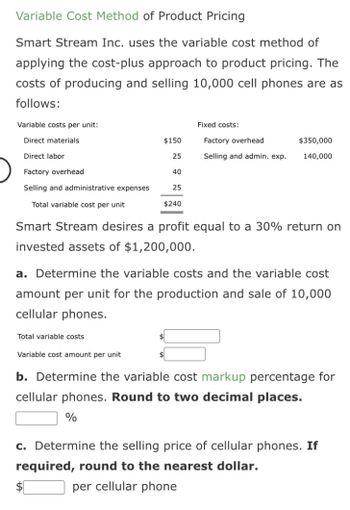
Which Of The Following Is A Variable Cost

Imagine running a lemonade stand on a scorching summer day. The sun beats down, kids clamor for a refreshing drink, and you’re scrambling to keep up with the demand. You notice something interesting: the more lemonade you sell, the more lemons, sugar, and cups you need to buy. But no matter how many cups you sell, the price of the stand itself, or the colorful sign you made, remains the same.
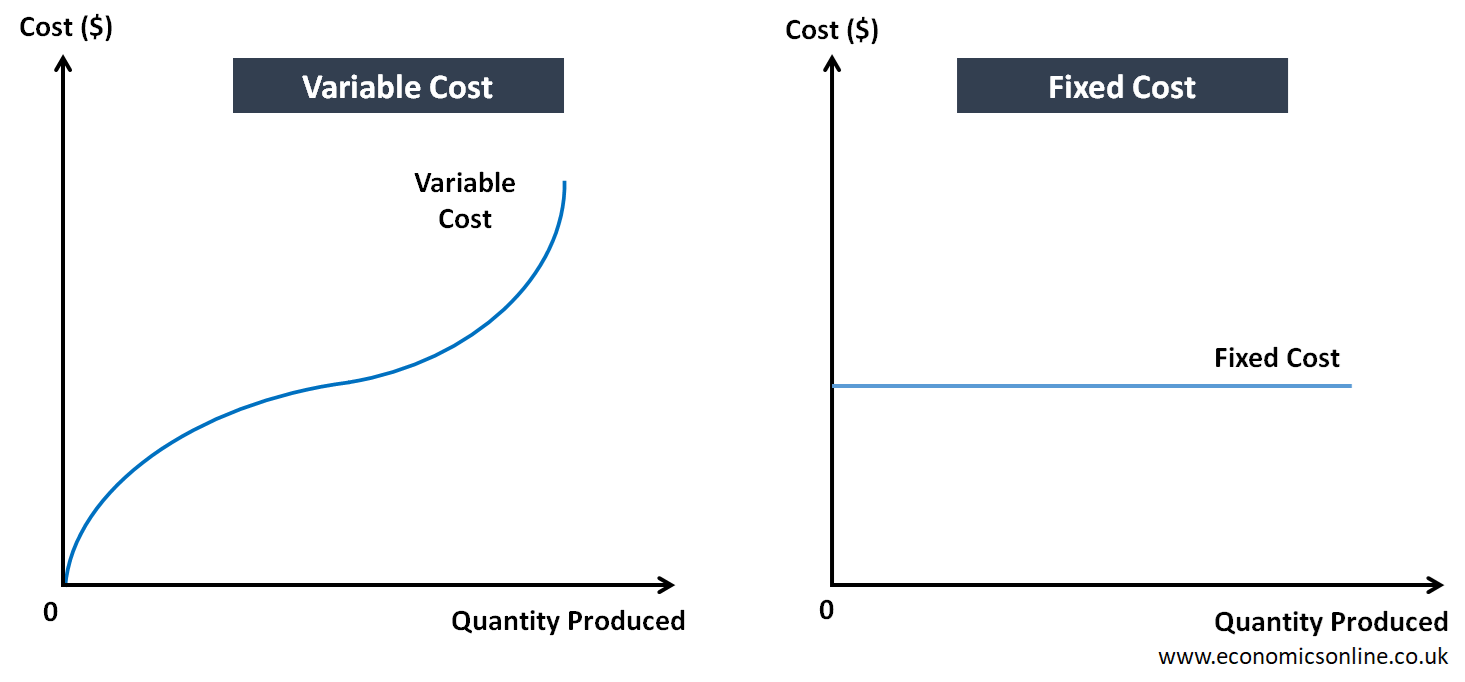
At its core, this highlights the essence of a variable cost. It's the cost that fluctuates in direct proportion to the volume of production. Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for businesses of all sizes, from that small lemonade stand to multinational corporations, as it significantly impacts pricing strategies, profitability analysis, and overall financial decision-making.
Understanding Variable Costs
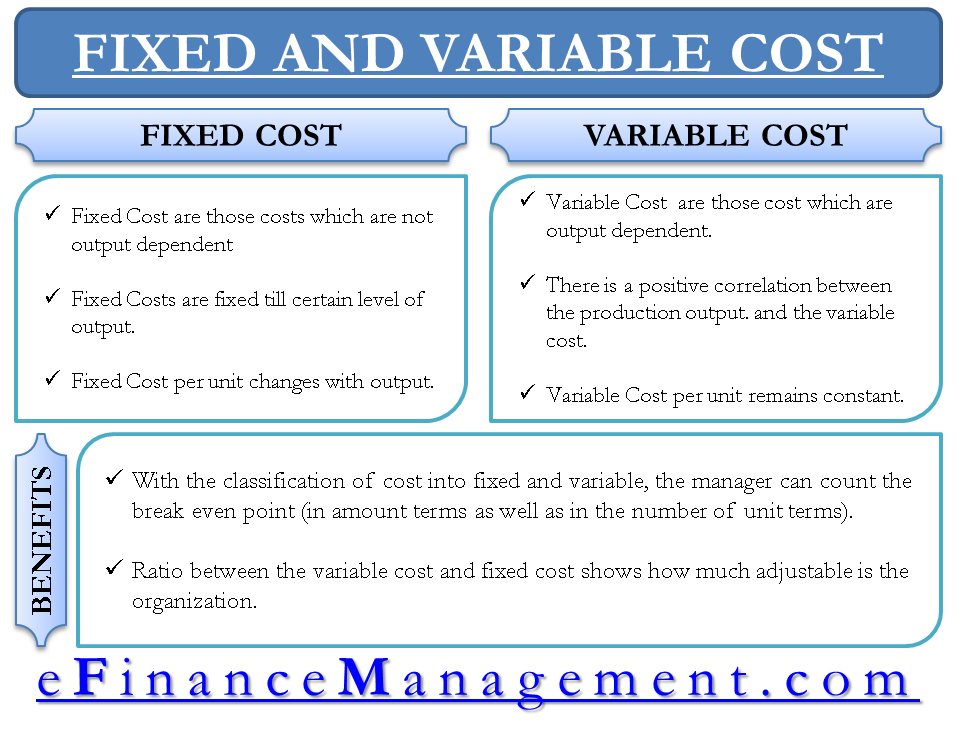
So, what exactly are variable costs? In simple terms, they are expenses that change as a company's production volume increases or decreases. Think of them as costs directly tied to the making and selling of each product or service.
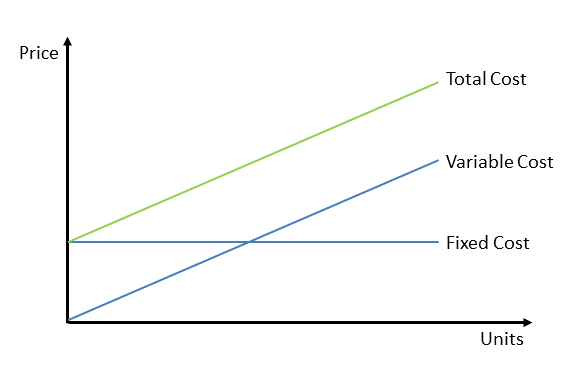
Unlike fixed costs, which remain constant regardless of production levels, variable costs are dynamic. This distinction is fundamental in cost accounting and managerial economics.
Key Characteristics of Variable Costs
Several characteristics define variable costs. These traits set them apart from other types of expenses and are essential to consider for effective financial management.
- Direct Proportionality: Variable costs increase or decrease in direct proportion to production volume. If you double production, you generally double the variable costs.
- Per-Unit Basis: Variable costs are often calculated on a per-unit basis, allowing businesses to easily determine the cost of producing each individual item or service.
- Controllable: In many cases, businesses have some control over their variable costs. They might be able to negotiate better prices with suppliers, find more efficient ways to use materials, or reduce labor costs.
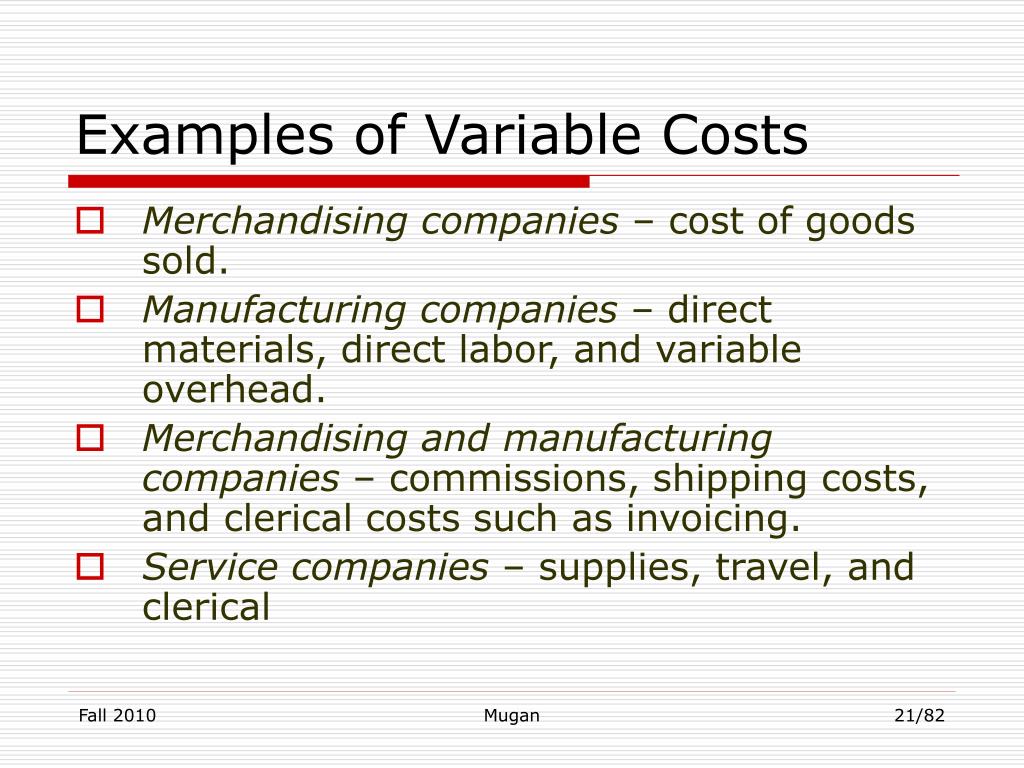
Examples of Variable Costs
To make the concept more tangible, let's look at some common examples of variable costs across different industries.
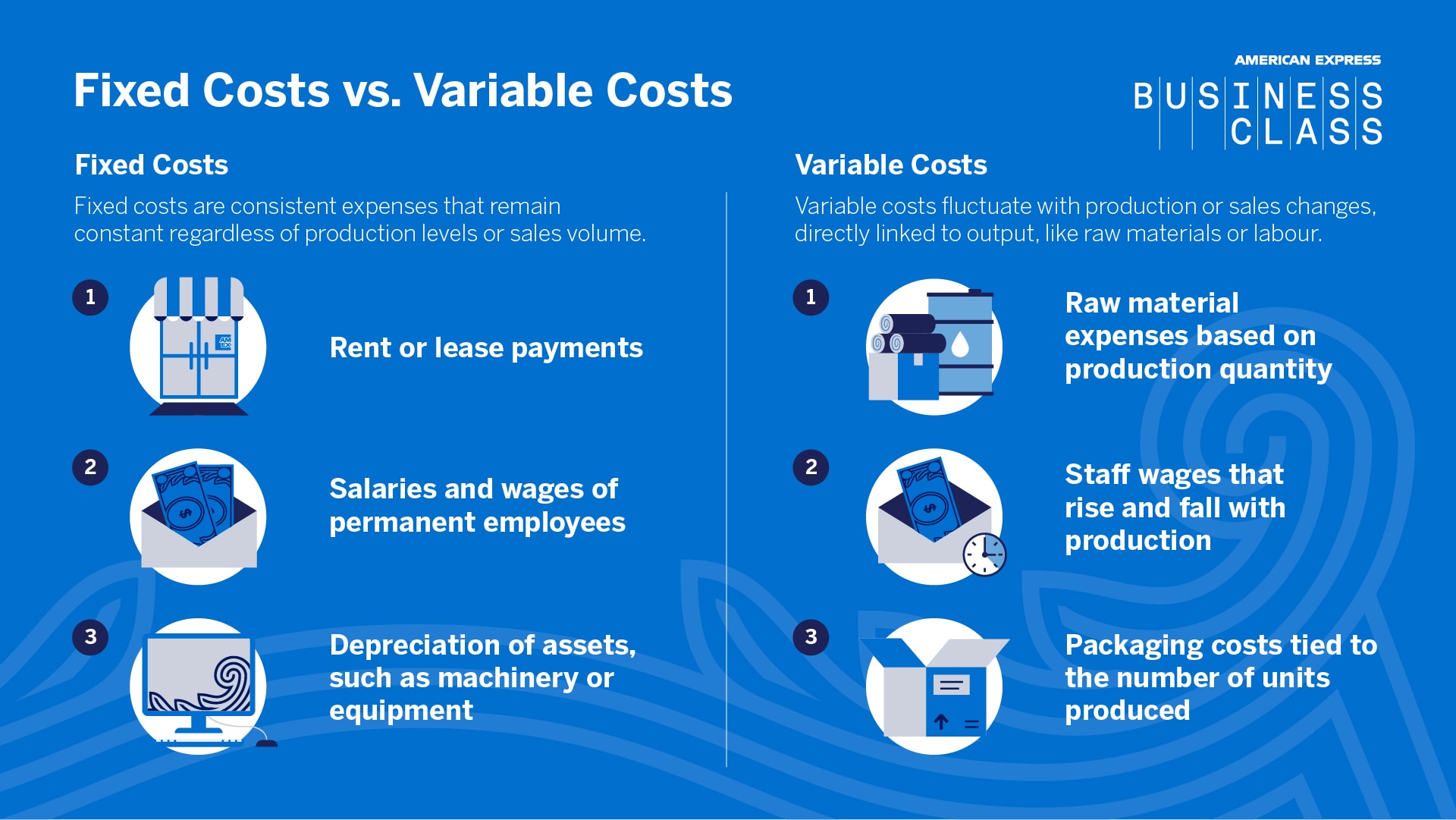
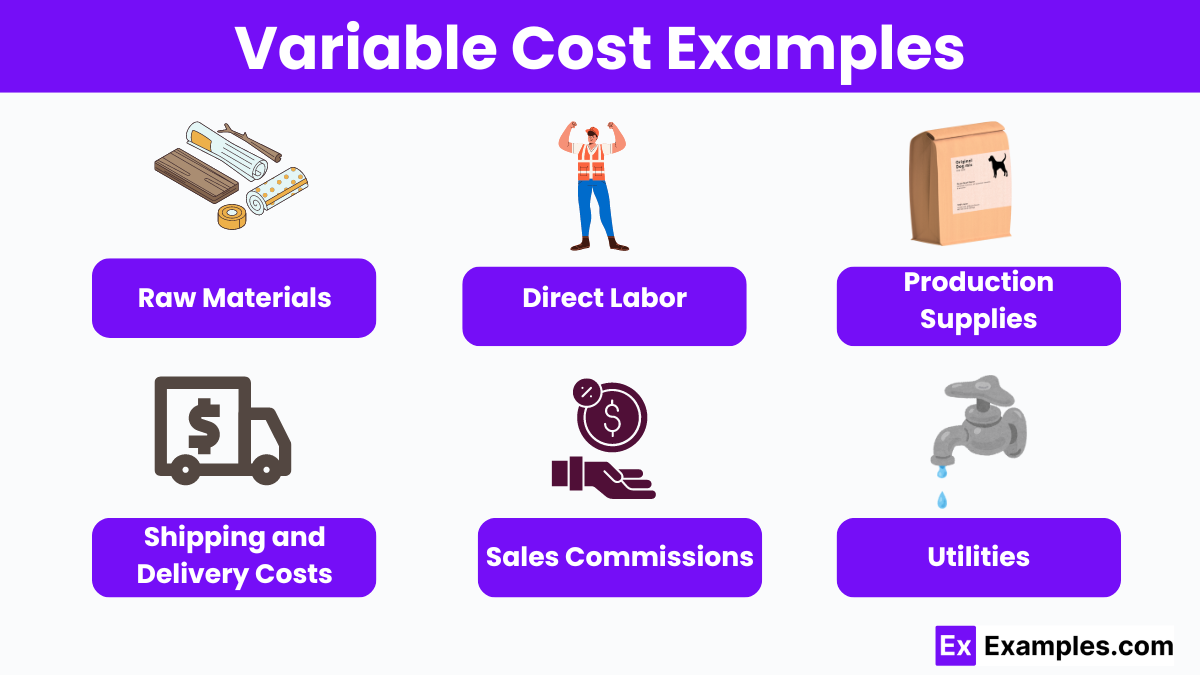
For a manufacturing company, raw materials are a prime example. The more widgets they produce, the more steel, plastic, and other components they need.
Direct labor, or the wages paid to workers directly involved in production, is another key variable cost. If the company needs to produce more widgets, it will likely need to hire more workers or pay existing workers overtime.
Sales commissions are also considered variable costs. These are a percentage of revenue paid to sales staff and will increase if sales increase.
Other variable costs might include packaging, shipping, and utilities directly related to the production process.
Differentiating Variable Costs from Fixed Costs
The ability to differentiate between variable and fixed costs is essential for effective cost management. Misclassifying costs can lead to inaccurate profitability calculations and poor decision-making.
Fixed costs, on the other hand, remain constant regardless of production levels. Examples include rent, salaries of administrative staff, insurance premiums, and depreciation of equipment.
It's important to note that some costs may have both fixed and variable components. These are known as semi-variable costs. For example, a utility bill might have a fixed monthly charge plus a variable charge based on consumption.
Impact on Business Decisions
Understanding variable costs has a significant impact on several critical business decisions. Here's how:
Pricing Strategies: Variable costs are a key factor in determining the minimum price a company can charge for its products or services. The price must cover variable costs plus a contribution margin to cover fixed costs and generate a profit.
Profitability Analysis: By accurately tracking variable costs, businesses can determine the profitability of individual products or services. This information can be used to make decisions about product mix, pricing, and marketing efforts.
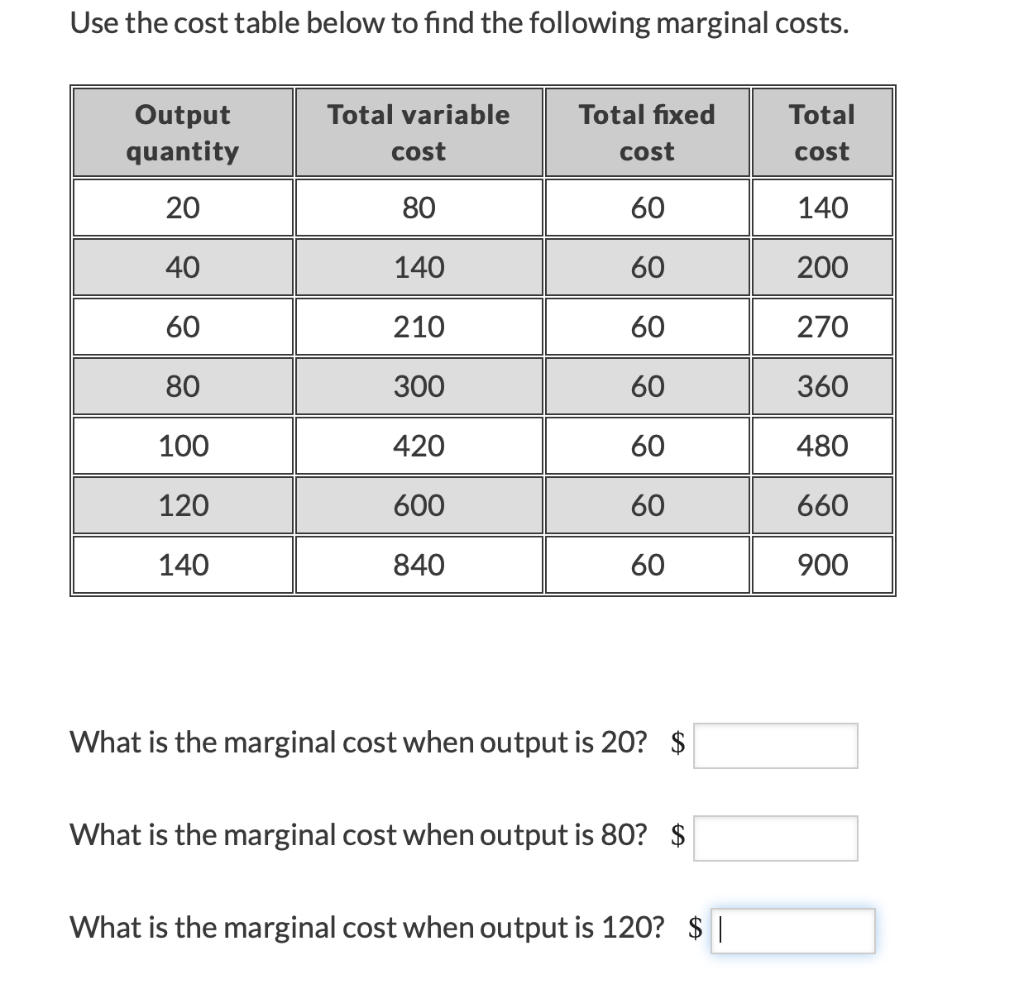
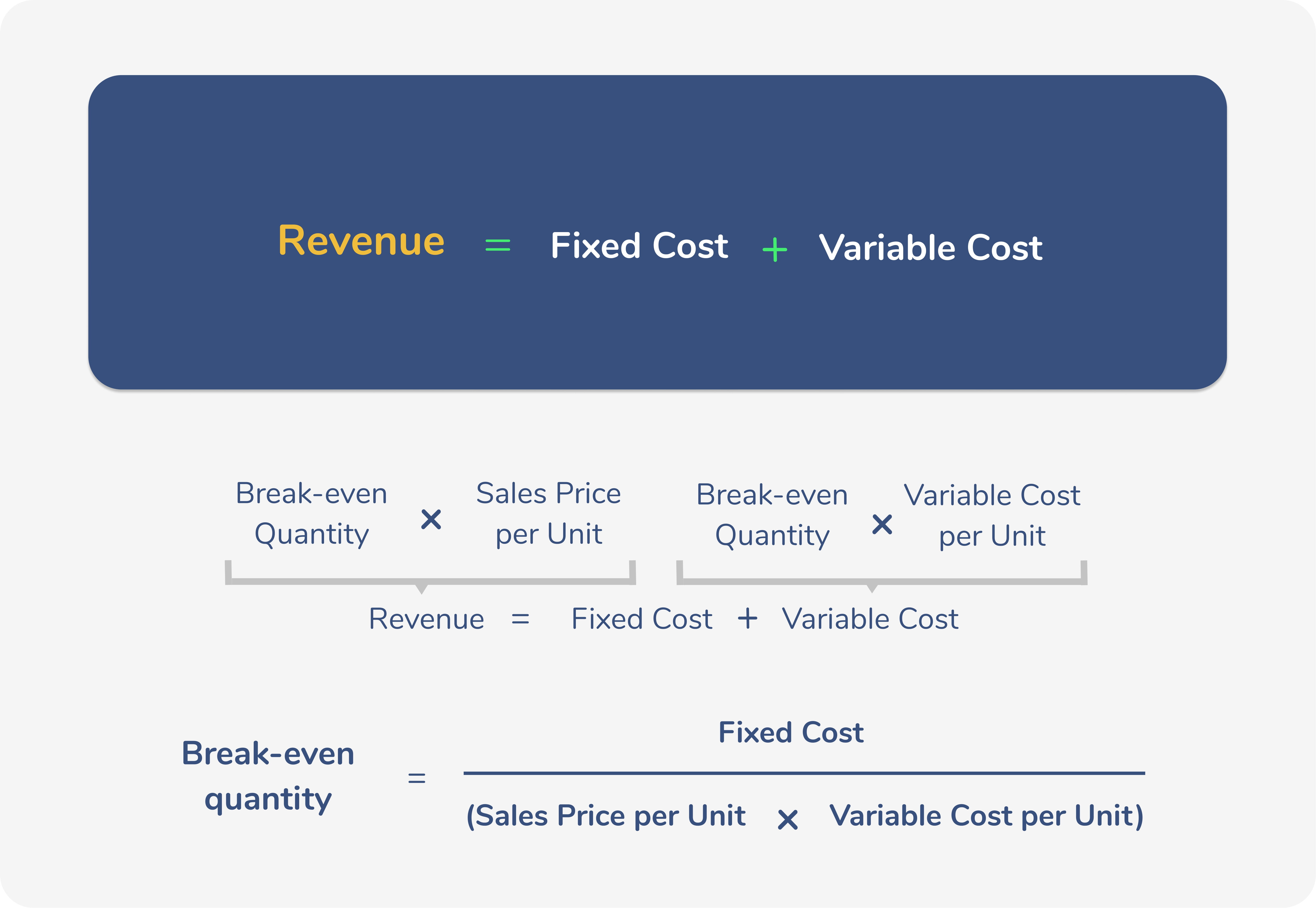
Break-Even Analysis: Variable costs are essential for calculating the break-even point, which is the level of sales needed to cover all costs. This information helps businesses understand the relationship between sales volume, costs, and profits.
Budgeting and Forecasting: Accurate forecasts of variable costs are crucial for developing realistic budgets and financial projections. This helps businesses plan for future expenses and manage their cash flow effectively.
Real-World Implications and Examples
Consider a coffee shop. The cost of coffee beans, milk, sugar, and cups are all variable costs. The rent on the shop space, the barista's salary (assuming they are paid a fixed amount), and the cost of the espresso machine are fixed costs.
A software company providing cloud-based services would have variable costs related to server usage and data storage. As more users subscribe to the service, the company incurs more costs for maintaining the servers and storing data. The salaries of the software developers, the rent on the office space, and the cost of marketing campaigns are fixed costs.
According to a report by the Investopedia, understanding variable costs is crucial for making informed decisions about production levels and pricing strategies. It allows businesses to optimize their operations and maximize profitability.
Conclusion
The concept of variable costs, while seemingly straightforward, plays a vital role in the financial health and strategic planning of businesses. By understanding how costs fluctuate with production volume, companies can make informed decisions about pricing, production levels, and overall profitability.
From the humble lemonade stand to the complex workings of a multinational corporation, the principle remains the same: accurately tracking and managing variable costs is essential for success. And the better you understand those costs, the brighter your business future will be.