](https://images.ctfassets.net/wob906kz2qeo/3P6UauzZQ2pQ4ukKuo0rB0/c0a0ec9612cbd5632758ec6689be1bc4/img-2022-11-ASC-606-inline-1200x425.png)