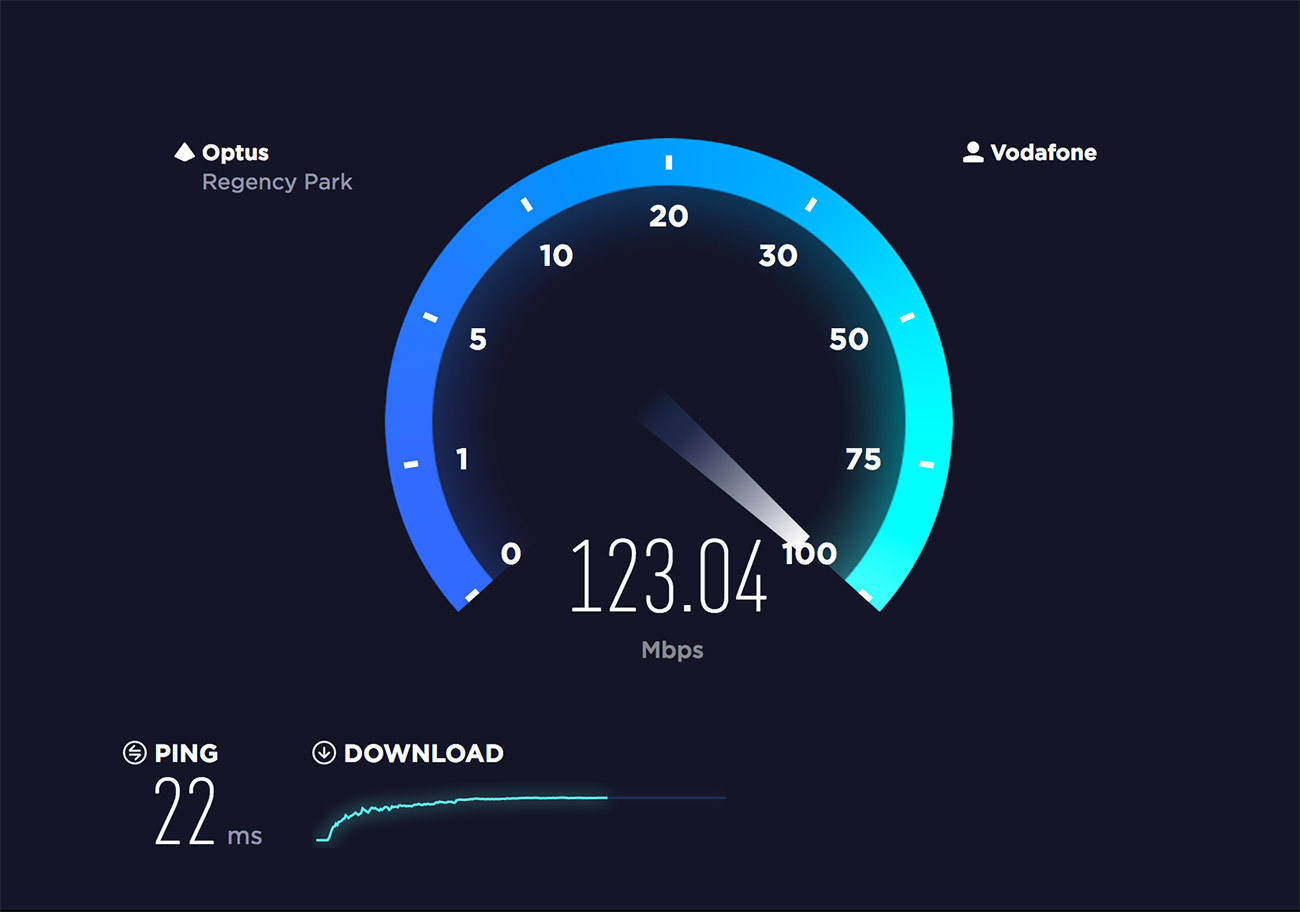
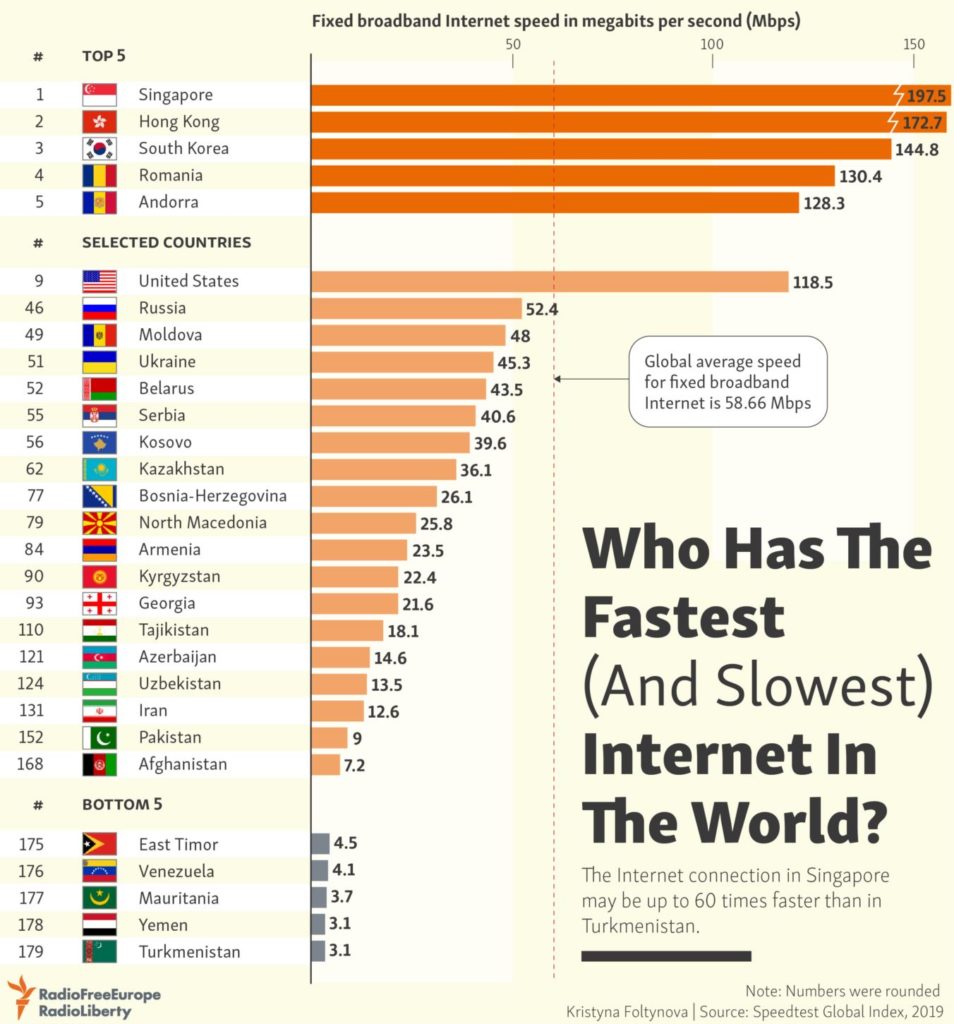
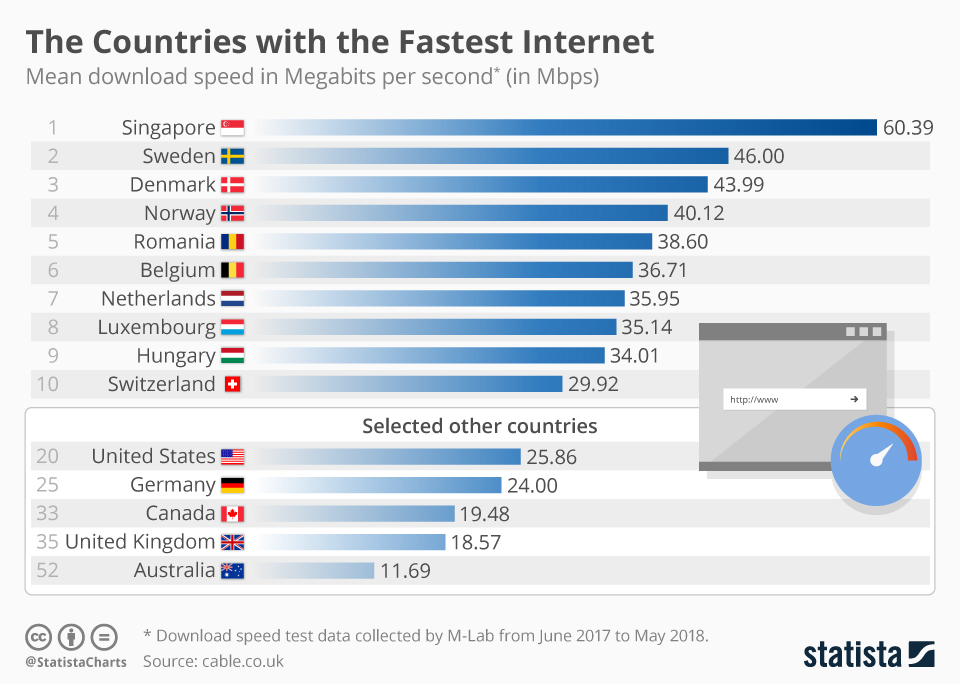
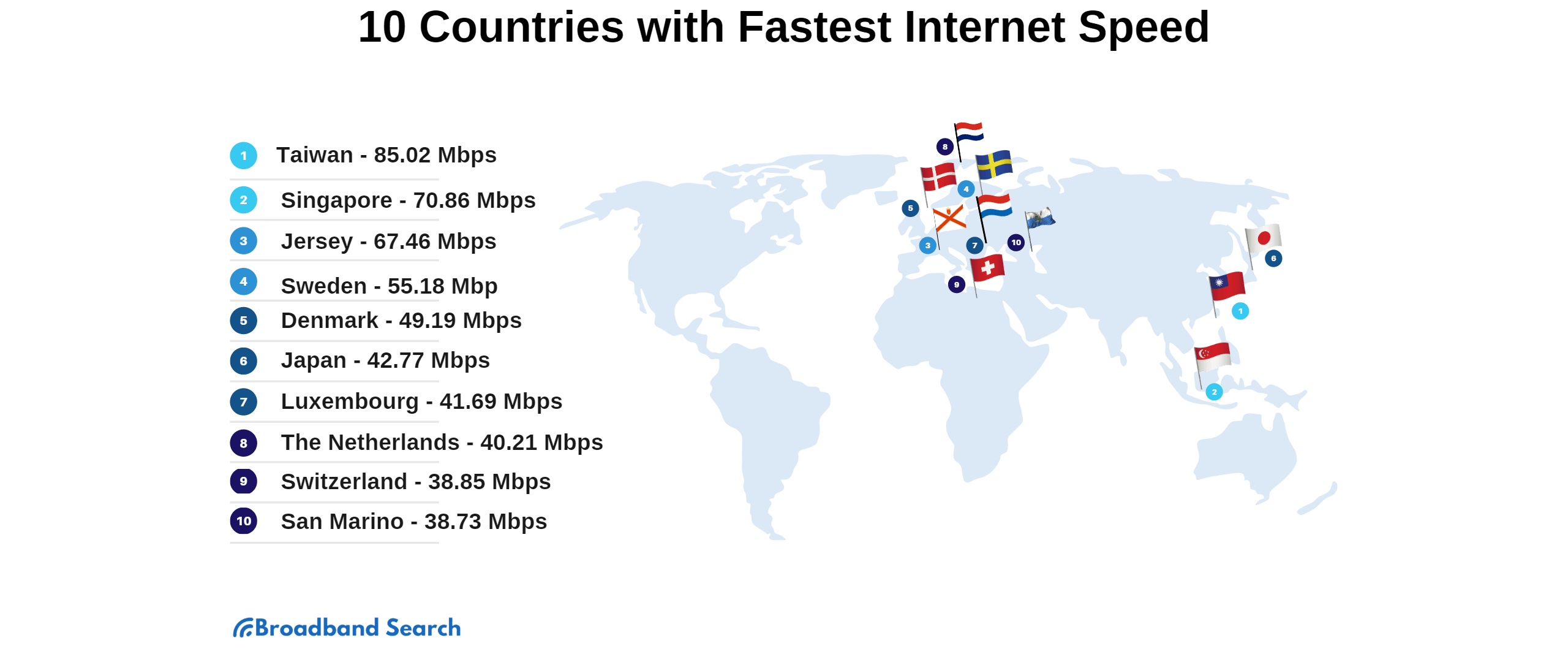
Which Internet Speed Is The Fastest
In an era defined by instant gratification and ever-increasing data demands, the question of internet speed reigns supreme. From seamless streaming to lag-free gaming and efficient remote work, the velocity of our online connections dictates our digital experience. But navigating the landscape of Mbps, Gbps, and emerging technologies can be daunting, leaving many wondering: which internet speed truly reigns as the fastest?
This article delves into the complexities of internet speed, exploring the technologies vying for the title of "fastest." We will examine the capabilities of fiber optics, the promises of 5G and upcoming 6G, and the potential of satellite internet. By dissecting the technical specifications and real-world performance of each contender, we aim to provide a clear understanding of the current state and future trajectory of internet speed.
Fiber Optics: The Reigning Champion
Currently, fiber optic internet holds the crown as the fastest widely available internet technology. Utilizing strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as light signals, fiber boasts significantly higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to traditional copper-based technologies like DSL and cable.
This translates to faster download and upload speeds, more stable connections, and an overall smoother online experience. Fiber optic networks are capable of delivering symmetrical speeds, meaning that upload and download speeds are equal, a critical advantage for activities like video conferencing and cloud-based collaboration.
Understanding Fiber Speed Tiers
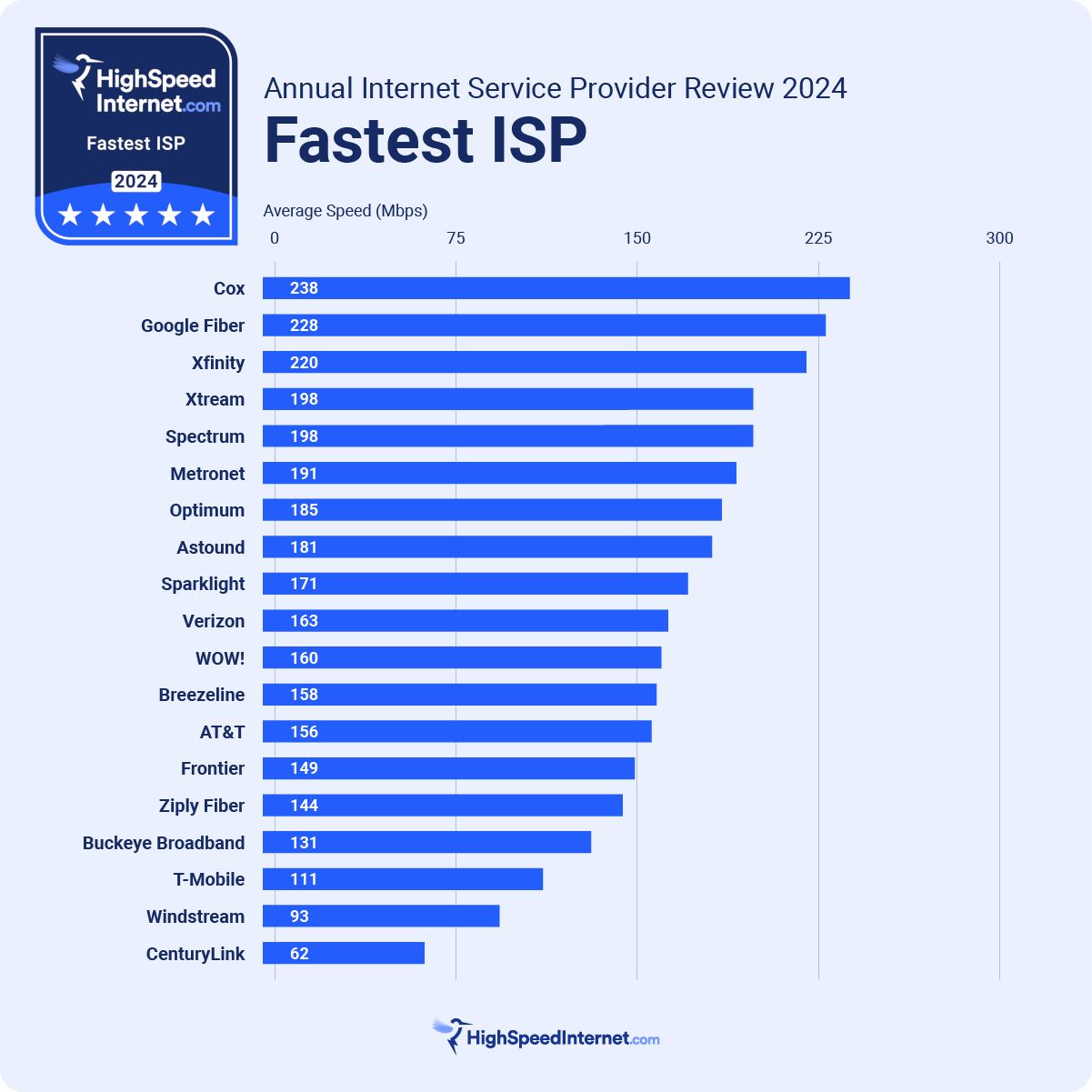
Fiber internet is typically offered in tiers, ranging from several hundred Mbps to multiple Gbps. Google Fiber, for instance, offers plans reaching up to 8 Gbps in select areas. Verizon Fios and AT&T Fiber also provide gigabit-level speeds, showcasing the immense potential of this technology.
However, the availability of fiber optic internet remains a significant limitation. Deployment costs are high, requiring extensive infrastructure upgrades that are often concentrated in densely populated urban areas.
5G and 6G: The Wireless Challengers
5G, the fifth generation of wireless technology, has emerged as a strong contender in the race for faster internet speeds. Leveraging higher radio frequencies and advanced network architectures, 5G promises significantly faster speeds and lower latency compared to its predecessor, 4G LTE.
While theoretically capable of delivering gigabit speeds, real-world 5G performance varies greatly depending on factors like network infrastructure, device capabilities, and proximity to cell towers. Moreover, the rollout of 5G infrastructure is still ongoing, limiting its availability in many regions.
Looking ahead, 6G is already on the horizon, promising even more dramatic improvements in speed and latency. Envisioned to operate at terahertz frequencies, 6G aims to support ultra-high-bandwidth applications like holographic communication and advanced augmented reality.
Satellite Internet: Bridging the Digital Divide
Satellite internet offers a viable solution for connecting remote and rural areas where wired and wireless infrastructure is limited. Services like Starlink, using a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, are delivering increasingly faster speeds and lower latency compared to traditional geostationary satellite internet.
While satellite internet has made significant strides, it still faces challenges in consistently delivering speeds comparable to fiber or even 5G. Weather conditions can impact signal strength, and latency remains higher than with wired connections.
The Future of Internet Speed
The quest for faster internet speeds is a continuous pursuit, driven by the ever-increasing demands of our digital lifestyles. While fiber optic internet currently holds the title of fastest widely available technology, 5G and the eventual emergence of 6G promise to revolutionize wireless connectivity.
"The future of internet speed will likely involve a hybrid approach, leveraging the strengths of various technologies to deliver seamless and high-performance connectivity wherever people are."
Advancements in hardware and software will also play a crucial role in optimizing internet speeds and ensuring a smooth user experience. The key is not simply achieving higher speeds, but also minimizing latency and ensuring consistent, reliable performance.

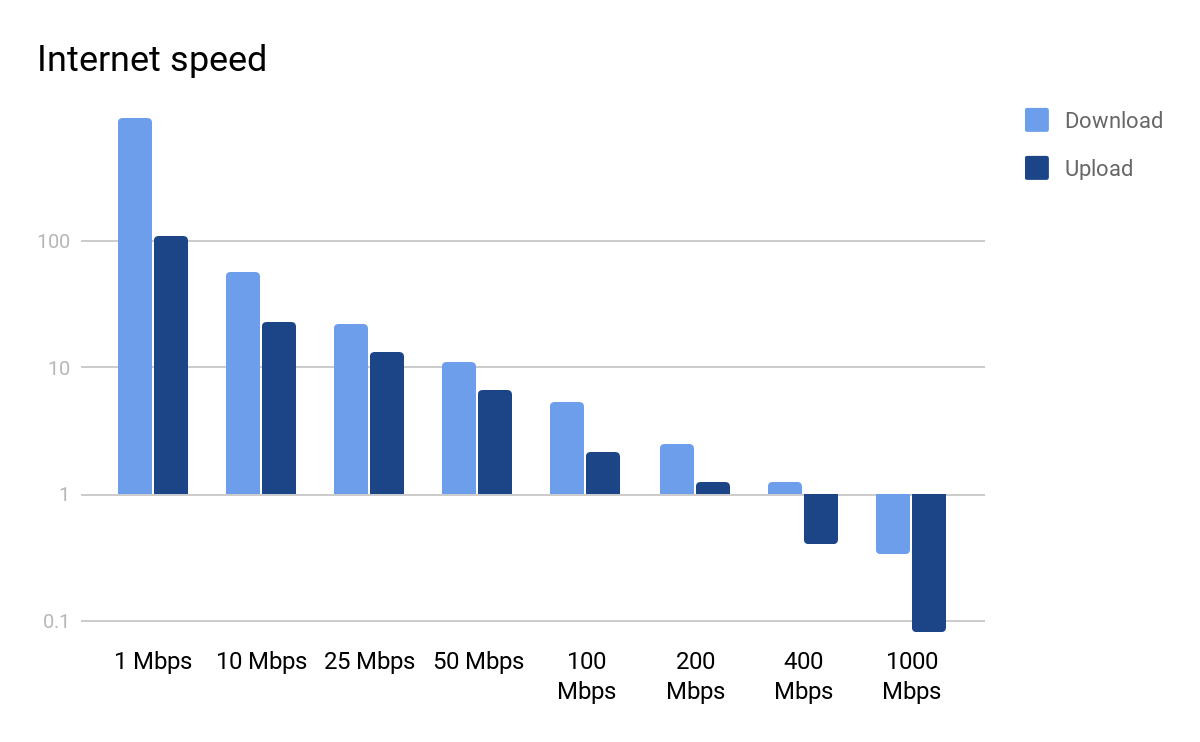
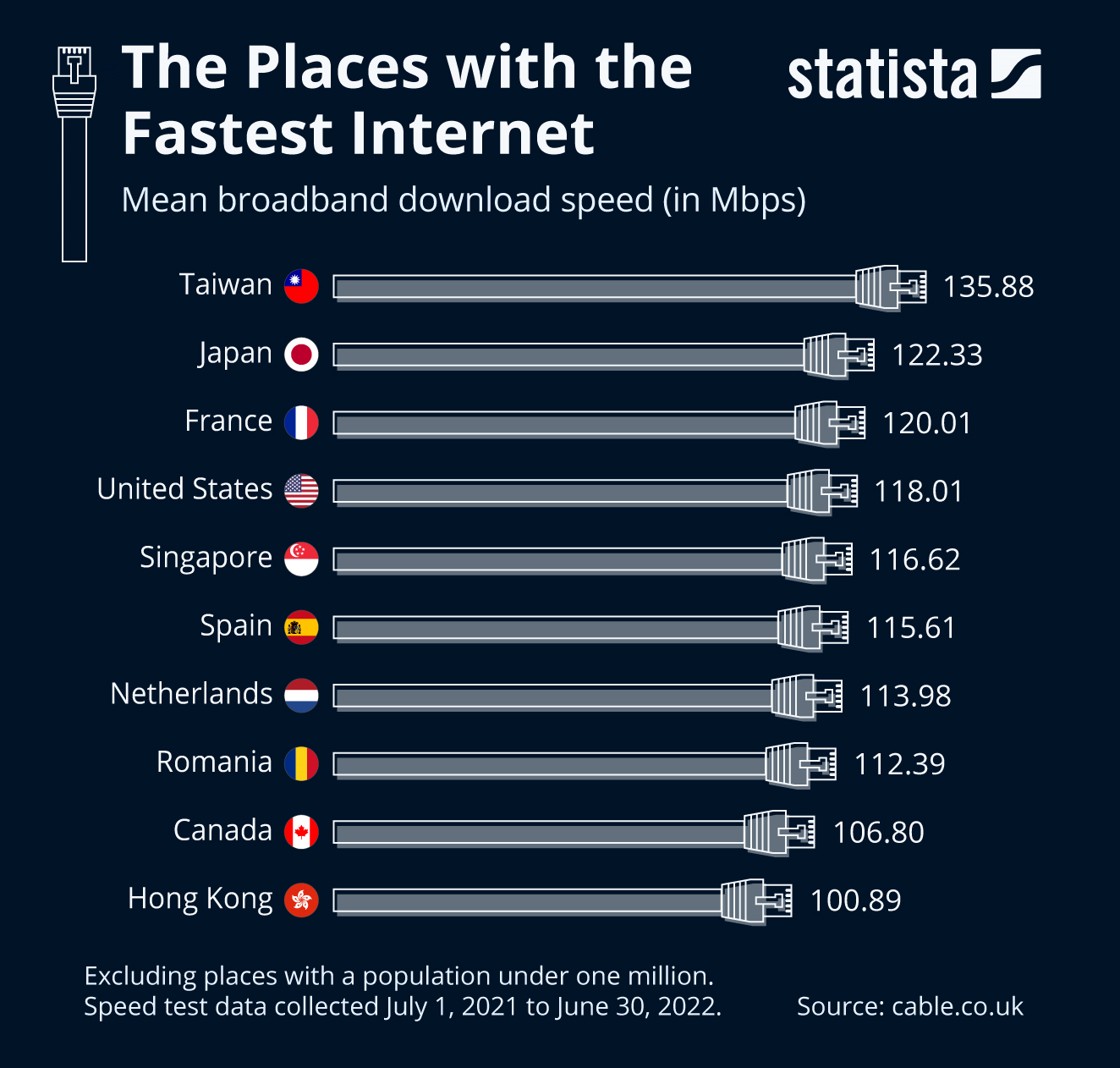
![Which Internet Speed Is The Fastest Who Has the Fastest Internet in the World? [Infographic]](https://www.webfx.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/top-10-1-768x563.png)

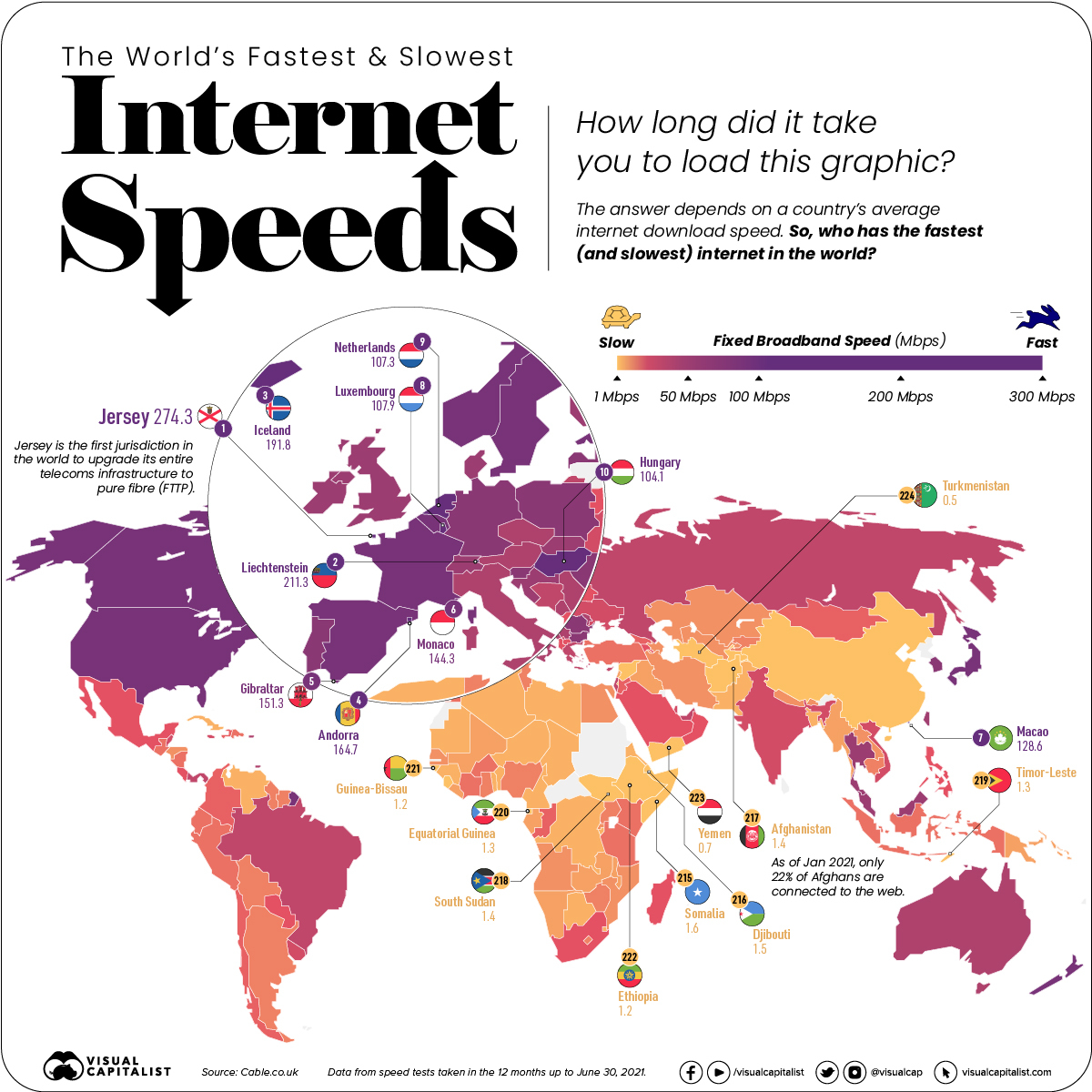
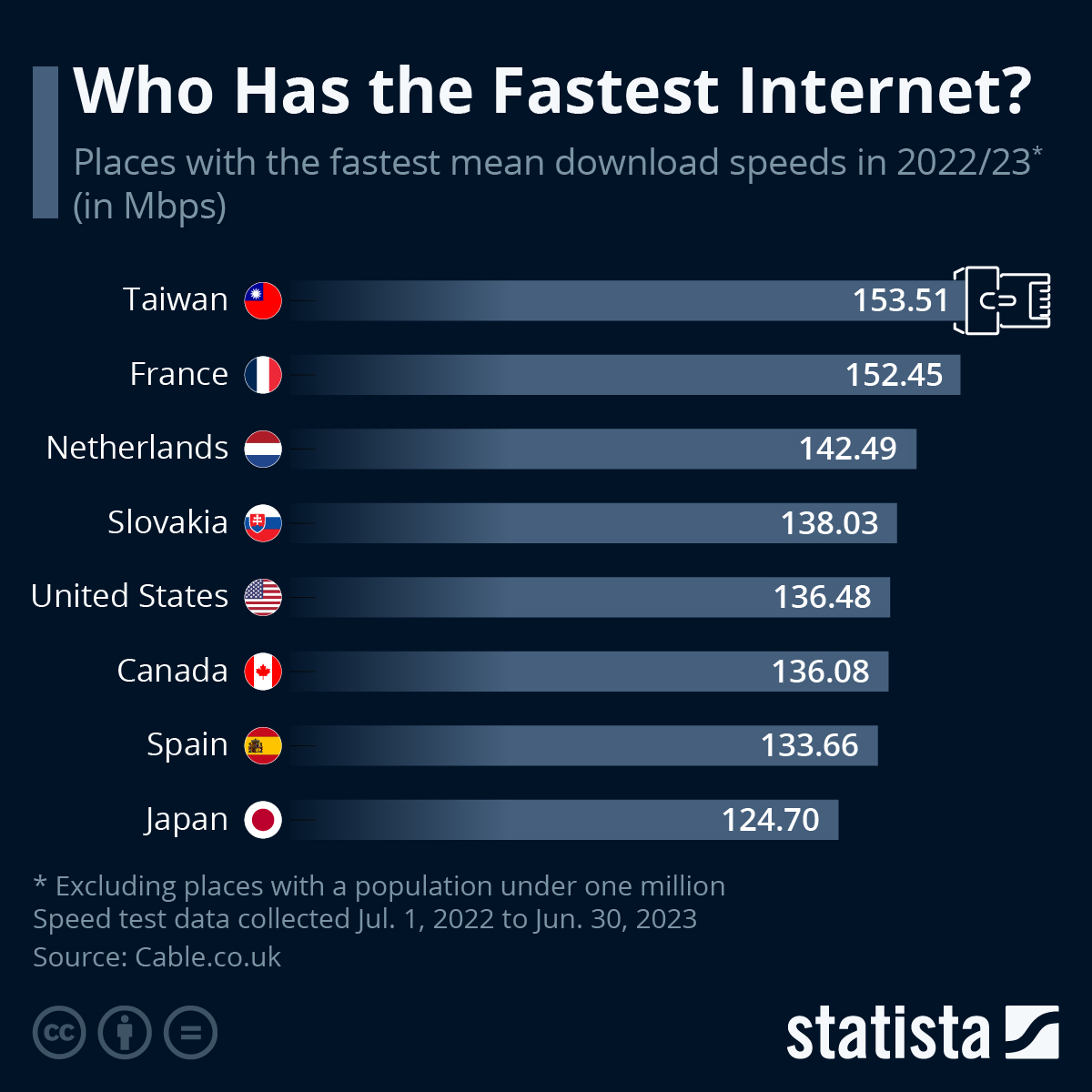

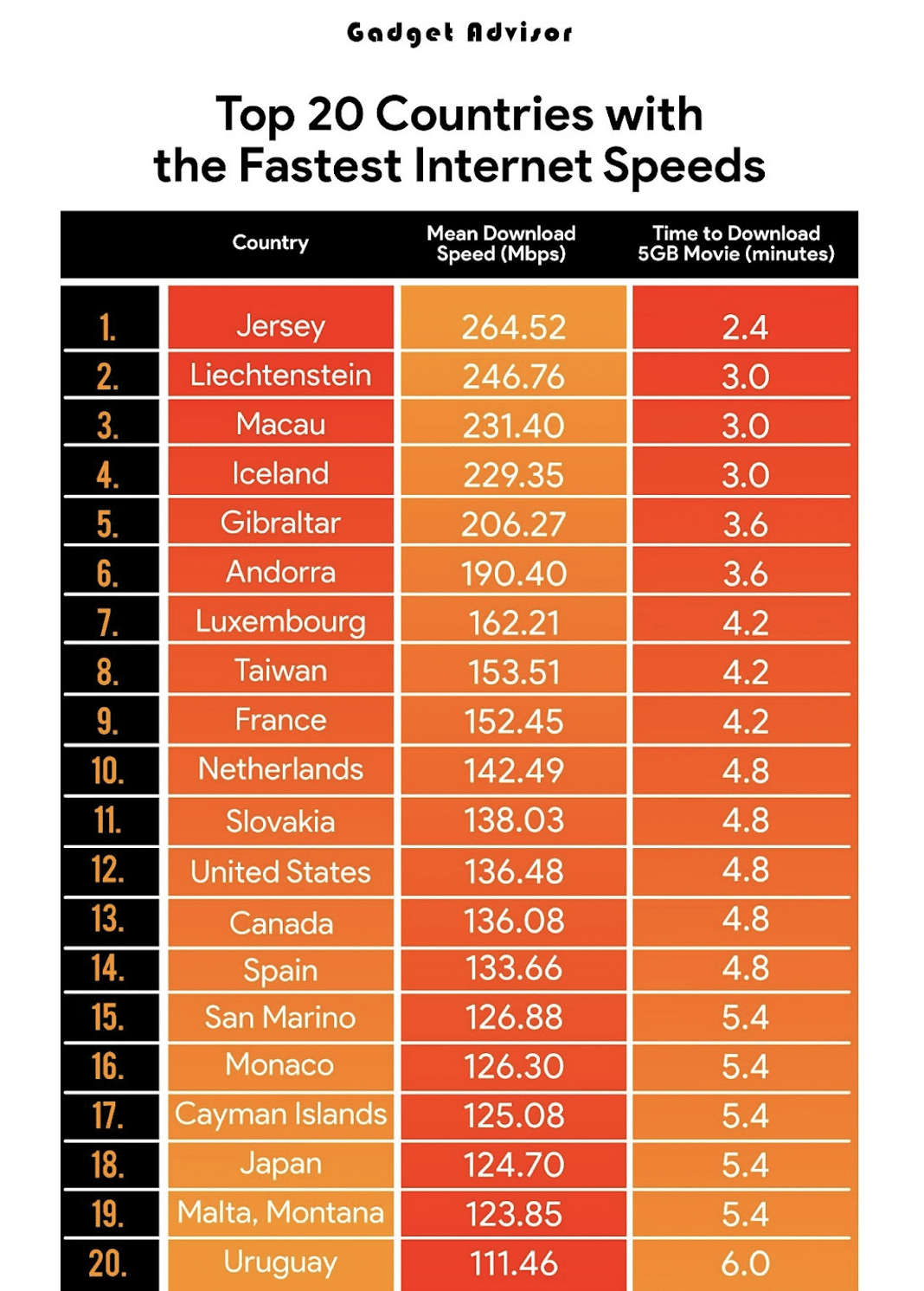
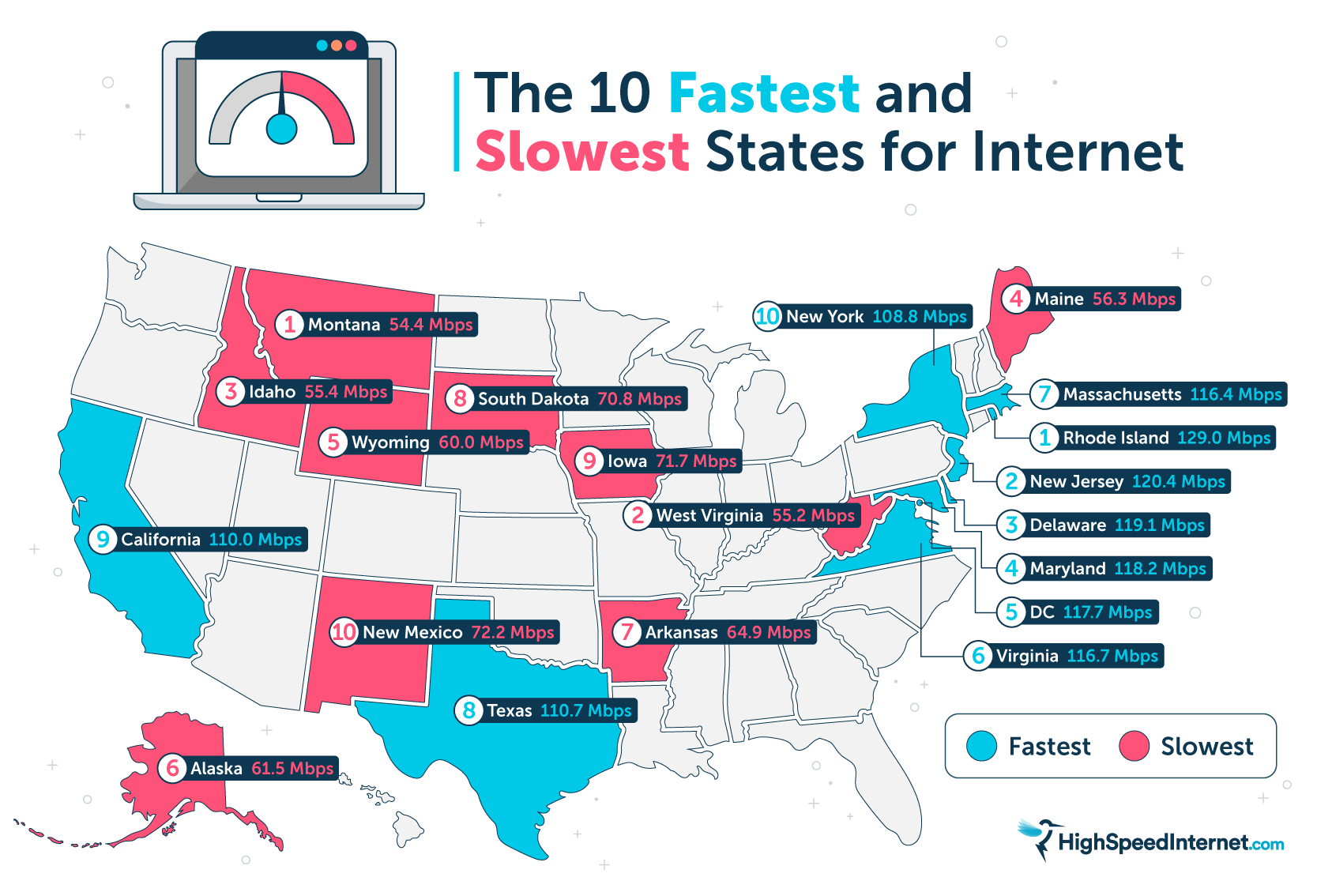
![Which Internet Speed Is The Fastest These U.S. States Have The Fastest Internet Speeds [Infographic]](https://imageio.forbes.com/blogs-images/niallmccarthy/files/2016/04/20160429_Internet_Speed.jpg?format=jpg&height=900&width=1600&fit=bounds)
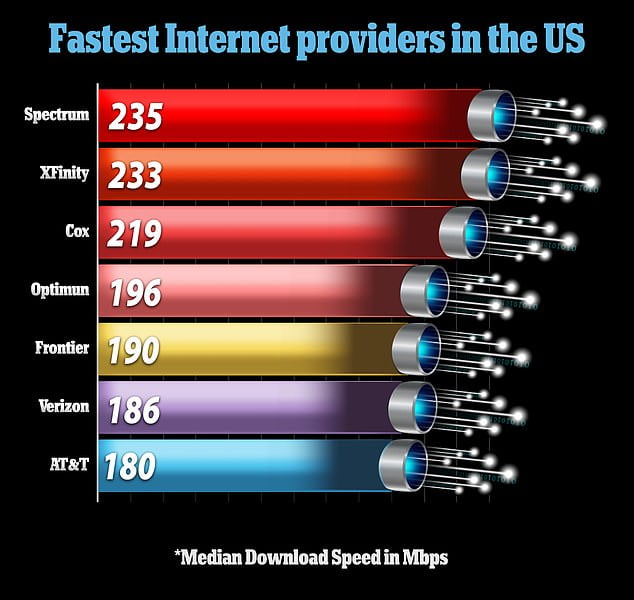
![Which Internet Speed Is The Fastest Who Has the Fastest Internet in the World? [Infographic] - WebFX](https://www.webfx.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/mobile-1.png)