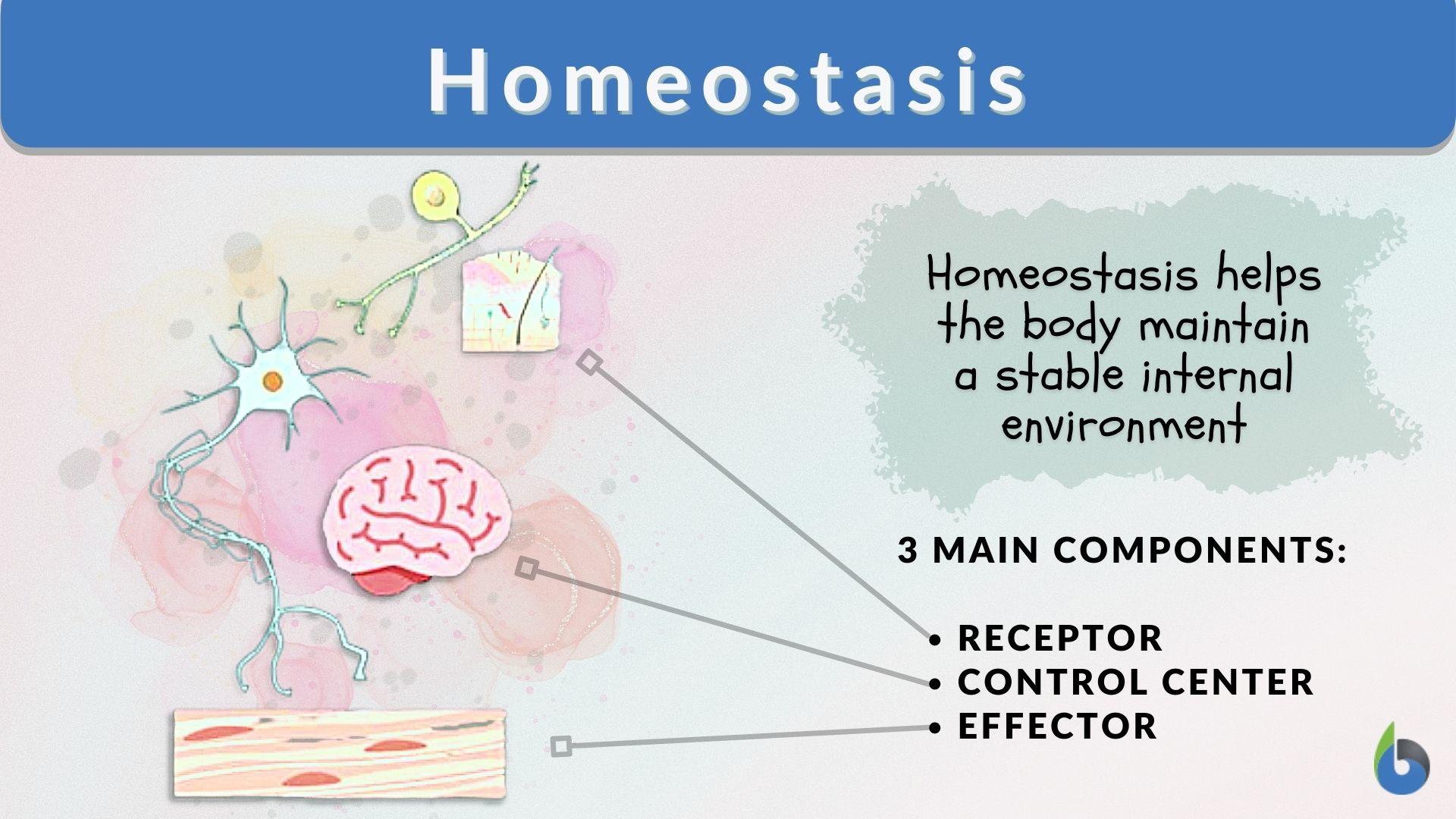
Which Helps To Maintain A Normal Range Of On Earth.
Maintaining a normal range of temperatures on Earth is a complex interplay of factors, crucial for supporting life as we know it. From the sun's radiant energy to the planet's atmospheric blanket, a delicate balance governs our climate.
This article delves into the primary mechanisms that contribute to this thermal equilibrium, exploring the roles of greenhouse gases, the albedo effect, and oceanic currents. Understanding these processes is vital for comprehending the impacts of human activities on the global climate system.
The Greenhouse Effect: A Natural Blanket
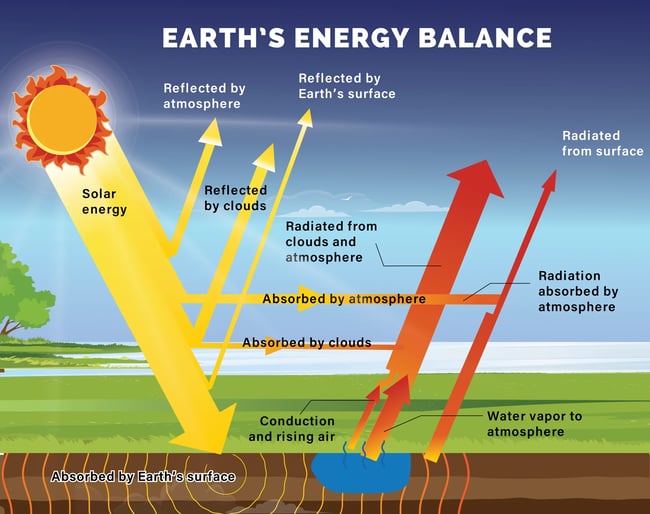
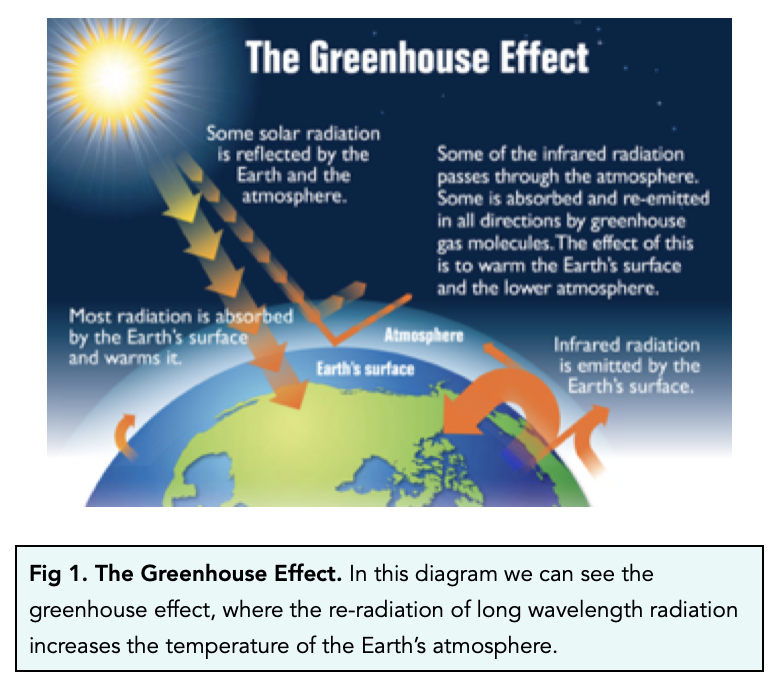
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon essential for maintaining Earth's temperature within a habitable range. Certain gases in the atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases, trap heat radiating from the Earth's surface.
These gases, including water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3), allow sunlight to pass through but absorb a portion of the outgoing infrared radiation. This process warms the lower atmosphere and the Earth's surface.
Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's average temperature would be significantly colder, rendering the planet largely uninhabitable. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the greenhouse effect raises Earth's average temperature from approximately -18°C (0°F) to a more hospitable 15°C (59°F).
The Role of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a key greenhouse gas that plays a significant role in regulating Earth's temperature. Natural sources of CO2 include volcanic eruptions, respiration of plants and animals, and decomposition of organic matter.
However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy production, have drastically increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations. This increase enhances the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming.
Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) shows that atmospheric CO2 concentrations have risen from pre-industrial levels of around 280 parts per million (ppm) to over 410 ppm in recent years, a level unprecedented in at least the past 800,000 years.
Albedo: Reflecting Sunlight
The albedo effect refers to the reflectivity of a surface. Surfaces with high albedo, such as snow and ice, reflect a large portion of incoming solar radiation back into space.
Surfaces with low albedo, such as forests and oceans, absorb more solar radiation. This difference in reflectivity plays a crucial role in regulating Earth's temperature.
Changes in land cover, such as deforestation and the melting of ice sheets, can alter the Earth's albedo and influence global temperatures. Melting ice, for example, reduces Earth's albedo, leading to increased absorption of solar radiation and further warming.
Impact of Ice Melt
The ongoing melting of polar ice caps and glaciers is a significant concern due to its impact on albedo. As ice melts, it exposes darker surfaces, such as ocean water or land, which absorb more solar radiation.
This positive feedback loop accelerates warming and contributes to sea level rise. Studies published in Nature Climate Change have shown a clear correlation between declining Arctic sea ice extent and increased global temperatures.
The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) continuously monitors ice cover and provides data highlighting the rapid decline in Arctic sea ice extent over the past few decades.
Oceanic Currents: Redistributing Heat
Oceanic currents play a vital role in redistributing heat around the globe. Warm currents transport heat from the equator towards the poles, while cold currents transport cold water from the poles towards the equator.
This circulation of heat helps to moderate regional climates and influence global weather patterns. The Gulf Stream, for example, is a warm current that significantly warms Western Europe, making its climate milder than other regions at similar latitudes.
Changes in ocean currents, driven by factors such as temperature and salinity, can have significant impacts on regional and global climates. Disruptions to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a major ocean current system, could lead to significant cooling in Europe and changes in precipitation patterns worldwide.
Thermohaline Circulation
Thermohaline circulation is a global ocean current driven by differences in water density, which is influenced by temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline). This circulation pattern plays a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate over long timescales.
As seawater freezes at the poles, it leaves behind salt, increasing the salinity of the remaining water. This dense, salty water sinks and flows along the ocean floor, driving the thermohaline circulation.
Climate change-induced melting of ice sheets and increased freshwater runoff can disrupt thermohaline circulation by reducing the salinity of polar waters. This disruption could have significant consequences for global climate patterns.
Conclusion
Maintaining a normal range of temperatures on Earth is a complex process governed by the interplay of the greenhouse effect, albedo, and oceanic currents. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, are altering the balance of these factors, leading to global warming and climate change.
Understanding these processes is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change and protect the planet for future generations. Continued research and monitoring of these critical climate factors are essential for informing policy decisions and promoting sustainable practices.